|
Meandrina Meandrites
''Meandrina meandrites'', commonly known as maze coral, is a species of colonial stony coral in the family Meandrinidae. It is found primarily on outer coral reef slopes in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Description ''Meandrina meandrites'' forms massive hemispherical heads or develops into substantial flat plates and can grow to nearly in diameter. Some small colonies are cone-shaped and are not attached to the substrate. These resemble young colonies of rose coral ('' Manicina areolata'') and may be found in sandy or muddy areas some way from reefs. The corallites, the calcareous cups secreted by the polyps, are wide. The raised walls between the corallites are formed from fine but widely separated transverse ridges called septa and meander over the surface of the coral. There is a slight indentation running along the crest of the walls where the septa from adjoining corallites meet. The polyps are large but are only protruded at night when they cover and obscure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda
) , anthem = "God Save the King" , song_type = National song , song = " Hail to Bermuda" , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , mapsize2 = , map_caption2 = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title2 = English settlement , established_date2 = 1609 (officially becoming part of the Colony of Virginia in 1612) , official_languages = English , demonym = Bermudian , capital = Hamilton , coordinates = , largest_city = Hamilton , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2016 , government_type = Parliamentary dependency under a constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Rena Lalgie , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Edward David Burt , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Senate , lower_house = House of Assembly , area_km2 = 53.2 , area_sq_mi = 20.54 , area_rank = , percent_water = 27 , elevation_max_m = 79 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
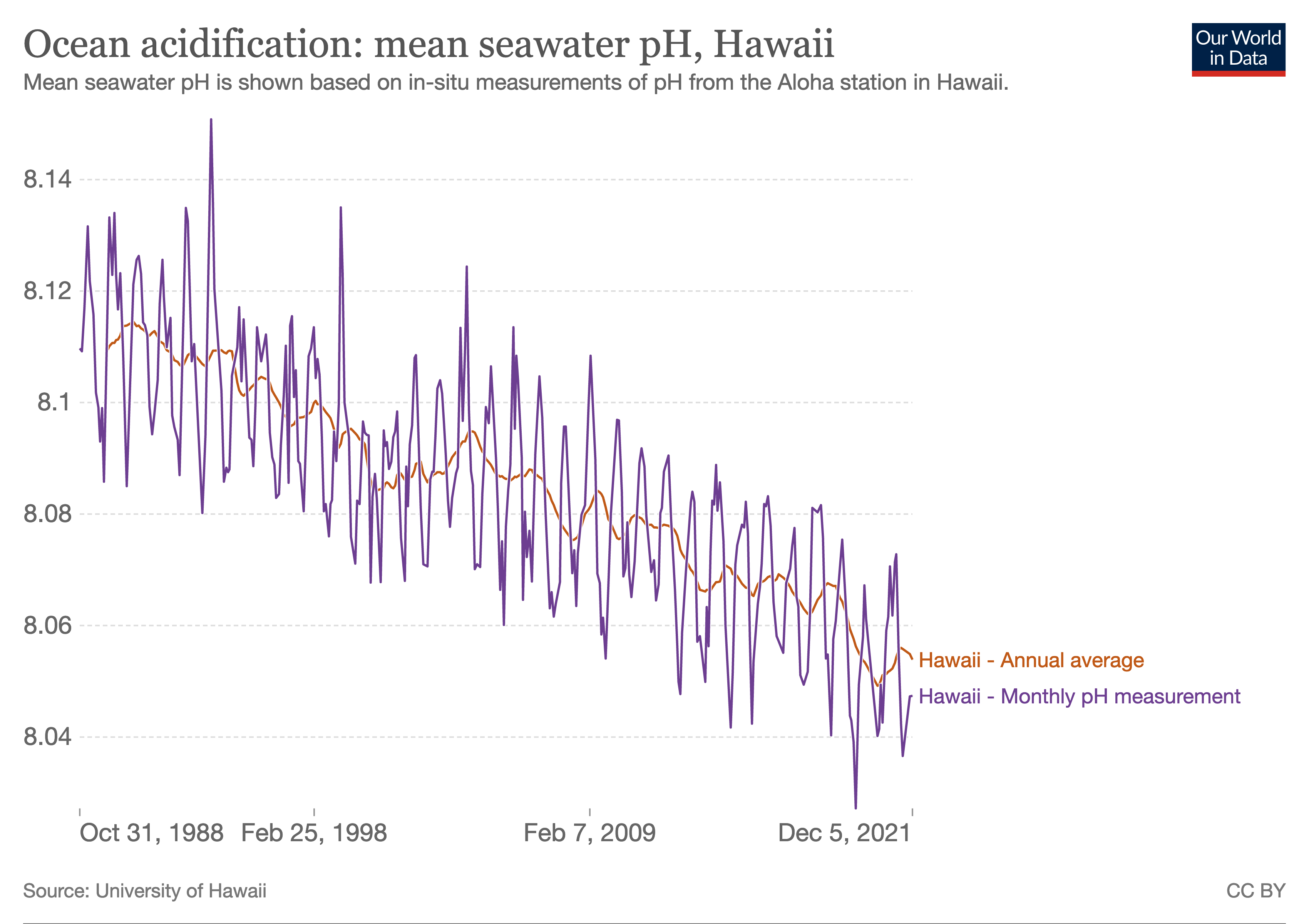
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxide emissions from human activities which have led to atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels of more than 410 ppm (in 2020). The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. This leads to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (H+). The free hydrogen ions (H+) decrease the pH of the ocean, therefore increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). A decrease in pH corresponds to a decrease in the concentration of carbonate ions, which are the main building block for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells and skeletons. Marine calcifying organisms, like mollusks, oysters and corals, are particularly affected by this as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichocoenia Stokesi
''Dichocoenia'' is a monotypic genus of stony coral in the family Meandrinidae. It is represented by a single species, ''Dichocoenia stokesii'', which is commonly known as pineapple coral, elliptical star coral, or pancake star coral. It is found in the Caribbean Sea and the western Atlantic Ocean. ''Dichocoenia stokesii'' has irregular calyces and its form can be either a massive, hemispherical hump or a flat, platform-like structure. Description ''Dichocoenia stokesi'' is a massive colonial coral that forms rounded humps up to in diameter or thick plates. It is recognisable by the fact that many of the corallites, the stony cups from which the coral polyps protrude, can be oval, or elongated. They can be up to long and only wide. Others are circular or Y-shaped and all have raised rims. The columella, the central axial structure in the corallite, is fragile and spongy. The polyps are large and well-separated with a diameter of about . The colour is variable and can be whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Band Disease
Black band disease is a coral disease in which corals develop a black band. It is characterized by complete tissue degradation due to a pathogenic microbial consortium. The mat is present between apparently healthy coral tissue and freshly exposed coral skeleton. Appearance Black band disease was first observed on reefs in Belize in 1973 by A. Antonius, who described the pathogen he found infecting corals as '' Oscillatoria membranacea'', one of the cyanobacteria. The band color may be blackish brown to red depending on the vertical position of a cyanobacterial population associated with the band. The vertical position is based on a light intensity-dependent photic response of the cyanobacterial filaments, and the color (due to the cyanobacterial pigment phycoerythrin) is dependent on the thickness of the band. The band is approximately thick and ranges in width from to White specks may be present on surface, at times forming dense white patches. The pathogenic microbial mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurantimonadaceae
The ''Aurantimonadaceae'' are a small family of marine bacteria. Notable Species ''Aurantimonas coralicida'' causes a white plague in corals. ''Fulvimarina pelagi'' was isolated from seawater, and takes the form of nonmotile rods. ''Fulvimarina pelagi'' is an obligate aerobe, and obtains its nourishment chemoheterotrophically. It tests positive for oxidase and catalase, and contains carotenoid pigments, possibly to protect against solar radiation. Etymology The name ''Aurantimonas'' derives from: New Latin ''aurantus'', orange-coloured; Greek ''monas'' (μονάς), a unit; to mean an orange-coloured unicellular organism. Members of the genus ''Aurantimonas'' can be referred to as aurantimonads (''viz.'' trivialisation of names). Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates that are commonly referred to as algae) that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxanthellae produce the majority of coral colouration, the coral tissue becomes transparent, revealing the coral skeleton made of calcium carbonate. Most bleached corals appear bright white, but some are blue, yellow, or pink due to pigment proteins in the coral. The leading cause of coral bleaching is rising ocean temperature due to climate change. A temperature about 1 °C (or 2 °F) above average can cause bleaching. According to the United Nations Environment Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. They do not qualify as threatened, near threatened, or (before 2001) conservation dependent. Species cannot be assigned the "Least Concern" category unless they have had their population status evaluated. That is, adequate information is needed to make a direct, or indirect, assessment of its risk of extinction based on its distribution or population status. Evaluation Since 2001 the category has had the abbreviation "LC", following the IUCN 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1). Before 2001 "least concern" was a subcategory of the "Lower Risk" category and assigned the code "LR/lc" or lc. Around 20% of least concern taxa (3261 of 15636) in the IUCN database still use the code "LR/lc", which indicates they have not been re-evaluate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List Of Threatened Species
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the International Union for Conservation of Nature, IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to International Unio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau, Bahamas, Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama Islands were inhabited by the Lucayan people, Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-Taino language, speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida and Cuba; it is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Spanning , Florida ranks 22nd in area among the 50 states, and with a population of over 21 million, it is the third-most populous. The state capital is Tallahassee, and the most populous city is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the ninth-most populous in the United States; other urban conurbations with over one million people are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Various Native American groups have inhabited Florida for at least 14,000 years. In 1513, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León became the first k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |