|
Medullary Sinuses
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and other languages present number categories of singular or plural, both of which are cited by using the hash sign (#) or by the numero signs "No." and "Nos." respectively. Some languages also have a dual, trial and paucal number or other arrangements. The count distinctions typically, but not always, correspond to the actual count of the referents of the marked noun or pronoun. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see "Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal means to express differences of number. One widespread distinction, found in English and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Staging
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that has spread to the limit of what the assessment measures. The stage generally takes into account the size of a tumor, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many regional (nearby) lymph nodes it has spread to (if any), and whether it has appeared in more distant locations (metastasized). The staging system is not applicable to astrocytoma, which is instead expressed as "grade I–IV". Grade IV astrocytoma, more commonly referred to as glioblastoma multiforme, is a universally fatal primary brain cancer most commonly seen in the seventh decade of life. TNM staging system Cancer staging can be divided into a clinical stage and a pathologic stage. In the TNM (Tumor, Node, Metastasis) system, clinical stage and pathologic stage are deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheobronchial Lymph Nodes
The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi. Structure These lymph nodes form four main groups including paratracheal, tracheobronchial, bronchopulmonary and pulmonary nodes. # ''Paratracheal nodes'' are located on either side of the trachea. # ''Tracheobronchial nodes'' can be divided into three nodes including left and right superior tracheobronchial nodes, and the inferior trachiobronchial node. The two superior tracheobronchial nodes are located on either side of trachea just before its bifurcation. The inferior tracheobronchial node is located just below the bifurcation in the angle between the two bronchi. # ''Bronchopulmonary nodes'' situate in the hilum of each lung. # ''Pulmonary nodes'' are embedded the lung substance on the larger branches of the bronchi. The ''afferents'' of the tracheobronchial glands drain the lungs and bronchi, the thoracic part of the trachea and the heart; some o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraaortic Lymph Nodes
The periaortic lymph nodes (also known as lumbar) are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs. The periaortic lymph nodes are different from the paraaortic lymph nodes. The periaortic group is the general group, that is subdivided into: preaortic, paraaortic, and retroaortic groups. The paraaortic group is synonymous with the lateral aortic group. Divisions The periaortic lymph node group is divided into three subgroups: preaortic, paraaortic, and retroaortic: * The preaortic group drains the gastrointestinal viscera. They can be subdivided into three groups: the celiac nodes, the superior mesenteric nodes, and the inferior mesenteric nodes. *The paraaortic group (also known as lateral aortic group) drains the iliac nodes, the ovaries, the testes and other pelvic organs. The lateral group nodes are located adjacent to the aorta, anterior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Lymph Nodes
Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human groin. Located in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region, they are grouped into superficial and deep lymph nodes. The superficial have three divisions: the superomedial, superolateral, and inferior superficial. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes * The superficial inguinal lymph nodes are the inguinal lymph nodes that form a chain immediately below the inguinal ligament. They lie deep to the fascia of Camper that overlies the femoral vessels at the medial aspect of the thigh. They are bounded superiorly by the inguinal ligament in the femoral triangle; laterally by the border of the sartorius muscle, and medially by the adductor longus muscle. They are divided into three groups: * inferior – inferior of the saphenous opening of the leg, receive drainage from lower legs * superolateral – on the side of the saphenous opening, receive drainage from the side buttocks and the lower abdominal wall. * superomedial – located at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Lymph Nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation. Classification There are approximately 300 lymph nodes in the neck, and they can be classified in a number of different ways. History The classification of the cervical lymph nodes is generally attributed to Henri Rouvière in his 1932 publication "Anatomie des Lymphatiques de l'Homme" Rouviere described the cervical lymph nodes as a collar which surrounded the upper aerodigestive tract, consisting of submental, facial, submandibular, parotid, mastoid, occipital and retropharyngeal nodes, together with two chains that run in the long axis of the neck, the anterior cervical and postero-lateral cervical groups. However, this system was based upon anatomical landmarks found in dissection, making it imperfectly suited to the nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
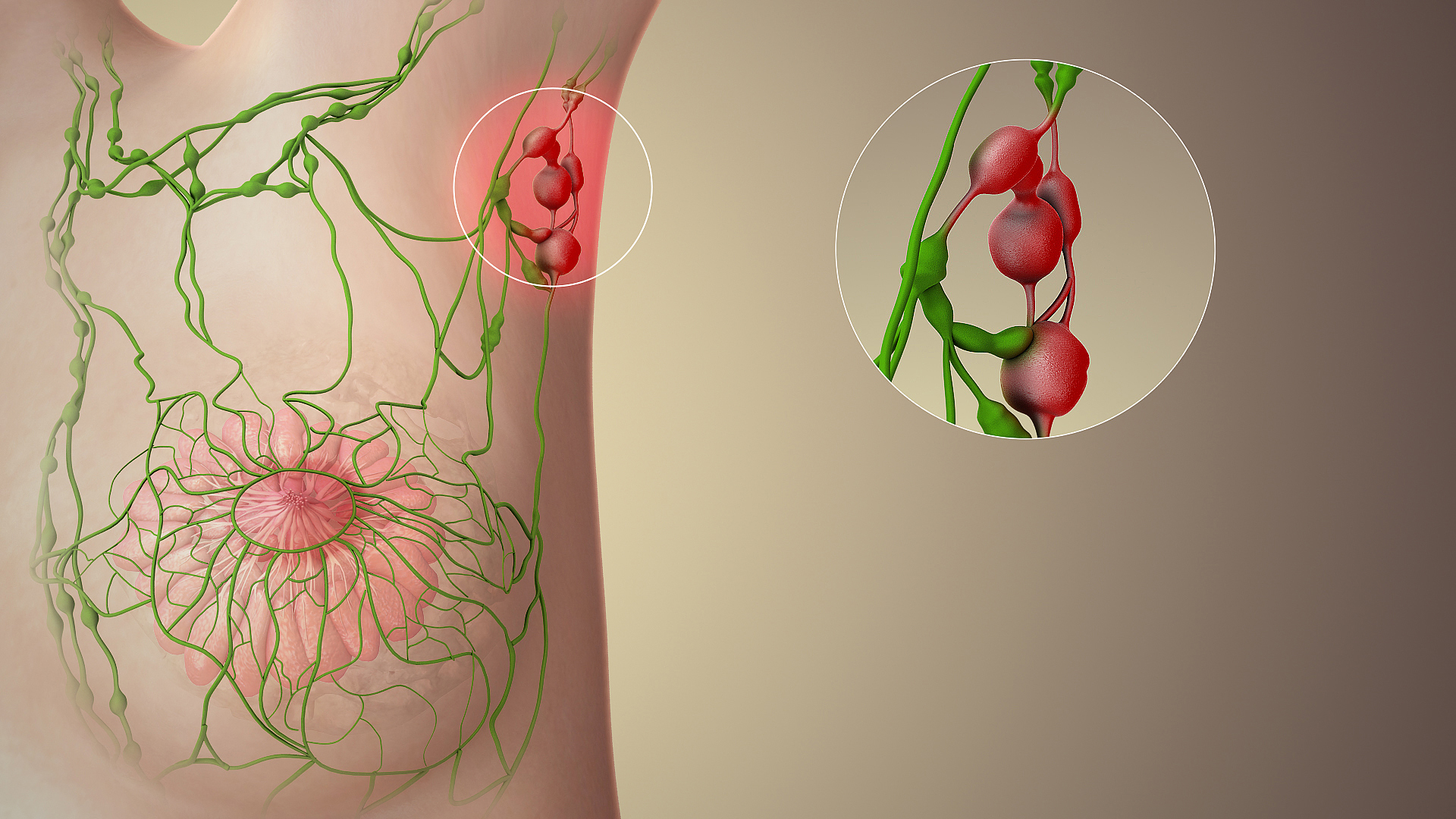
Axillary Lymph Nodes
The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and the abdomen above the level of the navel, and the vessels from the upper limb. They are divided in several groups according to their location in the armpit. These lymph nodes are clinically significant in breast cancer, and metastases from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes are considered in the staging of the disease. Structure The axillary lymph nodes are arranged in six groups: # Anterior (pectoral) group: Lying along the lower border of the pectoralis minor behind the pectoralis major, these nodes receive lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast and superficial vessels from the anterolateral abdominal wall above the level of the umbilicus. # Posterior (subscapular) group: Lying in front of the subscapularis muscle, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic Vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood. Because it is derived from interstitial fluid, with which blood and surrounding cells continually exchange substances, lymph undergoes continual change in composition. It is generally similar to blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood. Lymph returns pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilum (anatomy)
In human anatomy, the hilum (; plural hila), sometimes formerly called a hilus (; plural hili), is a depression or fissure where structures such as blood vessels and nerves enter an organ. Examples include: * Hilum of kidney, admits the renal artery, vein, ureter, and nerves * Splenic hilum, on the surface of the spleen, admits the splenic artery, vein, lymph vessels, and nerves * Hilum of lung, a triangular depression where the structures which form the root of the lung enter and leave the viscus * Hilum of lymph node, the portion of a lymph node where the efferent vessels exit * Hilus of dentate gyrus, part of hippocampus The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , ' seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, ... that contains the mossy cells. {{Authority control Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabecula
A trabecula (plural trabeculae, from Latin for "small beam") is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally has a mechanical function, and is usually composed of dense collagenous tissue (such as the trabecula of the spleen). It can be composed of other material such as muscle and bone. In the heart, muscles form trabeculae carneae and septomarginal trabeculae. Cancellous bone is formed from groupings of trabeculated bone tissue. In cross section, trabeculae of a cancellous bone can look like septa, but in three dimensions they are topologically distinct, with trabeculae being roughly rod or pillar-shaped and septa being sheet-like. When crossing fluid-filled spaces, trabeculae may offer the function of resisting tension (as in the penis, see for example trabeculae of corpora cavernosa and trabeculae of corpus spongiosum) or providing a cell fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)