|
Meissel–Mertens Constant
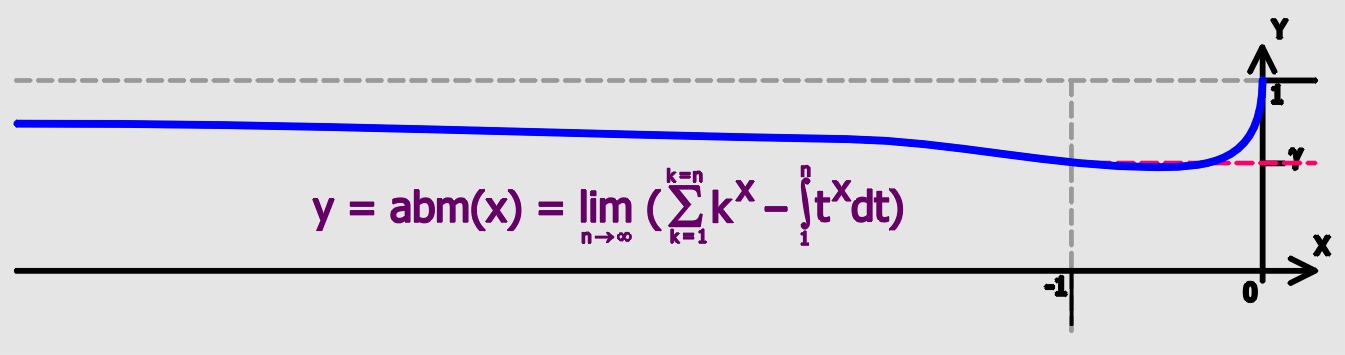
The Meissel–Mertens constant (named after Ernst Meissel and Franz Mertens), also referred to as Mertens constant, Kronecker's constant, Hadamard– de la Vallée-Poussin constant or the prime reciprocal constant, is a mathematical constant in number theory, defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series summed only over the primes and the natural logarithm of the natural logarithm: :M = \lim_ \left( \sum_ \frac - \ln(\ln n) \right)=\gamma + \sum_ \left \ln\! \left( 1 - \frac \right) + \frac \right Here γ is the Euler–Mascheroni constant, which has an analogous definition involving a sum over all integers (not just the primes). The value of ''M'' is approximately :''M'' ≈ 0.2614972128476427837554268386086958590516... . Mertens' second theorem establishes that the limit exists. The fact that there are two logarithms (log of a log) in the limit for the Meissel–Mertens constant may be thought of as a consequence of the combination of the prime num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Mascheroni Constant
Euler's constant (sometimes also called the Euler–Mascheroni constant) is a mathematical constant usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma (). It is defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series and the natural logarithm, denoted here by \log: :\begin \gamma &= \lim_\left(-\log n + \sum_^n \frac1\right)\\ px&=\int_1^\infty\left(-\frac1x+\frac1\right)\,dx. \end Here, \lfloor x\rfloor represents the floor function. The numerical value of Euler's constant, to 50 decimal places, is: : History The constant first appeared in a 1734 paper by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, titled ''De Progressionibus harmonicis observationes'' (Eneström Index 43). Euler used the notations and for the constant. In 1790, Italian mathematician Lorenzo Mascheroni used the notations and for the constant. The notation appears nowhere in the writings of either Euler or Mascheroni, and was chosen at a later time perhaps because of the constant's connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergence Of The Sum Of The Reciprocals Of The Primes
The sum of the reciprocals of all prime numbers diverges; that is: \sum_\frac1p = \frac12 + \frac13 + \frac15 + \frac17 + \frac1 + \frac1 + \frac1 + \cdots = \infty This was proved by Leonhard Euler in 1737, and strengthens Euclid's 3rd-century-BC result that there are infinitely many prime numbers and Nicole Oresme's 14th-century proof of the divergence of the sum of the reciprocals of the integers (harmonic series). There are a variety of proofs of Euler's result, including a lower bound for the partial sums stating that \sum_\frac1p \ge \log \log (n+1) - \log\frac6 for all natural numbers . The double natural logarithm () indicates that the divergence might be very slow, which is indeed the case. See Meissel–Mertens constant. The harmonic series First, we describe how Euler originally discovered the result. He was considering the harmonic series \sum_^\infty \frac = 1 + \frac + \frac + \frac + \cdots = \infty He had already used the following " product formula" to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Post
The ''Financial Post'' was an English Canadian business newspaper, which published from 1907 to 1998. In 1998, the publication was folded into the new ''National Post'',"Black says Post to merge with new paper". '' The Globe and Mail'', July 23, 1998. although the name ''Financial Post'' has been retained as the banner for that paper's business section and also lives on in the ''Post''s monthly business magazine, ''Financial Post Business''. The ''Financial Post'' started publication in 1907 by John Bayne Maclean."Publishing Inc. on the move". ''The Globe and Mail, April 9, 1983. It was a weekly publication, and one of the core assets of Maclean's media business, which eventually became Maclean-Hunter. The paper was purchased by Sun Media in 1987, and expanded into a daily tabloid on February 1, 1988, and added home delivery newspaper in 1990, with a reformatted ''Financial Post Magazine'' following shortly after. In 1998, Sun Media sold the ''Financial Post'' to Hollinger, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brun's Constant
In number theory, Brun's theorem states that the sum of the reciprocals of the twin primes (pairs of prime numbers which differ by 2) converges to a finite value known as Brun's constant, usually denoted by ''B''2 . Brun's theorem was proved by Viggo Brun in 1919, and it has historical importance in the introduction of sieve methods. Asymptotic bounds on twin primes The convergence of the sum of reciprocals of twin primes follows from bounds on the density of the sequence of twin primes. Let \pi_2(x) denote the number of primes ''p'' ≤ ''x'' for which ''p'' + 2 is also prime (i.e. \pi_2(x) is the number of twin primes with the smaller at most ''x''). Then, for ''x'' ≥ 3, we have : \pi_2(x) =O\left(\frac \right). That is, twin primes are less frequent than prime numbers by nearly a logarithmic factor. It follows from this bound that the sum of the reciprocals of the twin primes converges, or stated in other words, the twin primes form a small set. In explicit terms the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nortel
Nortel Networks Corporation (Nortel), formerly Northern Telecom Limited, was a Canadian Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications and data networking equipment manufacturer headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It was founded in Montreal, Quebec, in 1895 as the Northern Electric and Manufacturing Company. Until an antitrust settlement in 1949, Northern Electric was owned principally by Bell Canada and the Western Electric, Western Electric Company of the Bell System, producing large volumes of telecommunication equipment based on licensed Western Electric designs. At its height, Nortel accounted for more than a third of the total valuation of all companies listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX), employing 94,500 people worldwide. In 2009, Nortel filed for bankruptcy protection in Canada and the United States, triggering a 79% decline of its corporate stock price. The bankruptcy case was the List of corporate collapses and scandals, largest in Canadian h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and Computer hardware, consumer electronics. It has been referred to as "the most powerful company in the world" and one of the world's List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands due to its market dominance, data collection, and technological advantages in the area of artificial intelligence. Its parent company Alphabet Inc., Alphabet is considered one of the Big Tech, Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Amazon (company), Amazon, Apple Inc., Apple, Meta Platforms, Meta, and Microsoft. Google was founded on September 4, 1998, by Larry Page and Sergey Brin while they were Doctor of Philosophy, PhD students at Stanford University in California. Together they own about 14% of its publicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number Theorem
In mathematics, the prime number theorem (PNT) describes the asymptotic distribution of the prime numbers among the positive integers. It formalizes the intuitive idea that primes become less common as they become larger by precisely quantifying the rate at which this occurs. The theorem was proved independently by Jacques Hadamard and Charles Jean de la Vallée Poussin in 1896 using ideas introduced by Bernhard Riemann (in particular, the Riemann zeta function). The first such distribution found is , where is the prime-counting function (the number of primes less than or equal to ''N'') and is the natural logarithm of . This means that for large enough , the probability that a random integer not greater than is prime is very close to . Consequently, a random integer with at most digits (for large enough ) is about half as likely to be prime as a random integer with at most digits. For example, among the positive integers of at most 1000 digits, about one in 2300 is prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mertens' Theorems
In number theory, Mertens' theorems are three 1874 results related to the density of prime numbers proved by Franz Mertens.F. Mertens. J. reine angew. Math. 78 (1874), 46–6Ein Beitrag zur analytischen Zahlentheorie/ref> "Mertens' theorem" may also refer to his theorem in analysis. Theorems In the following, let p\le n mean all primes not exceeding ''n''. Mertens' first theorem: : \sum_ \frac - \log n does not exceed 2 in absolute value for any n\ge 2. () Mertens' second theorem: :\lim_\left(\sum_\frac1p -\log\log n-M\right) =0, where ''M'' is the Meissel–Mertens constant (). More precisely, Mertens proves that the expression under the limit does not in absolute value exceed : \frac 4 +\frac 2 for any n\ge 2. Mertens' third theorem: :\lim_\log n\prod_\left(1-\frac1p\right)=e^ \approx 0.561459483566885, where γ is the Euler–Mascheroni constant (). Changes in sign In a paper on the growth rate of the sum-of-divisors function published in 1983, Guy Robin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primes Harmonic
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow method of checking the primality of a given number n, called trial division, tests whether n is a multiple of any integer between 2 and \sqrt. Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error, and the AKS primality test, which always pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Logarithm
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant , which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to . The natural logarithm of is generally written as , , or sometimes, if the base is implicit, simply . Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving , , or . This is done particularly when the argument to the logarithm is not a single symbol, so as to prevent ambiguity. The natural logarithm of is the power to which would have to be raised to equal . For example, is , because . The natural logarithm of itself, , is , because , while the natural logarithm of is , since . The natural logarithm can be defined for any positive real number as the area under the curve from to (with the area being negative when ). The simplicity of this definition, which is matched in many other formulas involving the natural logarithm, leads to the term "natural". The definition of the natural logarithm can the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Meissel
Daniel Friedrich Ernst Meissel (31 July 1826, Eberswalde, Brandenburg Province – 11 March 1895, Kiel) was a German astronomer who contributed to various aspects of number theory. See also *Meissel–Lehmer algorithm *Meissel–Mertens constant The Meissel–Mertens constant (named after Ernst Meissel and Franz Mertens), also referred to as Mertens constant, Kronecker's constant, Hadamard– de la Vallée-Poussin constant or the prime reciprocal constant, is a mathematical constant in n ... External links * 1826 births 1895 deaths 19th-century German astronomers 19th-century German mathematicians Number theorists {{Germany-astronomer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

