|
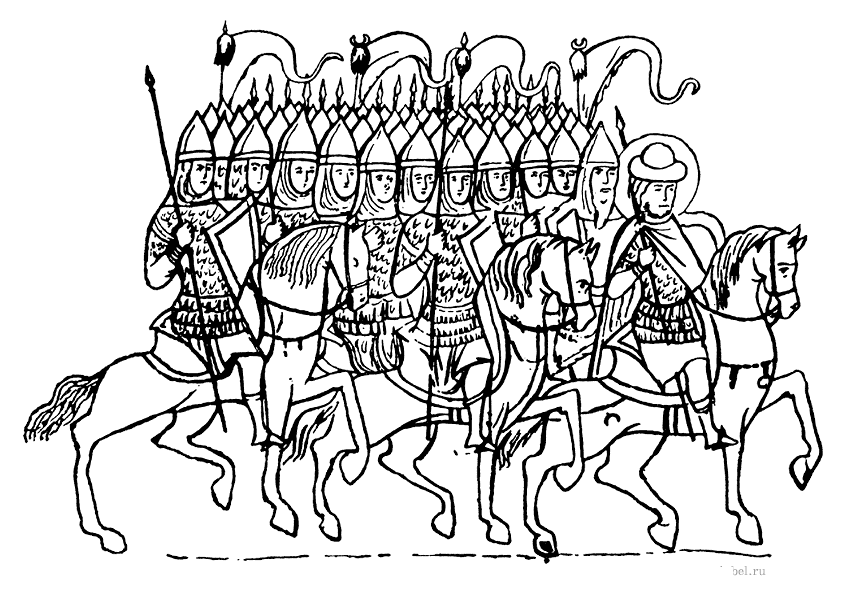
Medieval Russian Army
The armies of the Rus' principalities emerged in the 13th century out of the military of Kievan Rus', shattered by the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus'. The princely Rus' armies from 1240 to 1550 were characterised by feudalism, consisting of cavalry armies of noble militia and their armed servants. Before the Mongol invasion Before Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, a Rus' prince would be accompanied by his druzhina, a small retinue of heavy cavalry, who would often fight dismounted (eq. Battle on the Ice). Massively heavy armor was used, mostly Scandinavian-style. However, these squads, as a rule, did not exceed the number of several hundred men, and were unsuitable for united actions under a single command. At the same time, the main part of the Kievan Rus' army was the militia infantry. It was inferior to Druzhina in armament and the ability to own it. The militia used axes and hunting spears ("rogatina"). Swords were rarely used, and they had no armor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of Kievan Rus'
The military of Kievan Rus served as the armed forces of Kievan Rus' between the 9th to 13th century. It was mainly characterised by infantry armies of town militia that were supported by druzhyna cavalry. Composition Tribal militia known as '' voyi'' formed the basis of the army in Kievan Rus' until the tax reform of Olga of Kiev in the middle of the 10th century. In the subsequent period, under Svyatoslav I of Kiev and Volodimer I of Kiev, druzhyna played a dominant role. It consisted of senior members – the boyars – along with the rank-and-file ‘youths’ ("otroki"). The regiments of city militia, raised by the decision of the veche, were formed in the 11th century. These regiments received weapons and horses for a campaign from the prince. Tactics and equipment Before Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, a Prince would be accompanied by his druzhyna, a small retinue of heavy cavalry, who would often fight dismounted (eq. Battle on the Ice). Mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Sit River
The Battle of the Sit River was fought in the northern part of the present-day Sonkovsky District of Tver Oblast of Russia, close to the selo of ''Bozhonka'', on March 4, 1238 between the Mongol Hordes of Batu Khan and the Rus' under Grand Prince Yuri II of Vladimir-Suzdal during the Mongol invasion of Rus. Battle After the Mongols sacked his capital of Vladimir, Yuri fled across the Volga northward, to Yaroslavl, where he hastily mustered an army. He and his brothers then turned back toward Vladimir in hopes of relieving the city before the Mongols took it, but they were too late. Yuri sent out a force of 3,000 men under Dorozh to scout out where the Mongols were; whereupon Dorozh returned saying that Yuri and his force was already surrounded. As he tried to muster his forces, he was attacked by the Mongol force under Burundai and fled but was overtaken on the Sit River and died there along with his nephew, Prince Vsevolod of Yaroslavl.Robert Michell and Neville Forbes, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mounted Archery
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, for protecting the herds, and for war. It was a defining characteristic of the Eurasian nomads during antiquity and the medieval period, as well as the Iranian peoples, (Alans, Scythians, Sarmatians, Parthians, Sassanid Persians) and Indians in antiquity, and by the Hungarians, Mongols, Chinese, and the Turkic peoples during the Middle Ages. By the expansion of these peoples, the practice also spread to Eastern Europe (via the Sarmatians and the Huns), Mesopotamia, and East Asia. In East Asia, horse archery came to be particularly honored in the samurai tradition of Japan, where horse archery is called Yabusame. The term mounted archer occurs in medieval English sources to describe a soldier who rode to battle but who dismounted to shoot. ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
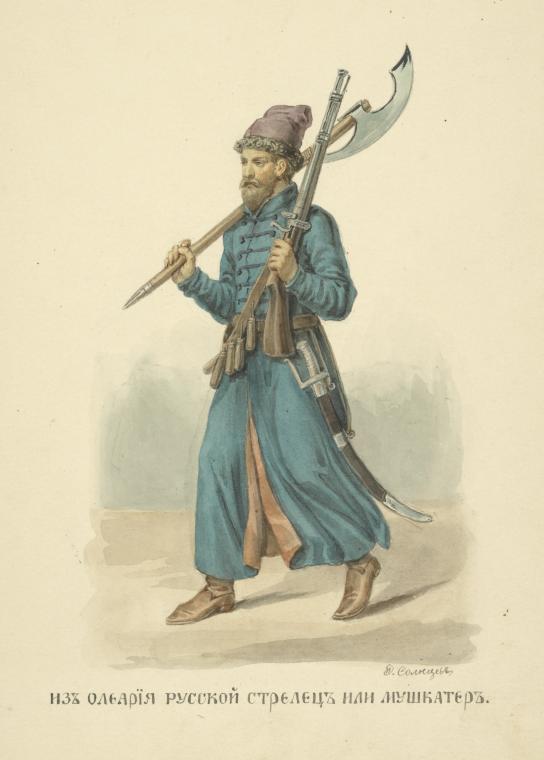
Streltsy
, image = 01 106 Book illustrations of Historical description of the clothes and weapons of Russian troops.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = , dates = 1550–1720 , disbanded = , country = Tsardom of Russia , allegiance = Streltsy Department , branch = , type = Infantry , role = , size = , command_structure = Russian Army , garrison = Moscow , garrison_label = , nickname = , patron = Saint George , motto = , colors = , colors_label = , march = , mascot = , anniversaries = , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = Siege of KazanLivonian WarBattle of MolodiPolish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)Smolensk WarRusso-Polish War (1654–1667)Great Northern War , battles_label = , decorations = , battle_honours = , battle_honours_label = , flying_hours = , website = , current_commander = , commander1 = , commander1_label = , commander2 = , commander2_label = , commander3 = , commander3_label = , commander4 = , commander4_label = , comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier. Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus'' ("hook gun"), was applied to many different forms of firearms from the 15th to 17th centuries, it originally referred to "a hand-gun with a hook-like projection or lug on its under surface, useful for steadying it against battlements or other objects when firing". These "hook guns" were in their earliest forms of defensive weapons mounted on German city walls in the early 15th century. The addition of a shoulder stock, priming pan, and matchlock mechanism in the late 15th century turned the arquebus into a handheld firearm and also the first firearm equipped with a trigger. The exact dating of the matchlock's appearance is disputed. It could have appeared in the Ottoman Empire as early as 1465 and in Europe a little before 1475. The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Military Tactics And Organization
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigten, Khorchins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brockhaus And Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary B43 202-1
Brockhaus may refer to: * Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus (1772–1823), German encyclopedia publisher and editor ** F.A. Brockhaus AG, his publishing firm ** ''Brockhaus Enzyklopädie'', an encyclopedia published by the firm ** 27765 Brockhaus, an asteroid named for him * Hermann Brockhaus Hermann Brockhaus (January 28, 1806 – January 5, 1877) was a German Orientalist born in Amsterdam. He was a leading authority on Sanskrit and Persian languages. He was the son of publisher Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus and brother-in-law to ... (1806–1877), German orientalist See also * Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary, a Russian-language encyclopedia {{disambiguation, surname German-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kholop
A kholop ( rus, холо́п, p=xɐˈlop) was a type of feudal serf in Kievan Rus', then in Russia between the 10th and early 18th centuries. Their legal status was close to that of slaves. Etymology The word ''kholop'' was first mentioned in a chronicle for the year of 986. The word is cognate with Slavic words translated as "man" or "boy" (modern Ukrainian: хлопець (''khlopets''), Polish: ''chłopiec'', Bulgarian: ''хлапе''/''хлапак''). ''Chlap/chlop'' (pronounced khlap/khlop) is a synonym for "man" in Slovak (''chlapec'' thus being the diminutive). Such transitions between the meanings "young person" and "servant" (in both directions) are commonplace, as evident from the English use of "boy" in the sense of "domestic servant". Kholops The ''Russkaya Pravda,'' a legal code of the late Kievan Rus, details the status and types of ''kholops'' of the time. In the 11th–12th centuries, the term referred to different categories of dependent people and especia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Class People
Service class people (russian: служилые люди, sluzhilyye lyudi) were a class of free people in the Tsardom of Russia in the 14th to the 17th centuries, obliged to perform military or administrative service on behalf of the state. Background There were two main groups of service people: * ''hereditary servitors'' ''("servitors by birth")'', included Boyars, noblemen and "Boyars' children". They served in the "Landed army", and received land and serfs for their service. * ''chosen servitors ("servitors by contract"),'' included Streltsy, Cossacks and clerks. They served in the infantry or administration, and were paid in coin. ;In Siberia In early Siberia, service-men and ''promyshlenik''s (promyshlenniki) were the two main classes of the Russian population. Service-men were nominally servants of the tsar, had certain legal rights and duties and could expect pay if they were lucky. ''Promyshlenik''s were free men who made their living any way they could. A minor g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of modern Russia. The Republic prospered as the easternmost trading post of the Hanseatic League and its Slavic, Baltic and Finnic people were much influenced by the culture of the Viking-Varangians and Byzantine people. Name The state was called "Novgorod" and "Novgorod the Great" (''Veliky Novgorod'', russian: Великий Новгород) with the form "Sovereign Lord Novgorod the Great" (''Gosudar Gospodin Veliky Novgorod'', russian: Государь Господин Великий Новгород) becoming common in the 15th century. ''Novgorod Land'' and ''Novgorod volost usually referred to the land belonging to Novgorod. ''Novgorod Republic'' itself is a much later term, although the polity was described as a republic as early a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar". Initially, the ethnonym ''Tatar'' possibly referred to the . That confederation was eventually incorporated into the when unified the various steppe tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Mail Armor
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including: *Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and people of Russia, regardless of ethnicity *Russophone, Russian-speaking person (, ''russkogovoryashchy'', ''russkoyazychny'') * Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages * Russian alphabet * Russian cuisine *Russian culture *Russian studies Russian may also refer to: *Russian dressing *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith *Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series * Russian (solitaire), a card game * "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album '' '' by Caravan Palace * Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 *The South African name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |