|
Megalograptoidea
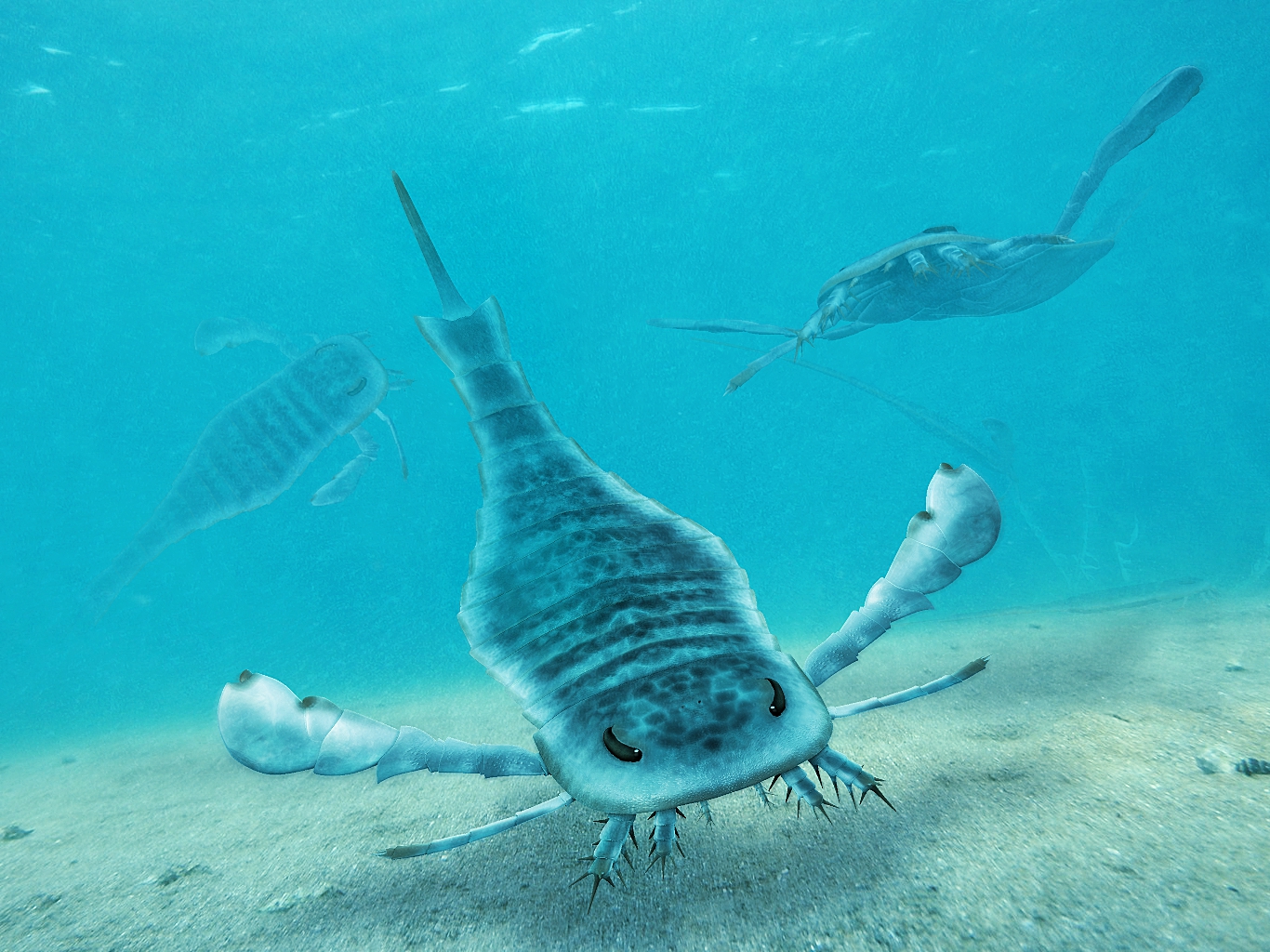
Carcinosomatoidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of the superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Eurypterina. Some carcinosomatoid genera have been suggested to have been fully marine as opposed to living in near-shore brackish or hypersaline environments. The majority of carcinosomatoid taxa are known from the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia. Isolated and fragmentary fossils from the Late Silurian of Vietnam and the Czech Republic show that the terranes of Annamia and Perunica were within the geographical range of the carcinosomatoids. Only a few basal carcinosomatoids (e.g. ''Carcinosoma'' and ''Paracarcinosoma'') have been found in deeper waters whilst the more derived forms, such as ''Mixopterus'' and ''Lanarkopterus'' have not. Basal carcinosomatoids (Carcinosomatidae) are likely responsible for the fossil remains in Vietnam and the Czech Republi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterina
Eurypterina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Eurypterine eurypterids are sometimes informally known as "swimming eurypterids". They are known from fossil deposits worldwide, though primarily in North America and Europe. Seventy-five percent of eurypterid species are eurypterines; this represents 99% of specimens. The superfamily Pterygotioidea is the most species-rich clade, with 56 species, followed by the Adelophthalmoidea with 43 species; as sister taxa, they comprise the most derived eurypterines. Pterygotioidea includes the pterygotids, which are the only eurypterids known to have a cosmopolitan distribution. Though more numerous both in specimens and taxa, the eurypterines have the shorter temporal range of the two eurypterid suborders. They first appeared around the same time as the Stylonurina in the Middle Ordovician. The suborder faced a slow extinction during the Middle and Late Devo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
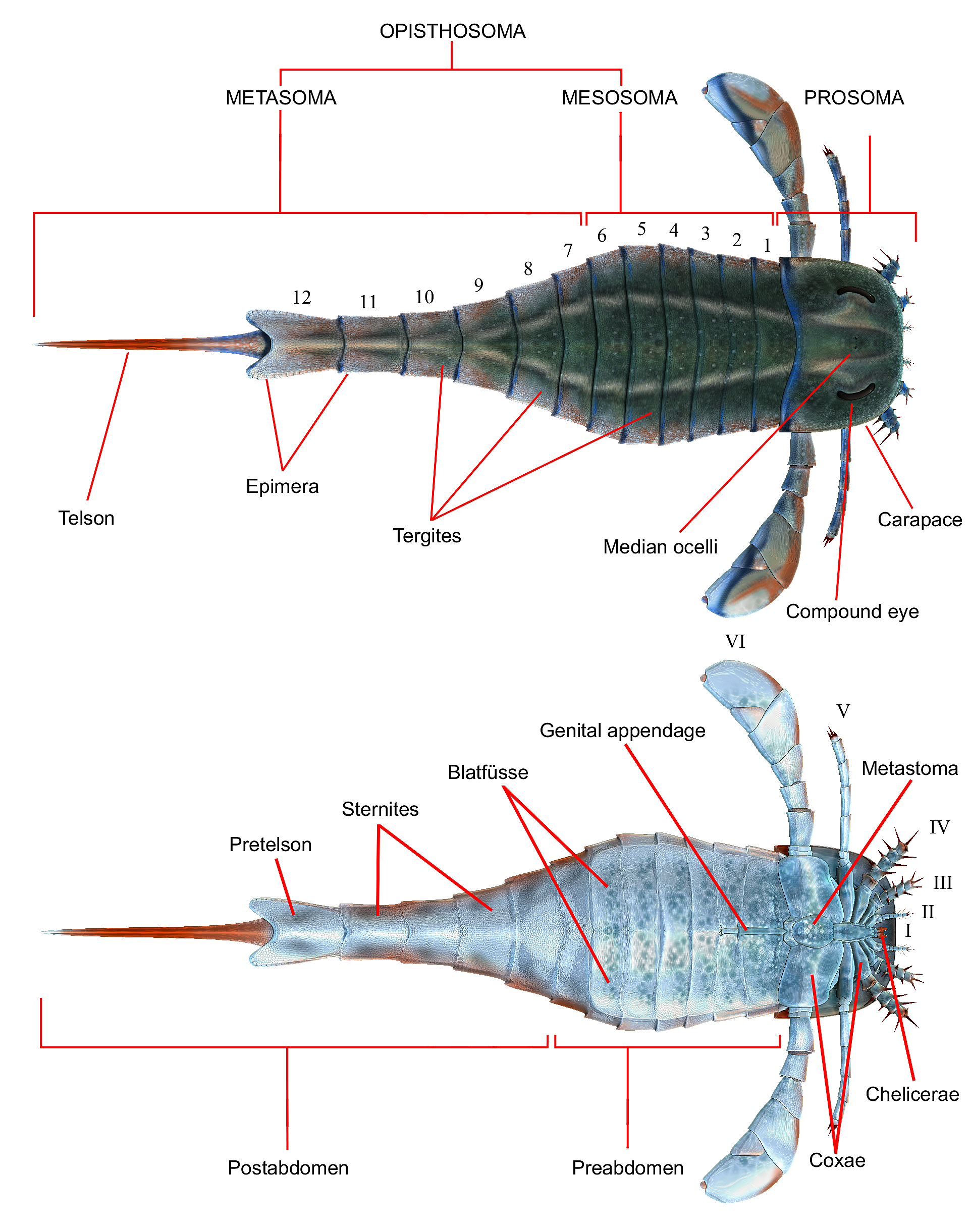
Eurypterid
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the Order (biology), order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 Myr, million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic Chelicerata, chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygotioidea
Pterygotioidea (the name deriving from the type genus ''Pterygotus'', meaning "winged one") is a superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Pterygotioids were the most derived members of the infraorder Diploperculata and the sister group of the adelophthalmoid eurypterids. The group includes the basal and small hughmilleriids, the larger and specialized slimonids and the famous pterygotids which were equipped with robust and powerful cheliceral claws. Though the more primitive hughmilleriids were small, '' Hughmilleria wangi'' being the smallest of all pterygotioids at just in length, later members of the group, particularly in the Pterygotidae, would become the largest known arthropods to ever exist with several genera surpassing in length. Among all currently recognized eurypterid clades, the Pterygotioidea is the most diverse, containing over 50 species in 10 genera. With the number of recognized eurypterid species being around 250, pterygotio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains. The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at 1 . Tectonic history Baltica formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga by the collision of three Archaean-Proterozoic continental blocks: Fennoscandia (including the exposed Baltic Shield), Sarmatia (Ukrainian Shield and Voronezh Massif), and Volgo-Uralia (covered by younger deposits). Sarmatia and Volgo-Uralia formed a proto-craton (sometimes called "Proto-Baltica") at c. 2.0 Ga which collided with Fennoscandia c. 1.8–1.7 Ga. The sutures between these three blocks were reactivated during the Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic. 750–600 million years ago, Baltica and Laurentia rotated clockwise together and drifted away from the Equator towa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic one, being found only in a single geographical location. Qualification The caveat “in appropriate habitat” is used to qualify the term "cosmopolitan distribution", excluding in most instances polar regions, extreme altitudes, oceans, deserts, or small, isolated islands. For example, the housefly is highly cosmopolitan, yet is neither oceanic nor polar in its distribution. Related terms and concepts The term pandemism also is in use, but not all authors are consistent in the sense in which they use the term; some speak of pandemism mainly in referring to diseases and pandemics, and some as a term intermediate between endemism and cosmopolitanism, in effect regarding pandemism as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanarkopterus
''Lanarkopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid with one recognised species, ''Lanarkopterus dolichoschelus''. ''Lanarkopterus'' was long seen as a species of the closely related '' Mixopterus'', though more complete specimens discovered in the 1960s determined that it differed in several aspects, enough to warrant a separate genus. Specimens of the genus have been recovered from deposits of Late Silurian age in Scotland. Description ''Lanarkopterus'' was a small to moderately large (ranging in size from less than 10 centimeters to over 30 centimeters) mixopterid eurypterid that like its close relative '' Mixopterus'' appeared almost scorpion-like with a broad and trilobed preabdomen, a narrow and tapering postabdomen and a sharped and curved telsonic spine. History of discovery Specimens of ''Lanarkopterus'' were first noted by Peach and Horne (1899) in the Ludlowian fish beds of the Lesmahagow and Hagshaw Hills Silurian inliers in Ayrshire and Lanarkshire, Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
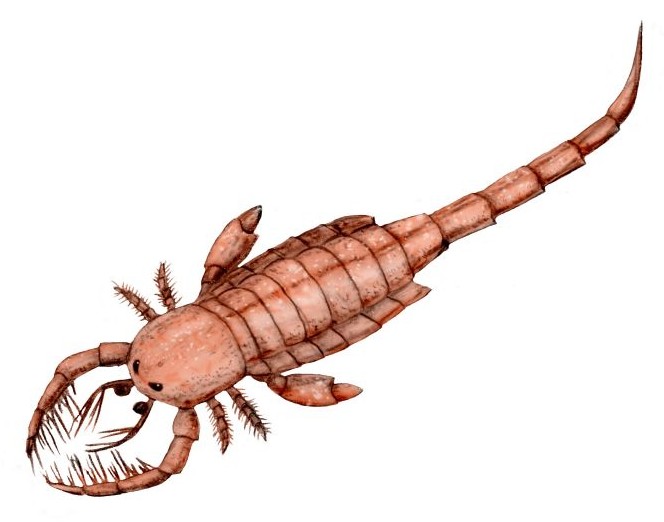
Mixopterus
''Mixopterus'' is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Mixopterus'' have been discovered in deposits from Late Silurian age, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from two continents; Europe and North America.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 18.5 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils18.5.pdf (PDF). Description ''Mixopterus'' was a medium-sized predatory eurypterid. The largest species, ''M. simonsoni'', reached lengths of 75 cm (29.5 in). It was characterised by a robust exoskeleton with scattered tubercles or semicircular scales. The prosoma (head) was subquadrate, protruding antemedially. The chelicerae (claws in front of the mouth) were small. The two first pairs of legs of ''Mixopterus'' (appendages II and III) were highly specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracarcinosoma
''Eusarcana'' (meaning "true flesh") is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Eusarcana'' have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from the Early Silurian to the Early Devonian. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, the genus contains three species, ''E. acrocephalus'', ''E. obesus'' and ''E. scorpionis'', from the Silurian-Devonian of Scotland, the Czech Republic and the United States respectively. ''Eusarcana'' is known for its odd proportions and features; the broad abdomen, thin and long tail, spined and forward-facing walking appendages and sharp and curved tail spike differentiate it from most other eurypterids, but are shared with other carcinosomatid eurypterids. The triangular carapace, oddly positioned forward-facing eyes differentiate the genus further from its closest relatives. At 80 centimetres (31.5 in) in length, ''E. scorpionis'' represents a moderately large species of eurypterid, and far exceeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinosoma
''Carcinosoma'' (meaning "crab body") is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Carcinosoma'' are restricted to deposits of late Silurian (Late Llandovery to Early Pridoli) age. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, which the genus lends its name to, ''Carcinosoma'' contains seven species from North America and Great Britain. Carcinosomatid eurypterids had unusual proportions and features compared to other eurypterids, with a broad abdomen, thin and long tail and spined and forward-facing walking appendages. They were not as streamlined as other groups but had considerably more robust and well developed walking appendages. In ''Carcinosoma'', these spined walking appendages are thought to have been used to create a trap to capture prey in. The telson (the posteriormost division of the body) of ''Carcinosoma'' appears to have possessed distinct segmentation, ''Carcinosoma'' is the only known eurypterid to possess this feature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annamia (terrane)
''Annamia'' is a small genus of gastromyzontid loaches native to Southeast Asia. There are two species, though one of them is of doubtful validity and identity: * ''Annamia normani'' ( Hora, 1931), found in the Mekong basin * ''Annamia thuathienensis'' H. D. Nguyễn & V. H. Nguyễn, 2005, found in Vietnam (''species inquirenda In biological classification, a ''species inquirenda'' is a species of doubtful identity requiring further investigation. The use of the term in English-language biological literature dates back to at least the early nineteenth century. The term t ...'') References * Gastromyzontidae Fish of Asia {{Cypriniformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |