|
MedCalc
__NOTOC__ MedCalc is a statistical software package designed for the biomedical sciences. It has an integrated spreadsheet for data input and can import files in several formats (Microsoft Excel, Excel, SPSS, Comma-separated values, CSV, ...). MedCalc includes basic parametric and non-parametric statistical procedures and graphs such as descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Mann–Whitney U test, Mann–Whitney test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, Wilcoxon test, chi-squared distribution, χ2 test, correlation, linear regression, linear as well as Nonlinear regression, non-linear regression, logistic regression, and multivariate statistics. Survival analysis includes Cox regression (Proportional hazards model) and Kaplan–Meier estimator, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Procedures for method evaluation and method comparison include ROC curve analysis, Bland–Altman plot, as well as Deming regression, Deming and Passing–Bablok regression. The software also includes reference interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MedCalc Software
__NOTOC__ MedCalc is a statistical software package designed for the biomedical sciences. It has an integrated spreadsheet for data input and can import files in several formats (Excel, SPSS, CSV, ...). MedCalc includes basic parametric and non-parametric statistical procedures and graphs such as descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Mann–Whitney test, Wilcoxon test, χ2 test, correlation, linear as well as non-linear regression, logistic regression, and multivariate statistics. Survival analysis includes Cox regression (Proportional hazards model) and Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Procedures for method evaluation and method comparison include ROC curve analysis, Bland–Altman plot, as well as Deming and Passing–Bablok regression. The software also includes reference interval estimation, meta-analysis and sample size calculations. The first DOS version of MedCalc was released in April 1993 and the first version for Windows was available in November 1996. Version 15.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Statistical Packages
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of statistical analysis packages. General information Operating system support ANOVA Support for various ANOVA methods Regression Support for various Regression analysis, regression methods. Time series analysis Support for various time series analysis methods. Charts and diagrams Support for various statistical charts and diagrams. Other abilities See also * Comparison of computer algebra systems * Comparison of deep learning software * Comparison of numerical-analysis software * Comparison of survey software * Comparison of Gaussian process software * List of scientific journals in statistics * List of statistical packages Footnotes References Further reading * * * * * {{Statistical software Comparisons of mathematical software, Statistical packages Statistical software, Statistics-related lists Mathematical and quantitative methods (economics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Software
Statistical software are specialized computer programs for analysis in statistics and econometrics. Open-source * ADaMSoft – a generalized statistical software with data mining algorithms and methods for data management * ADMB – a software suite for non-linear statistical modeling based on C++ which uses automatic differentiation * Chronux – for neurobiological time series data * DAP – free replacement for SAS * Environment for DeveLoping KDD-Applications Supported by Index-Structures (ELKI) a software framework for developing data mining algorithms in Java * Epi Info – statistical software for epidemiology developed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Apache 2 licensed * Fityk – nonlinear regression software (GUI and command line) * GNU Octave – programming language very similar to MATLAB with statistical features * gretl – gnu regression, econometrics and time-series library * intrinsic Noise Analyzer (iNA) – For analyzing intrinsic fluctua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Statistical Packages
Statistical software are specialized computer programs for analysis in statistics and econometrics. Open-source * ADaMSoft – a generalized statistical software with data mining algorithms and methods for data management * ADMB – a software suite for non-linear statistical modeling based on C++ which uses automatic differentiation * Chronux – for neurobiological time series data * DAP – free replacement for SAS * Environment for DeveLoping KDD-Applications Supported by Index-Structures (ELKI) a software framework for developing data mining algorithms in Java * Epi Info – statistical software for epidemiology developed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Apache 2 licensed * Fityk – nonlinear regression software (GUI and command line) * GNU Octave – programming language very similar to MATLAB with statistical features * gretl – gnu regression, econometrics and time-series library * intrinsic Noise Analyzer (iNA) – For analyzing intrinsic fluctuat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passing–Bablok Regression
Passing–Bablok regression is a method from robust statistics for nonparametric regression analysis suitable for method comparison studies introduced by Wolfgang Bablok and Heinrich Passing in 1983. The procedure is adapted to fit linear errors-in-variables models. It is symmetrical and is robust in the presence of one or few outliers. The Passing-Bablok procedure fits the parameters a and b of the linear equation y = a + b * x using non-parametric methods. The coefficient b is calculated by taking the shifted median of all slopes of the straight lines between any two points, disregarding lines for which the points are identical or b = -1. The median is shifted based on the number of slopes where b < -1 to create an approximately consistent estimator. The estimator is therefore close in spirit to the Theil-Sen estimator. The parameter is calculated by [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bland–Altman Plot
A Bland–Altman plot (difference plot) in analytical chemistry or biomedicine is a method of data plotting used in analyzing the agreement between two different assays. It is identical to a Tukey mean-difference plot, the name by which it is known in other fields, but was popularised in medical statistics by J. Martin Bland and Douglas G. Altman. Agreement versus correlation Bland and Altman drive the point that any two methods that are designed to measure the same parameter (or property) should have good correlation when a set of samples are chosen such that the property to be determined varies considerably. A high correlation for any two methods designed to measure the same property could thus in itself just be a sign that one has chosen a widespread sample. A high correlation does not necessarily imply that there is good agreement between the two methods. Construction Consider a sample consisting of n observations (for example, objects of unknown volume). Both assay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Chemistry (journal)
''Clinical Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering the field of clinical chemistry. It is the official journal of the American Association for Clinical Chemistry. The journal was first published in 1955 on a bi-monthly basis "to raise the level at which chemistry is practiced in the clinical laboratory"; monthly publication commenced in 1964.Rej, R. Clin Chem 50:2415-58 (2004) The editor-in-chief is Nader Rifai (Harvard Medical School). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in PubMed/MEDLINE and the Science Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 8.327. References External links * {{Official website, http://intl.clinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.Herrera Ortiz AF., Cadavid Camacho E, Cubillos Rojas J, Cadavid Camacho T, Zoe Guevara S, Tatiana Rincón Cuenca N, Vásquez Perdomo A, Del Castillo Herazo V, & Giraldo Malo R. A Practical Guide to Perform a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 2022;7(4):47–57. https://doi.org/10.21801/ppcrj.2021.74.6 Not only can meta-analyses provide an estimate of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deming Regression
In statistics, Deming regression, named after W. Edwards Deming, is an errors-in-variables model which tries to find the line of best fit for a two-dimensional dataset. It differs from the simple linear regression in that it accounts for errors in observations on both the ''x''- and the ''y''- axis. It is a special case of total least squares, which allows for any number of predictors and a more complicated error structure. Deming regression is equivalent to the maximum likelihood estimation of an errors-in-variables model in which the errors for the two variables are assumed to be independent and normally distributed, and the ratio of their variances, denoted ''δ'', is known. In practice, this ratio might be estimated from related data-sources; however the regression procedure takes no account for possible errors in estimating this ratio. The Deming regression is only slightly more difficult to compute than the simple linear regression. Most statistical software packages used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROC Curve
A receiver operating characteristic curve, or ROC curve, is a graphical plot that illustrates the diagnostic ability of a binary classifier system as its discrimination threshold is varied. The method was originally developed for operators of military radar receivers starting in 1941, which led to its name. The ROC curve is created by plotting the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR) at various threshold settings. The true-positive rate is also known as sensitivity, recall or ''probability of detection''. The false-positive rate is also known as ''probability of false alarm'' and can be calculated as (1 − specificity). The ROC can also be thought of as a plot of the power as a function of the Type I Error of the decision rule (when the performance is calculated from just a sample of the population, it can be thought of as estimators of these quantities). The ROC curve is thus the sensitivity or recall as a function of fall-out. In general, if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
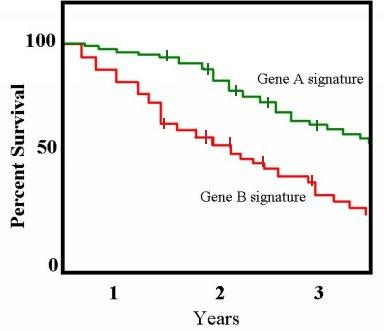
Kaplan–Meier Estimator
The Kaplan–Meier estimator, also known as the product limit estimator, is a non-parametric statistic used to estimate the survival function from lifetime data. In medical research, it is often used to measure the fraction of patients living for a certain amount of time after treatment. In other fields, Kaplan–Meier estimators may be used to measure the length of time people remain unemployed after a job loss, the time-to-failure of machine parts, or how long fleshy fruits remain on plants before they are removed by frugivores. The estimator is named after Edward L. Kaplan and Paul Meier, who each submitted similar manuscripts to the ''Journal of the American Statistical Association''. The journal editor, John Tukey, convinced them to combine their work into one paper, which has been cited almost 61,000 times since its publication in 1958. The estimator of the survival function S(t) (the probability that life is longer than t) is given by: : \widehat S(t) = \prod\limits_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |