|
Endowment Effect
In psychology and behavioral economics, the endowment effect, also known as divestiture aversion, is the finding that people are more likely to retain an object they own than acquire that same object when they do not own it. The endowment theory can be defined as "an application of prospect theory positing that loss aversion associated with ownership explains observed exchange asymmetries." This is typically illustrated in two ways. In a valuation paradigm, people's maximum willingness to pay (WTP) to acquire an object is typically lower than the least amount they are willing to accept (WTA) to give up that same object when they own it—even when there is no cause for attachment, or even if the item was only obtained minutes ago. In an exchange paradigm, people given a good are reluctant to trade it for another good of similar value. For example, participants first given a pen of equal expected value to that of a coffee mug were generally unwilling to trade, whilst participants f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreading Activation
Spreading activation is a method for searching associative networks, biological and artificial neural networks, or semantic networks.Fähndrich, J. (2018). Semantic decomposition and marker passing in an artificial representation of meaning. Technische Universitaet Berlin (Germany)/ref> The search process is initiated by labeling a set of source nodes (e.g. concepts in a semantic network) with weights or "activation" and then iteratively propagating or "spreading" that activation out to other nodes linked to the source nodes. Most often these "weights" are real values that decay as activation propagates through the network. When the weights are discrete this process is often referred to as marker passing. Activation may originate from alternate paths, identified by distinct markers, and terminate when two alternate paths reach the same node. However brain studies show that several different brain areas play an important role in semantic processing.Karalyn Patterson, Peter J. Nesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-referential Encoding
Self-referential encoding is a method of organizing information in one's memory in which one interprets incoming information in relation to oneself, using one's self-concept as a background.Rogers, T. B., Kuiper, N. A., & Kirker, W. S. (1977). Self-reference and the encoding of personal information. ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 35''(9), 677–688. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.35.9.677 Examples include being able to attribute personality traits to oneself or to identify recollected episodes as being personal memories of the past.Benoit, R. G., Gilbert, S. J., Volle, E., & Burgess, P. W. (2010). When I think about me and simulate you: Medial rostral prefrontal cortex and self-referential processes. ''Neuroimage, 50''(3), 1340–1349. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.091 The implications of self-referential processing are evident in many psychological phenomena. For example, the "cocktail party effect" notes that people attend to the sound of their names even during other c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attachment Theory
Attachment theory is a psychological and evolutionary framework, concerning the relationships between humans, particularly the importance of early bonds between infants and their primary caregivers. Developed by psychiatrist and psychoanalyst John Bowlby (1907–90), the theory posits that infants need to form a close relationship with at least one primary caregiver to ensure their survival, and to develop healthy social and emotional functioning. Pivotal aspects of attachment theory include the observation that infants seek proximity to attachment figures, especially during stressful situations. Secure attachments are formed when caregivers are sensitive and responsive in social interactions, and consistently present, particularly between the ages of six months and two years. As children grow, they use these attachment figures as a secure base from which to explore the world and return to for comfort. The interactions with caregivers form patterns of attachment, which in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superadditive
In mathematics, a function f is superadditive if f(x+y) \geq f(x) + f(y) for all x and y in the domain of f. Similarly, a sequence a_1, a_2, \ldots is called superadditive if it satisfies the inequality a_ \geq a_n + a_m for all m and n. The term "superadditive" is also applied to functions from a boolean algebra to the real numbers where P(X \lor Y) \geq P(X) + P(Y), such as lower probabilities. Examples of superadditive functions * The map f(x) = x^2 is a superadditive function for nonnegative real numbers because f(x + y) = (x + y)^2 = x^2 + y^2 + 2 x y = f(x) + f(y) + 2 x y \ge f(x) + f(y). * The determinant is superadditive for nonnegative Hermitian matrix, that is, if A, B \in \text_n(\Complex) are nonnegative Hermitian then \det(A + B) \geq \det(A) + \det(B). This follows from the Minkowski determinant theorem, which more generally states that \det(\cdot)^ is superadditive (equivalently, concave) for nonnegative Hermitian matrices of size n: If A, B \in \text_n(\Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Economic Theory
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption, and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good or service is determined through a hypothetical maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production. This approach has often been justified by appealing to rational choice theory. Neoclassical economics is the dominant approach to microeconomics and, together with Keynesian economics, formed the neoclassical synthesis which dominated mainstream economics as "neo-Keynesian economics" from the 1950s onward. Classification The term was originally introduced by Thorstein Veblen in his 1900 article "Preconceptions of Economic Science", in which he related marginalists in the tradition of Alfred Marshall ''et al.'' to those in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
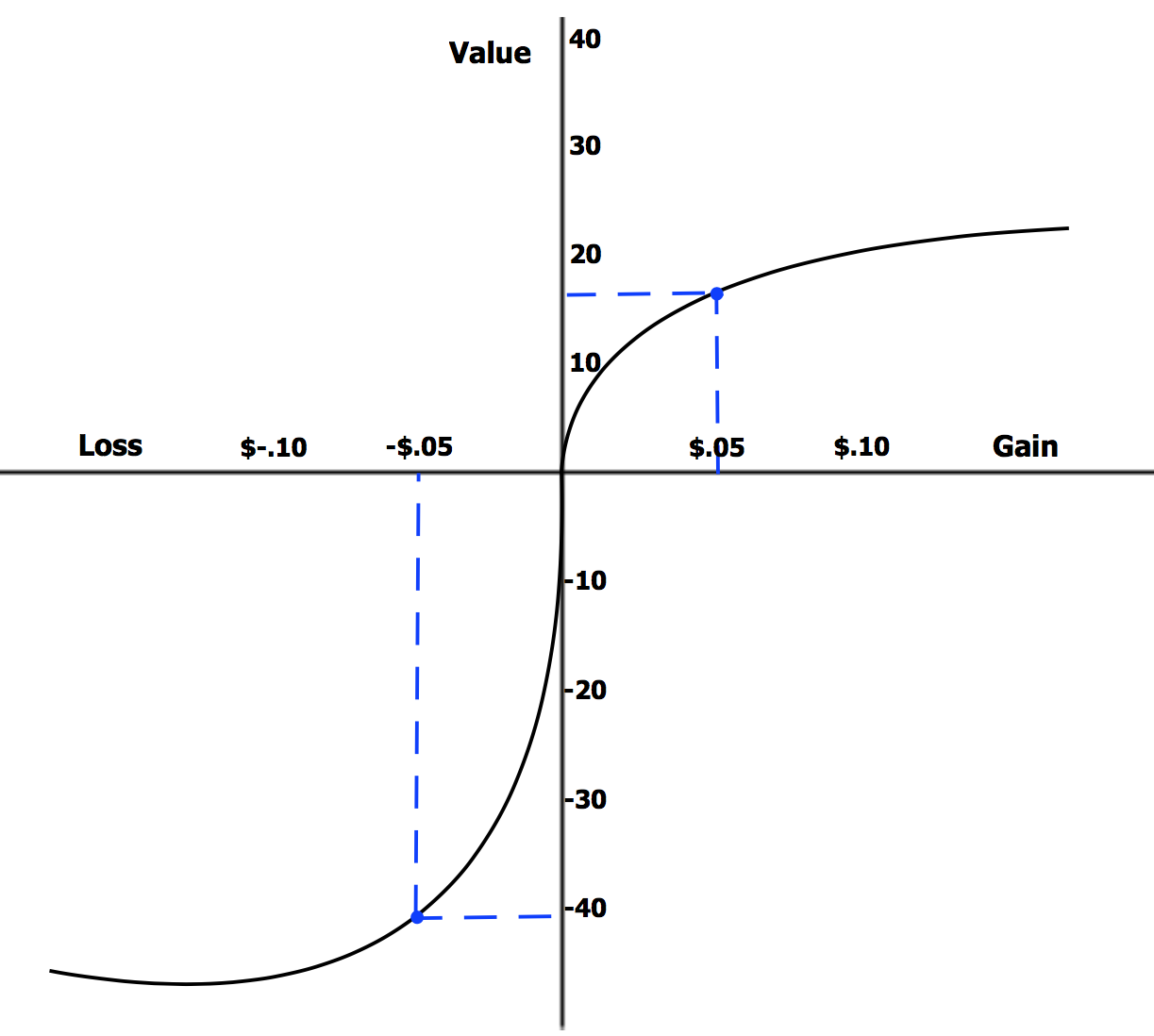
Prospect Theory
Prospect theory is a theory of behavioral economics, judgment and decision making that was developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1979. The theory was cited in the decision to award Kahneman the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Based on results from controlled studies, it describes how individuals assess their loss and gain perspectives in an asymmetric manner (see loss aversion). For example, for some individuals, the pain from losing $1,000 could only be compensated by the pleasure of earning $2,000. Thus, contrary to the expected utility theory (which models the decision that perfectly rational agents would make), prospect theory aims to describe the actual behavior of people. In the original formulation of the theory, the term ''prospect'' referred to the predictable results of a lottery. However, prospect theory can also be applied to the prediction of other forms of behaviors and decisions. Prospect theory challenges the expected utility theory deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Dependence
Reference dependence is a central principle in prospect theory and behavioral economics generally. It holds that people evaluate outcomes and express preferences relative to an existing reference point, or status quo. It is related to loss aversion and the endowment effect. In prospect theory it is appropriate to use the selected status quo to determine the reference point. However, depending on the particular research being conducted researchers have proven reference dependence from more than just well known brands and the status quo. The types of reference points used varies but studies have used individual goals, aspirations and social comparisons. Alternative reference points are used by researches commonly in the school of phycology but present some challenges to the methodologies of studies. Measuring reference dependence in field studies and laboratory experiments presents challenges as reference point values are unique to individuals, they are highly malleable and can be pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Gal
David Gal is Professor of Marketing at the University of Illinois at Chicago. He is best known for his critiques of behavioral economics, and in particular his critique of the behavioral economics concept of loss aversion. Academic career Gal received his Ph.D. from Stanford University in 2007. He joined the faculty of The Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University where he remained until 2014, at which time he joined the faculty of The University of Illinois at Chicago. His research has been published in Journal of Consumer Research, Journal of Marketing Research, Journal of Marketing, Judgment and Decision Making, Psychological Science, Management Science, and Journal of the American Statistical Association. It has been featured in the ''New York Times'', ''Wall Street Journal'', ''The Toronto Star'', ''Time'', ''Harvard Business Review'', and ''The Globe and Mail','' among other outlets. He was named a Marketing Science Institute Young Scholar in 2013 and a Market ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |