|
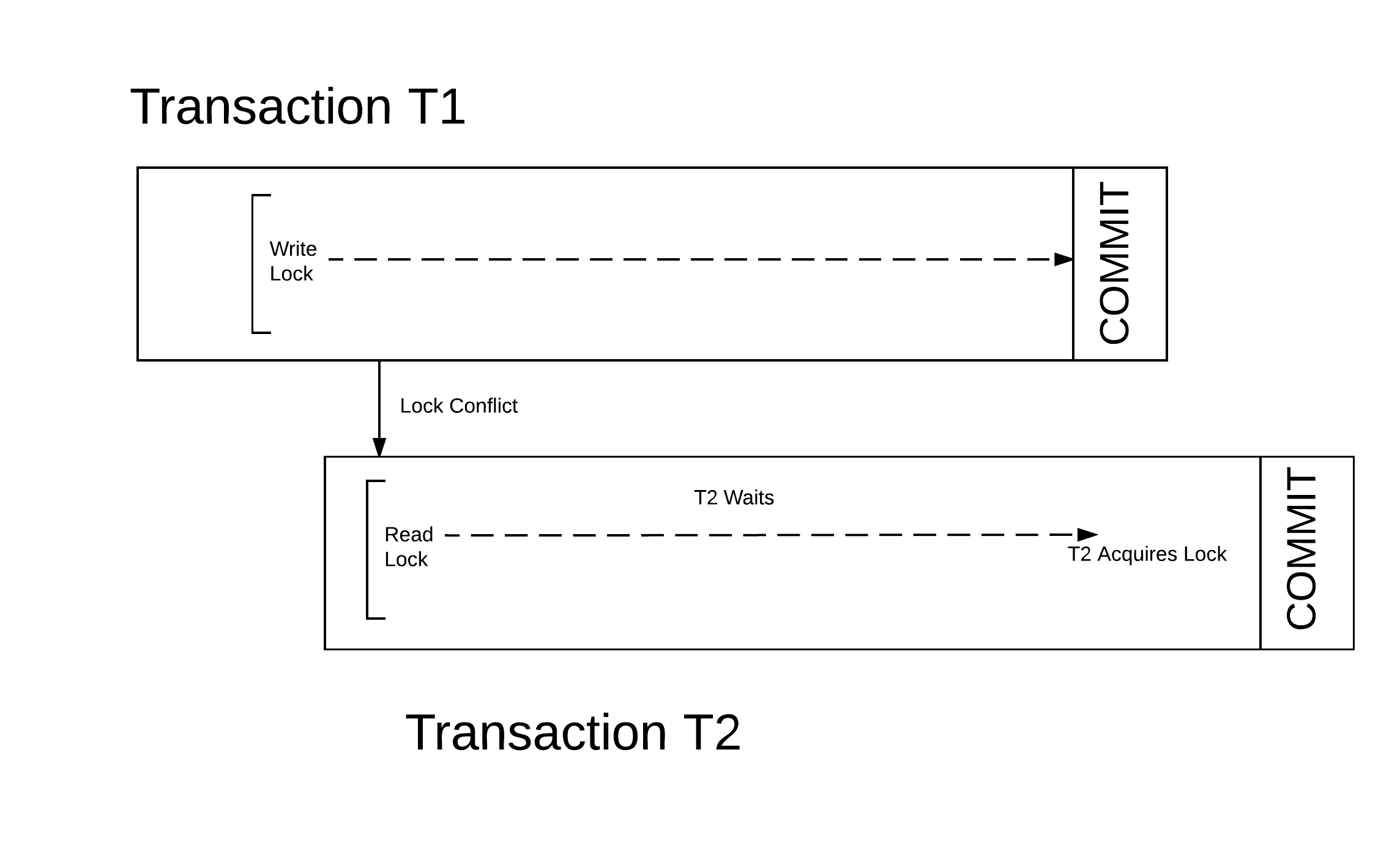
Memory Semantics (computing)
In computing and parallel processing, memory semantics refers to the process logic used to control access to shared memory locations, or at a higher level to shared variables in the presence of multiple threads or processors. Memory semantics may also be defined for transactional memory, where issues related to the interaction of transactions and locks, and user-level actions need to be defined and specified.''Towards transactional memory semantics for C++'' by Tatiana Shpeisman et al in ''Proceedings of the twenty-first annual symposium on Parallelism in algorithms and architectures'' 2009/ref> See also * Consistency model In computer science, a consistency model specifies a contract between the programmer and a system, wherein the system guarantees that if the programmer follows the rules for operations on memory, memory will be data consistency, consistent and th ... References {{Parallel_computing Consistency models Transaction processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computing, computation in which many calculations or Process (computing), processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: Bit-level parallelism, bit-level, Instruction-level parallelism, instruction-level, Data parallelism, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Memory Architecture
A shared-memory architecture (SM) is a distributed computing architecture in which the nodes share the same memory as well as the same storage.{{Cite web , title=Memory: Shared vs Distributed - UFRC , url=https://help.rc.ufl.edu/doc/Memory:_Shared_vs_Distributed , access-date=2024-03-13 , website=help.rc.ufl.edu It contrasts with shared-nothing architecture, in which each node has distinct memory and storage, and with shared-disk architecture, in which the nodes share the same storage but not the same memory. This is distinct from the use of shared memory between different programs or threads on a single node, with or without multiprocessing. See also * Distributed database A distributed database is a database in which data is stored across different physical locations. It may be stored in multiple computers located in the same physical location (e.g. a data centre); or maybe dispersed over a computer network, netwo ... * Shared memory References Distributed computin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marvin Victor Zelkowitz
Marvin Victor Zelkowitz (born 7 August 1945) is an American computer scientist and engineer. Zelkowitz earned a degree in mathematics from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in 1967 and a master's degree and doctorate in computer science at Cornell University in 1969 and 1971, respectively. He then taught at the University of Maryland, College Park. While holding a professorship within the Department of Computer Science and the University of Maryland Institute for Advanced Computer Studies (UMIACS), he was also affiliated with the Fraunhofer Center for Experimental Software Engineering, since renamed The Fraunhofer USA Center Mid-Atlantic (CMA). He is now Professor Emeritus, having retired in 2007. His early research (1968-early 1980s) was in programming languages. He worked on implementation of programming language features to aid in program development and debugging as well as ways to implement tests for runtime correctness of executable code. His later research dealt with sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transactional Memory
In computer science and computer engineering, engineering, transactional memory attempts to simplify concurrent programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an linearizability, atomic way. It is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to Shared memory (interprocess communication), shared memory in concurrent computing. Transactional memory systems provide high-level abstraction as an alternative to low-level thread synchronization. This abstraction allows for coordination between concurrent reads and writes of shared data in parallel systems. Motivation In concurrent programming, synchronization is required when parallel threads attempt to access a shared resource. Low-level thread synchronization constructs such as locks are pessimistic and prohibit threads that are outside a critical section from running the code protected by the critical section. The process of applying and releasing locks often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lock (computer Science)
In computer science, a lock or mutex (from mutual exclusion) is a synchronization primitive that prevents state from being modified or accessed by multiple threads of execution at once. Locks enforce mutual exclusion concurrency control policies, and with a variety of possible methods there exist multiple unique implementations for different applications. Types Generally, locks are ''advisory locks'', where each thread cooperates by acquiring the lock before accessing the corresponding data. Some systems also implement ''mandatory locks'', where attempting unauthorized access to a locked resource will force an exception in the entity attempting to make the access. The simplest type of lock is a binary semaphore. It provides exclusive access to the locked data. Other schemes also provide shared access for reading data. Other widely implemented access modes are exclusive, intend-to-exclude and intend-to-upgrade. Another way to classify locks is by what happens when the lock st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consistency Model
In computer science, a consistency model specifies a contract between the programmer and a system, wherein the system guarantees that if the programmer follows the rules for operations on memory, memory will be data consistency, consistent and the results of reading, writing, or updating memory will be predictable. Consistency models are used in Distributed computing, distributed systems like distributed shared memory systems or distributed data stores (such as filesystems, databases, optimistic replication systems or web caching). Consistency is different from coherence, which occurs in systems that are cache coherence, cached or cache-less, and is consistency of data with respect to all processors. Coherence deals with maintaining a global order in which writes to a single location or single variable are seen by all processors. Consistency deals with the ordering of operations to multiple locations with respect to all processors. High level languages, such as C++ and Java (progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consistency Models
In deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. A theory T is consistent if there is no formula \varphi such that both \varphi and its negation \lnot\varphi are elements of the set of consequences of T. Let A be a set of closed sentences (informally "axioms") and \langle A\rangle the set of closed sentences provable from A under some (specified, possibly implicitly) formal deductive system. The set of axioms A is consistent when there is no formula \varphi such that \varphi \in \langle A \rangle and \lnot \varphi \in \langle A \rangle. A ''trivial'' theory (i.e., one which proves every sentence in the language of the theory) is clearly inconsistent. Conversely, in an explosive formal system (e.g., classical or intuitionistic propositional or first-order logics) every inconsistent theory is trivial. Consistency of a theory is a syntactic notion, whose semantic counterpart is satisfiability. A theory is satisfiable if it has a model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |