|
Menia
Menia (fl. c. 500) was the queen of the Thuringians by marriage and the earliest named ancestor of the Gausian dynasty of the Lombards. She became a legendary figure after her death, strongly associated with gold and wealth. Only one other person is known by the name Menia, from a 9th-century polyptych of the Abbey of Saint-Remi. In origin it is probably a Germanic name, signifying collar, ring or necklace, and by extension treasure.Wolfram Brandes, "Das Gold der Menia: Ein Beispiel transkulturellen Wissenstransfers", ''Millennium'' 2 (2005): 175–226, esp. 181ff. Menia's marriage is recorded only in the ''Historia Langobardorum codicis Gothani''. According to that source, she was the wife of King Pissa, usually identified as Bisinus, king of the Thuringians. The same source and the other Lombard chronicles make Bisinus the father of Raicunda, first wife of Wacho, king of the Lombards. She may have been the daughter of Menia. Frankish sources, such as Venantius Fortunatus, make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bisinus
Bisinus (sometimes shortened to Bisin) was the king of Thuringia in the 5th century AD or around 500. He is the earliest historically attested ruler of the Thuringians. Almost nothing more about him can be said with certainty, including whether all the variations on his name in the sources refer to one or two different persons. His name is given as Bysinus, Bessinus or Bissinus in Frankish sources, and as Pissa, Pisen, Fisud or Fisut in Lombard ones. History Bisinus was the first husband of Menia, a fact attested only in the 9th-century ''Historia Langobardorum codicis Gothani''. He had a daughter, Raicunda, who became the first wife of the Lombard king Wacho (c. 510–540), a fact attested in all three of the main Lombard chronicles (two of which specify that he was king of the Thuringians). Menia later married a man (unnamed in the sources) of the Gausus family and became the mother of Audoin, who in 540 became the regent of Wacho's son by his third wife, Walthari, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertachar
Bertachar (or Berthachar) was a king of Thuringia from about 510 until about 525, co-ruling with his brothers Hermanfrid and Baderic. Bertachar was probably not a Thuringian himself. Frankish sources, such as Venantius Fortunatus, make the three brothers sons of King Bisinus. They are sometimes considered as sons of Bisinus' wife Menia, or else as sons of Basina, who is called a wife of Bisinus by the Frankish historian Gregory of Tours. Many scholars, however, reject Bisinus' marriage to Basina as ahistorical, leaving Menia as his only known wife. Bertachar's rule probably began between 507 and 511. He was murdered by his brother Hermanfrid, who later murdered Baderic to become sole ruler of Thuringia. This assassination may have taken place as early as 525. Bertachar had at least one daughter and, depending on the source, one or several sons. His sons are unnamed. His daughter, Radegund, married the Frankish king Chlothar I and founded Holy Cross Abbey Holy Cross Abbey ''(M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermanafrid
Hermanfrid (also Hermanifrid or Hermanafrid; , died 532) was the last independent king of the Thuringii in present-day Germany. He was one of three sons of King Bisinus and the Lombard Menia. His siblings were Baderic; Raicunda, married to the Lombard king Wacho; and Bertachar. Hermanfrid married Amalaberga, daughter of Amalafrida who was the daughter of Theodemir, between 507 and 511. Amalberga was also the niece of Theodoric the Great. It is unclear when Hermanfrid became king, but he is called king (''rex thoringorum'') in a letter by Theodoric dated to 507. He first shared the rule with his brothers Baderic and Bertachar, but later killed Bertachar in a battle in 529, leaving the young Radegund an orphan. According to Gregory of Tours, Amalaberga now stirred up Hermanfrid against his remaining brother. Once she laid out only half the table for a meal, and when questioned about the reason, she told him "A king who owns only of half of his kingdom deserved to have half of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grottasöngr
''Grottasöngr'' (or ''Gróttasöngr''; Old Norse: 'The Mill's Songs', or 'Song of Grótti') is an Old Norse poem, sometimes counted among the poems of the ''Poetic Edda'' as it appears in manuscripts that are later than the '' Codex Regius''. The tradition is also preserved in one of the manuscripts of Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'' along with some explanation of its context. The myth has also survived independently in modified forms in northern European folklore. ''Gróttasöngr'' had social and political impact in Sweden during the 20th century as it was modernized in the form of ''Den nya Grottesången'' by Viktor Rydberg, which described conditions in factories using the mill of ''Grottasöngr'' as a literary backdrop. ''Poetic Edda'' Though not originally included in the '' Codex Regius'', ''Gróttasöngr'' is included in many later editions of the ''Poetic Edda''. ''Gróttasöngr'' is the work song of two young slave girls bought in Sweden by the Danish King Frodi (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audoin
Alduin (Langobardic: ''Aldwin'' or ''Hildwin'', ; also called Auduin or Audoin) was king of the Lombards from 547 to 560. Life Audoin was of the Gausi, a prominent Lombard ruling clan, and according to the ''Historia Langobardorum'', the son of Menia, the Lombard wife of Basinus, king of the Thuringii.Wolfram Brandes, "Das Gold der Menia: Ein Beispiel transkulturellen Wissenstransfers", ''Millennium'' 2 (2005): 175–226, esp. 181ff. Audoin was half-brother to Hermanafrid (king of the Thuringii peoples) and Raicunda, the wife of the Lombard king Wacho. According to the ''Decem Libri'' of Gregory of Tours, in 531, Hermanafrid was defeated at the Battle of Unstrut, and so Thuringia was annexed to the Frankish empire. Hermanafrid traveled under safe conduct to meet with Theuderic at Zülpich. While walking along the city walls with Theuderic, Hermanafrid was thrown from the ramparts to his death. According to Procopius (History of the Wars V, 13), after Hermanafrid's death, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baderic
Baderic, Baderich, Balderich or Boderic (ca. 480 – 529), son of Bisinus and Menia, was a co-king of the Thuringii. He and his brothers Hermanfrid and Berthar succeeded their father Bisinus. After Hermanfrid defeated Berthar in battle, he invited King Theuderic I of Metz to help him defeat Baderic in return for half of the kingdom. Theuderic I agreed and Baderic was defeated and killed in 529. Hermanfrid became the sole king. Baderic is known to have two daughters: Ingund and Aregund, who became the 3rd and 4th wives respectively of Clothar I Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old" (French: le Vieux), (died December 561) also anglicised as Clotaire, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I. Chlothar's father, Clovis I, divided the kingdo ..., King of the Franks. Notes * 480s births 529 deaths Germanic warriors Kings of the Thuringians 6th-century rulers in Europe Year of birth uncertain {{Europe-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raicunda
Raicunda (? - 512), also known as Radikunda, Radegunda or Ranikunda was a Lombardic queen consort. She was the daughter of the Thurinigian king Bisinus and his Lombard wife Menia. She had three brothers named in the sources, Hermanafrid, Bertachar and Baderic, who divided the Thuringian kingdom after the death of their father. Raicunda went with her mother to the kingdom of the Lombards. She married the Lombard king Wacho Wacho (also Waccho; probably from ''Waldchis'') was king of the Lombards before they entered Italy from an unknown date (perhaps c. 510) until his death in 539. His father was Unichis. Wacho usurped the throne by assassinating (or having assassi ..., but died in 512 AD before leaving any children. Sources * Michael Kirchschlager: Runibergun. Vom Königreich der Thüringer. Verlag Kirchschlager, Arnstadt 2009, , S. 23 * Helmut Castritius, Dieter Geuenich, Matthias Werner (Hrsg.): Die Frühzeit der Thüringer. Archäologie, Sprache, Geschichte (= Reallexiko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohlhammer Verlag
W. Kohlhammer Verlag GmbH, or Kohlhammer Verlag, is a German publishing house headquartered in Stuttgart. History Kohlhammer Verlag was founded in Stuttgart on 30 April 1866 by . Kohlhammer had taken over the businesses of his late father-in-law, a 120-year-old printer and a profitable . The printing business, operating out of the back of a commercial building at 14 Urbanstrasse, became W. Kohlhammer Verlag and was funded by proceeds from the bathhouse until it was closed in 1890. Kohlhammer purchased the ''Deutsche Feuerwehrzeitung'' in 1882 and printed that publication until 1923. In 1872 Kohlhammer started a weekly newspaper, the ''Neue Deutsche Familienblatt'' that by 1914 had a circulation of 185,000. Contemporary Employees of Kohlhammer joined those of other Stuttgart-based companies in early 2016 to petition the mayor to abate traffic congestion hindering their operations inside the city. In 2017, Kohlhammer Verlag employed about 400 people in Stuttgart, Würzburg and Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
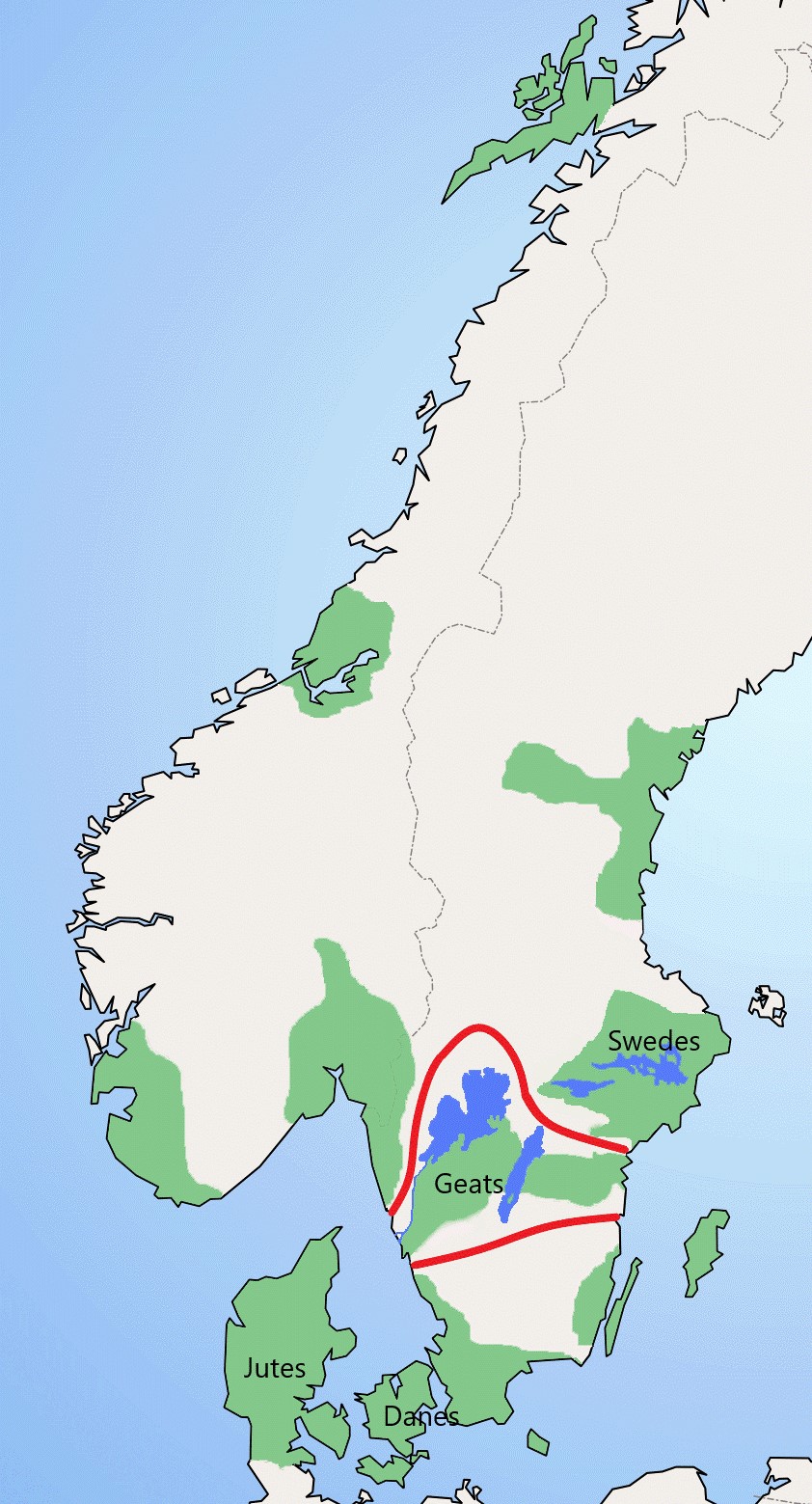
Geats
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Friuli
The Duchy of Friuli was a Lombard duchy in present-day Friuli, the first to be established after the conquest of the Italian peninsula in 568. It was one of the largest domains in ''Langobardia Major'' and an important buffer between the Lombard kingdom and the Slavs, Avars, and the Byzantine Empire. The original chief city in the province was Roman Aquileia, but the Lombard capital of Friuli was ''Forum Julii'', modern Cividale. Along with the dukes of Spoleto, Benevento and Trent, the lords of Friuli often attempted to establish their independence from the royal authority seated at Pavia, though to no avail. After the Lombard campaign of Charlemagne and the defeat of King Desiderius in 774, the last Friulian duke Hrodgaud ruled until 776. Upon his death, Friuli was incorporated as a march of the Carolingian Empire. History Origins The Venetian territory around ''Forum Iulii'', still devastated by the Gothic War, was the first in former Roman Italy to be conquered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into conflict with the Merovingian Franks, and it later came under their influence and Frankish control. The name is still used for one of modern Germany's federal states ('' Bundesländer''). First appearances The Thuringians do not appear in classical Roman texts under that name, but some have suggested that they were the remnants of the Suebic Hermanduri, the last part of whose name (''-duri'') could represent the same sound as (''-thuri'') and the Germanic suffix ''-ing'', suggests a meaning of "descendants of (the ermanuri)". This people were living near the Marcomanni. Tacitus in his "''Germania''", describes their homeland as being where the Elbe starts, but also having colonies at the Danube and even within the Roman province of Rhaetia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Florentius and later added the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather. He is the primary contemporary source for Merovingian history. His most notable work was his ''Decem Libri Historiarum'' (''Ten Books of Histories''), better known as the ''Historia Francorum'' (''History of the Franks''), a title that later chroniclers gave to it. He is also known for his accounts of the miracles of saints, especially four books of the miracles of Martin of Tours. St. Martin's tomb was a major pilgrimage destination in the 6th century, and St. Gregory's writings had the practical effect of promoting highly organized devotion. Biography Gregory was born in Clermont, in the Auvergne region of central Gaul. He was born into the upper stratum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |