|
Paracarcinosoma
''Eusarcana'' (meaning "true flesh") is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Eusarcana'' have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from the Early Silurian to the Early Devonian. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, the genus contains three species, ''E. acrocephalus'', ''E. obesus'' and ''E. scorpionis'', from the Silurian-Devonian of Scotland, the Czech Republic and the United States respectively. ''Eusarcana'' is known for its odd proportions and features; the broad abdomen, thin and long tail, spined and forward-facing walking appendages and sharp and curved tail spike differentiate it from most other eurypterids, but are shared with other carcinosomatid eurypterids. The triangular carapace, oddly positioned forward-facing eyes differentiate the genus further from its closest relatives. At 80 centimetres (31.5 in) in length, ''E. scorpionis'' represents a moderately large species of eurypterid, and far exceeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinosomatidae
Carcinosomatidae (the name deriving from the type genus ''Carcinosoma'', meaning "crab body")Meaning osomaat ''www.dictionary.com''. Retrieved 7 September 2018. is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. They were members of the superfamily Carcinosomatoidea, also named after ''Carcinosoma''. Fossils of carcinosomatids have been found in North America, Europe and Asia, the family possibly having achieved a worldwide distribution, and range in age from the Late Ordovician to the Early Devonian. They were among the most marine eurypterids, known almost entirely from marine environments. Carcinosomatids varied considerably in size, from species only a few centimetres in length to some of the largest known arthropods. The largest carcinosomatid species, ''Carcinosoma punctatum'', reached lengths of at least and rivalled the largest eurypterid of all, ''Jaekelopterus'', in size. Morphologically, carcinosomatids were highly distinct from other eurypterids, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
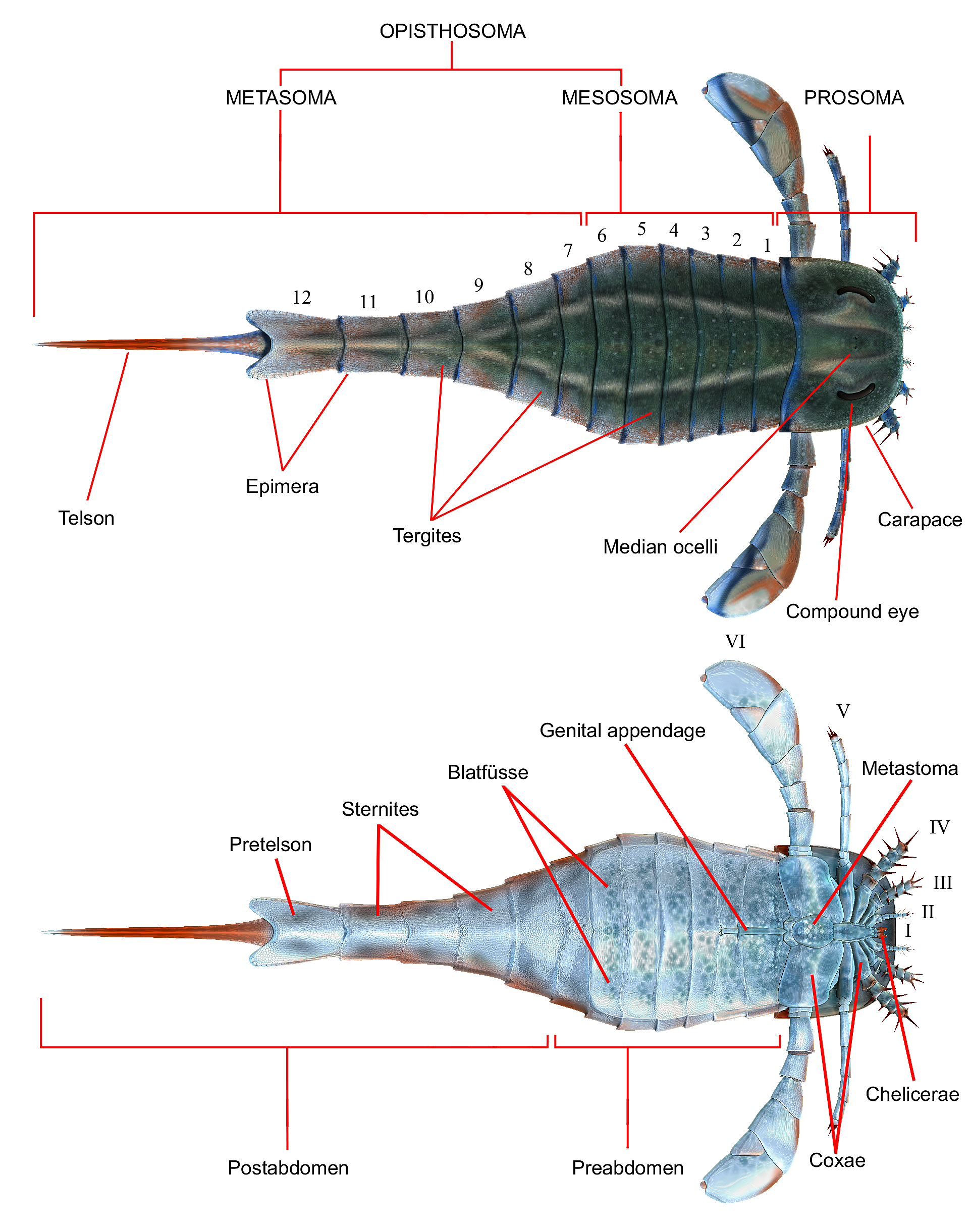
Carcinosoma
''Carcinosoma'' (meaning "crab body") is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Carcinosoma'' are restricted to deposits of late Silurian (Late Llandovery to Early Pridoli) age. Classified as part of the family Carcinosomatidae, which the genus lends its name to, ''Carcinosoma'' contains seven species from North America and Great Britain. Carcinosomatid eurypterids had unusual proportions and features compared to other eurypterids, with a broad abdomen, thin and long tail and spined and forward-facing walking appendages. They were not as streamlined as other groups but had considerably more robust and well developed walking appendages. In ''Carcinosoma'', these spined walking appendages are thought to have been used to create a trap to capture prey in. The telson (the posteriormost division of the body) of ''Carcinosoma'' appears to have possessed distinct segmentation, ''Carcinosoma'' is the only known eurypterid to possess this feature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterids
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event (or sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Mason Clarke
John Mason Clarke (April 15, 1857 – May 29, 1925) was an American teacher, geologist and paleontologist. __TOC__ Early career Born in Canandaigua, New York, the fifth of six children of Noah Turner Clarke and Laura Mason Merrill, he attended Canandaigua Academy where his father was teacher and principal. In 1873 he matriculated to Amherst College, where he graduated with a bachelor's degree in 1877. He returned to Canandaigua Academy and served as an instructor in various subjects. In 1879–1880 he worked as an assistant to Benjamin K. Emerson at Amherst, then he taught at the Utica Free Academy during 1880–1881. This was followed by work as an instructor at Smith College from 1881–1882, where he was made professor. During his second year at Smith, his first three scientific papers were published, concerning arthropods. It was at this point that he traveled to Göttingen University in 1883, where he hoped to study for a doctorate. However, an accusation of heterodox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laniatores
Laniatores is the largest suborder of the arachnid order Opiliones with over 4,000 described species worldwide. The majority of the species are highly dependent on humid environments and usually correlated with tropical and temperate forest habitats. Laniatores are typically (relatively) short-legged, hard-plated, spiny Opiliones, common under logs and stones, in leaf litter and in caves. They often have spiny pedipalps and paired or branched claws on the third and fourth pairs of legs.Pinto-da-Rocha ''et al.'' 2007: 17 The largest family is Gonyleptidae Sundevall, 1833, endemic of the Neotropics, with over 800 valid species and showing many cases of maternal and paternal care. Identification The dorsal scutum consists of a single piece, with the carapace or peltidium entirely fused with abdominal scutum. The pedipalpus is usually robust and armed with strong spines. The ovipositor is short and unsegmented (derived character state shared with the Dyspnoi). The penis is complex, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Woodward (geologist)
Henry Bolingbroke Woodward (24 November 1832 – 6 September 1921) was an English geologist and paleontologist known for his research on fossil crustaceans and other arthropods. Woodward was born Norwich, England on 24 November 1832 and was educated at Norwich School. He became assistant in the geological department of the British Museum in 1858, and in 1880 keeper of that department. He became Fellow of the Royal Society in 1873, LL.D (St Andrews) in 1878, president of the Geological Society of London (1894–1896). He was awarded the Murchison Medal in 1884 and Wollaston Medal in 1906. Woodward was president of the Geologists' Association for the years 1873 and 1874, president of the Malacological Society in 1893–1895, president of the Museums Association for the year 1900, and president of the Palaeontographical Society from 1895 (upon the death of incumbent president T. H. Huxley) to his own death in 1921. He published a ''Monograph of the British Fossil Crustacea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York (state)
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area. With 20.2 million people, it is the fourth-most-populous state in the United States as of 2021, with approximately 44% living in New York City, including 25% of the state's population within Brooklyn and Queens, and another 15% on the remainder of Long Island, the most populous island in the United States. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east; it has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. New York City (NYC) is the most populous city in the United States, and around two-thirds of the state's popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffalo Waterlime
Buffalo most commonly refers to: * Bubalina, including most "Old World" buffalo, such as water buffalo * Bison, including the American buffalo * Buffalo, New York Buffalo or buffaloes may also refer to: Animals * Bubalina, a subtribe of the tribe Bovini within the subfamily Bovinae ** African buffalo or Cape Buffalo (''Syncerus caffer'') ** ''Bubalus'', a genus of bovines including various water buffalo species ***Wild water buffalo (''Bubalus arnee'') *** Water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis'') **** Italian Mediterranean buffalo, a breed of water buffalo *** Anoa *** Tamaraw (''Bubalus mindorensis'') ***''Bubalus murrensis'', an extinct species of water buffalo that occupied riverine habitats in Europe in the Pleistocene * Bison, large, even-toed ungulates in the genus ''Bison'' within the subfamily Bovinae **American bison (''Bison bison''), also commonly referred to as the American buffalo or simply "buffalo" in North America **European bison is also known as the European buffalo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |