|
McAlpin's Corps
{{Infobox military unit , unit_name = McAlpin's Corps , image = , image_size = , caption = , country = {{flagcountry, Kingdom of Great Britain , allegiance = {{army, Kingdom of Great Britain , type = Loyalist local volunteer corps, (auxiliary troops) , branch = infantry , dates = 1777-1783 , specialization = infantry, fortification construction , command_structure = , size = battalion-corps (184) , current_commander = , garrison = Province of Quebec , ceremonial_chief = , nickname = McAlpin's Corps of Royalists, American Volunteers , motto = , colors = , march = , mascot = , battles = American Revolutionary War *Saratoga Campaign (1777) *Battle of Freeman's Farm (1777) , notable_commanders = General Sir William Howe General John Burgoyne Brigadier General Sir John Johnson Lieutenant General Sir Frederick Haldimand Major-Commandant Daniel McAlpin Major John Nairne Major Edward Jessup Major Patrick Ferguson , anniversaries = McAlpin's Corps, also known as McAlpin's Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliaries
Auxiliaries are support personnel that assist the military or police but are organised differently from regular forces. Auxiliary may be military volunteers undertaking support functions or performing certain duties such as garrison troops, usually on a part-time basis. Unlike a military reserve force, an auxiliary force does not necessarily have the same degree of training or ranking structure as regular soldiers, and it may or may not be integrated into a fighting force. Some auxiliaries, however, are militias composed of former active duty military personnel and actually have better training and combat experience than their regular counterparts. Historically, the designation ''auxiliary'' has also been given to foreign or allied troops in the service of a nation at war, most famously the eponymous ''Auxilia'' serving the Roman Empire. In the context of colonial troops, locally-recruited irregulars were often described as auxiliaries. Historical usage Roman auxiliaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were colonists in the Thirteen Colonies who remained loyal to the British Crown during the American Revolutionary War, often referred to as Tories, Royalists or King's Men at the time. They were opposed by the Patriots, who supported the revolution, and called them "persons inimical to the liberties of America." Prominent Loyalists repeatedly assured the British government that many thousands of them would spring to arms and fight for the crown. The British government acted in expectation of that, especially in the southern campaigns in 1780–81. Britain was able to effectively protect the people only in areas where they had military control, and in return, the number of military Loyalists was significantly lower than what had been expected. Due to the conflicting political views, loyalists were often under suspicion of those in the British military, who did not know whom they could fully trust in such a conflicted situation; they were often looked down upon. Pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortifications
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a military base or fortified military headquarters. A garrison is usually in a city, town, fort, castle, ship, or similar site. "Garrison town" is a common expression for any town that has a military base nearby. "Garrison towns" ( ar, أمصار, amsar) were used during the Arab Islamic conquests of Middle Eastern lands by Arab-Muslim armies to increase their dominance over indigenous populations. In order to occupy non-Arab, non-Islamic areas, nomadic Arab tribesmen were taken from the desert by the ruling Arab elite, conscripted into Islamic armies, and settled into garrison towns as well as given a share in the spoils of war. The primary utility of the Arab-Islamic garrisons was to control the indigenous non-Arab peoples of these conque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Royal Regiment Of New York
The King's Royal Regiment of New York, also known as Johnson's Royal Regiment of New York, King's Royal Regiment, King's Royal Yorkers, and Royal Greens, were one of the first Loyalist regiments, raised on June 19, 1776, in British Canada, during the American Revolutionary War. The King's Royal Regiment of New York was formed by exiled Loyalist leader, Sir John Johnson, from American refugees, fleeing rebel persecution, Retrieved July 4, 2015. the regiment served with distinction throughout the war, launching raids and relief missions into the |
Bateau
A bateau or batteau is a shallow-draft, flat-bottomed boat which was used extensively across North America, especially in the colonial period and in the fur trade. It was traditionally pointed at both ends but came in a wide variety of sizes. The name derives from the French word, ''bateau'', which is simply the word for boat and the plural, bateaux, follows the French, an unusual construction for an English plural. In the southern United States, the term is still used to refer to flat-bottomed boats, including those elsewhere called jon boats. Construction Bateaux were flat-bottomed and double-ended. They were built with heavy stems at bow and stern and a series of frames amidships, likely from natural oak crooks when available, and planked with sawn boards, likely pine although builders would have used whatever material was available. These boats would have varied from place to place, from builder to builder and also evolved over time, however in general, they were long and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Edward (village), New York
Fort Edward is a village in Washington County, New York, United States. It is part of the Glens Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area. The village population was 3,375 at the 2010 census. The name is derived from the younger brother of King George III, Edward Augustus, Duke of York and Albany. The village is part of the town of Fort Edward, which contains the county seat of Washington County just north of the village limits.Washington County, New York Retrieved Jan. 14, 2015. History Early history Fort Edward, or "The Fort", has been strategically important during its long and illustrious history, for it commands the and |
Albany, New York
Albany ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of New York, also the seat and largest city of Albany County. Albany is on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River, and about north of New York City. The city is known for its architecture, commerce, culture, institutions of higher education, and rich history. It is the economic and cultural core of the Capital District of the State of New York, which comprises the Albany–Schenectady–Troy Metropolitan Statistical Area, including the nearby cities and suburbs of Troy, Schenectady, and Saratoga Springs. With an estimated population of 1.1 million in 2013, the Capital District is the third most populous metropolitan region in the state. As of 2020, Albany's population was 99,224. The Hudson River area was originally inhabited by Algonquian-speaking Mohican (Mahican), who called it ''Pempotowwuthut-Muhhcanneuw''. The area was settled by Dutch colonists who, in 1614, built Fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the United States. In 1664, the Dutch Province of New Netherland in America was awarded by Charles II of England to his brother James, Duke of York. James raised a fleet to take it from the Dutch and the Governor surrendered to the English fleet without recognition from the Dutch West Indies Company that had authority over it. The province was renamed for the Duke of York, as its proprietor. England seized ''de facto'' control of the colony from the Dutch in 1664, and was given ''de jure'' sovereign control in 1667 in the Treaty of Breda and again in the Treaty of Westminster (1674). It was not until 1674 that English common law was applied in the colony. The colony was one of the Middle Colonies, and ruled at first directly from England. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
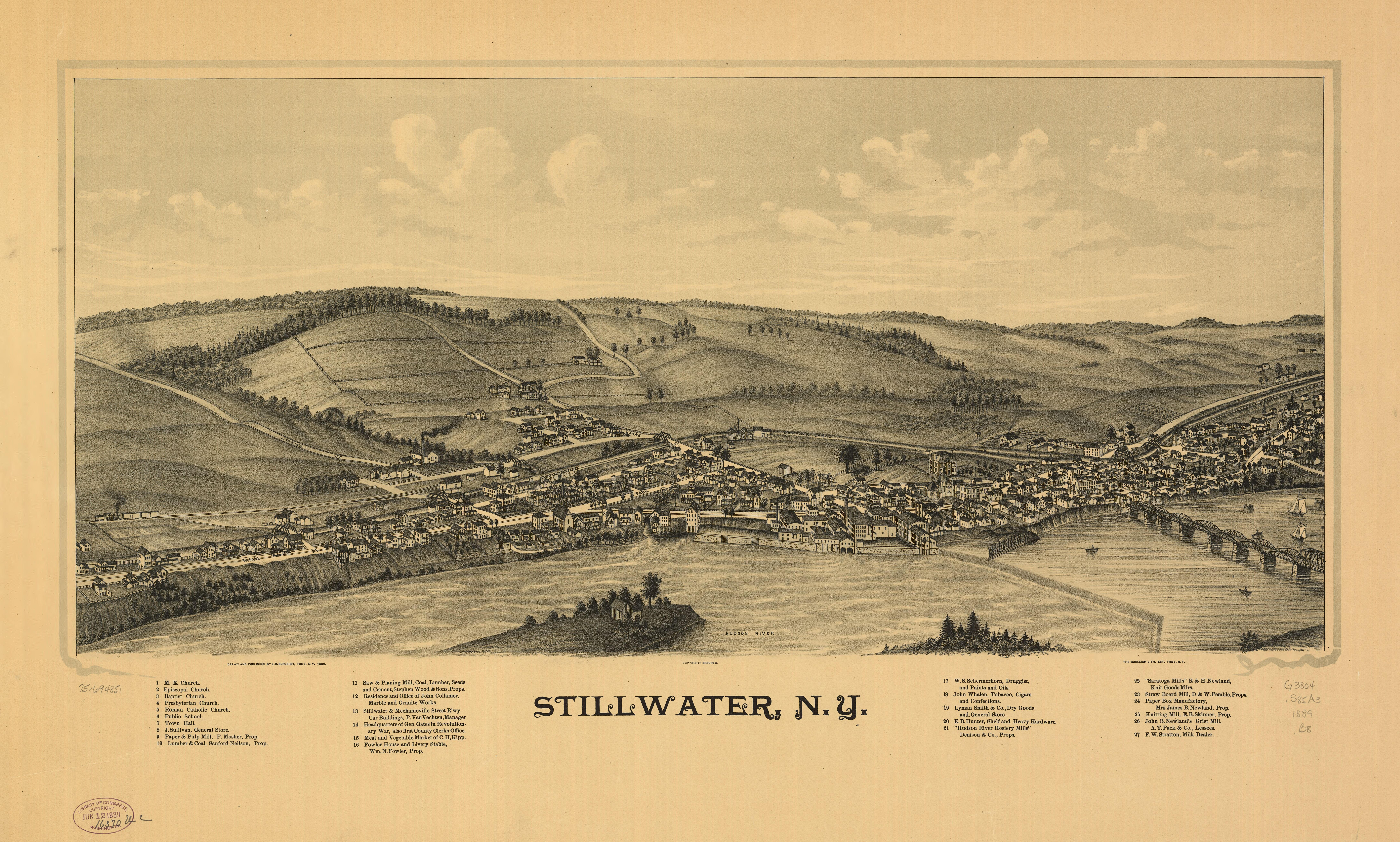
Stillwater, New York
Stillwater is a town in Saratoga County, New York, United States, with a population of 8,287 at the 2010 census. The town contains a village called Stillwater. The town is at the eastern border of the county, southeast of Saratoga Springs and borders both Rensselaer and Washington counties. Saratoga National Historical Park is located within the town's limits. There is a hamlet in Minerva, Essex County, New York, with the same name which has nothing to do with this town. History The area was occupied by Iroquois and Mohican natives when the colonial period began. In 1709, Peter Schuyler built Fort Ingoldsby in town because of its location on the frontier of the French and Indian Wars. A replica of Schuyler's fort currently serves as the Stillwater Blockhouse Museum. Settlers began arriving after 1730. During the American Revolution residents participated in the war, and part of the Battle of Saratoga was fought in the town so that the town now refers to itself as the turning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Royal Rifle Corps
The King's Royal Rifle Corps was an infantry rifle regiment of the British Army that was originally raised in British North America as the Royal American Regiment during the phase of the Seven Years' War in North America known in the United States as 'The French and Indian War.' Subsequently numbered the 60th Regiment of Foot, the regiment served for more than 200 years throughout the British Empire. In 1958, the regiment joined the Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire Light Infantry and the Rifle Brigade in the Green Jackets Brigade and in 1966 the three regiments were formally amalgamated to become the Royal Green Jackets. The KRRC became the 2nd Battalion, Royal Green Jackets. On the disbandment of the 1st Battalion, Royal Green Jackets in 1992, the RGJ's KRRC battalion was redesignated as the 1st Battalion, Royal Green Jackets, eventually becoming 2nd Battalion, The Rifles in 2007. History French and Indian War The King's Royal Rifle Corps was raised in the American colonies i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams' Rangers
{{Infobox military unit , unit_name= Adams' Rangers , image= Dr. Samuel Adams.png , image_size = 275px , caption = A woodcut of Dr. Samuel Adams, the future British Loyalist and American Revolutionary War military leader of Adams' Rangers, who was publicly humiliated in 1774 by being tied to a chair and hung from the sign of the Catamount Tavern in Arlington, New Hampshire Grants, in present-day Vermont, for falling out of favor with his enemies, the Green Mountain Boys, over land dealings in early Vermont , country = {{flagcountry, Kingdom of Great Britain , allegiance = {{flagcountry, Kingdom of Great Britain , type=infantry ( auxiliary troops) , branch= Loyalist local volunteer corps , dates=1777-1780 , specialization= scouting , command_structure= British Army under generals John Burgoyne, Simon Fraser, Baron Riedesel , size= company (70 men) and officers , current_commander= , garrison= Province of Quebec , ceremonial_chief= , nickname= Adams’ Company of Rangers , mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |