|
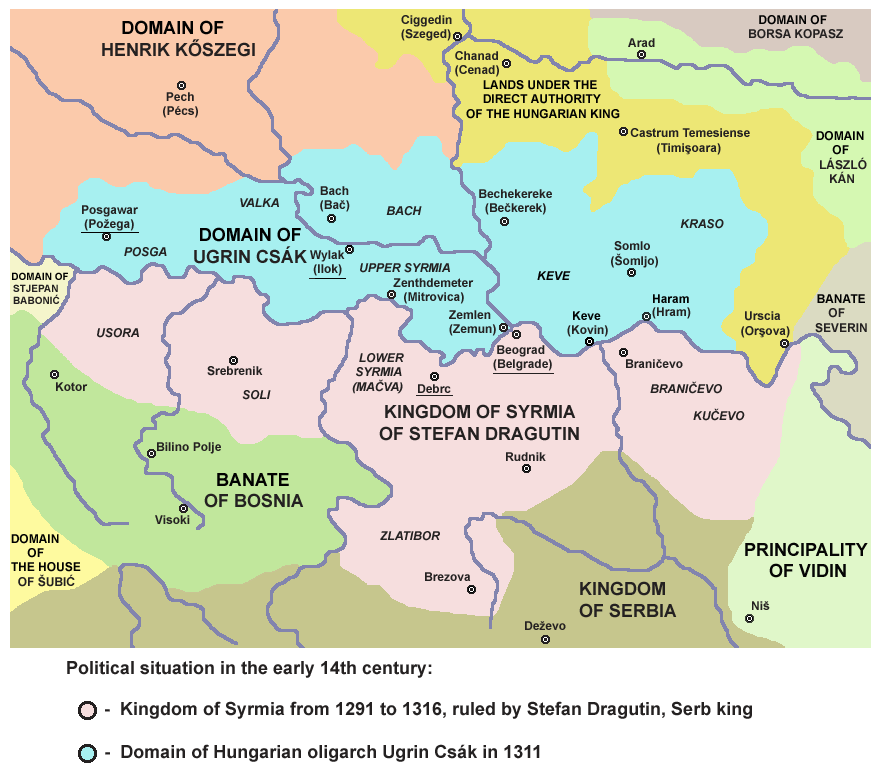
Mačva War
The Mačva War of 1268 was a brief conflict between the Kingdom of Hungary and the Kingdom of Serbia in the Duchy of Mačva (or Macsó), the southern realm of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary. War Taking advantage of the internal conflict and its consequences in Hungary, Stefan Uroš I brought an invasion force to Mačva, and did considerable damage to the city and the province in the spring of 1268. According to historian Judit Gál, when deciding on an invasion, those could also be taken into account that the Hungarian younger king Stephen entered into an alliance with the Byzantine Empire after the civil war (his daughter Anna was engaged to Andronikos Palaiologos), in addition to Stefan Uroš signed a peace treaty with the Republic of Ragusa in early 1268 to conclude the decade-long war with the Dalmatian maritime republic. Duke Béla of Macsó sought assistance from his grandfather Béla IV, who sent a royal army commanded by Stephen Csák, who marched into the south in or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mačva
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; hu, Macsó) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of Central Serbia, on a fertile plain between the Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is named after the region, although the region of Mačva includes only the northern part of this district. A small northern part of Mačva region is in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, in the Syrmia District. Name The region is named after a town of Mačva, which existed in the Medieval Ages near the river Sava. In the past, the region was also known as ''Lower Srem'', while the neighbouring region on the northern bank of the river Sava (present-day Srem) was known as ''Upper Srem''. In Serbian Cyrillic, the region is known as Мачва, in Serbian Latin, Bosnian and Croatian as ''Mačva'', in Hungarian as ''Macsó'' or ''Macsóság'', in Turkish as ''Maçva'', and in German as ''Matschva''. History Throughout history, the region of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world" , population_estimate = 90 000 in the XVI Century , currency = Ragusa perpera and others , common_languages = , title_leader = Rector as Head of state , leader1 = Nikša Sorgo , year_leader1 = 1358 , leader2 = Sabo Giorgi , year_leader2 = 1807-1808 , today = CroatiaBosnia and HerzegovinaMontenegro , footnotes = A Romance language similar to both Italian and Romanian. While present in the region even before the establishment of the Republic, Croatian, also referred to as ''Slavic'' or ''Illyrian'' at the time, had not become widely spoken until late 15th century. The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark (unit)
The Mark (from Middle High German: Marc, march, brand) is originally a medieval weight or mass unit, which supplanted the pound weight as a precious metals and coinage weight from the 11th century. The Mark is traditionally divided into 8 ounces or 16 lots. The Cologne mark corresponded to about 234 grams. Like the German systems, the French poids de marc weight system considered one "Marc" equal to 8 troy ounces. Just as the pound of 12 troy ounces (373 g) lent its name to the pound unit of currency, the mark lent its name to the mark unit of currency. Origin of the term The Etymological Dictionary of the German Language by Friedrich Kluge derives the word from the Proto-Germanic term ''marka'', "weight and value unit" (originally "division, shared"). The etymological dictionary by Wolfgang Pfeifer sees the Old High German ''marc'', "delimitation, sign", as the stem and assumes that ''marc'' originally meant "minting" (marking of a certain weight), later denoting the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Of Hungary, Duchess Of Macsó
Anna of Hungary (born 1226) was a daughter of Béla IV of Hungary and his wife, Maria Laskarina. Anna was a member of the House of Árpád. Anna gained many titles from her marriage to Rostislav Mikhailovich. Family Anna was the third of ten children borne to her parents. She was sister to three saints: Kinga, Margaret and Blessed Jolenta. Other siblings included Stephen V of Hungary and Elizabeth of Hungary, Duchess of Bavaria. Her paternal grandparents were Andrew II of Hungary and Gertrude of Merania, sister to Agnes of Merania. Her maternal grandparents were Theodore I Laskaris and Anna Komnena Angelina. Marriage In 1243, Anna married Rostislav Mikhailovich. Rostislav could not strengthen his rule in Halych, so he went to the court of King Béla IV of Hungary, and there he married Anna. Anna had always been her father's favourite daughter. He allowed her to exercise more and more influence over him. In his last will, Béla entrusted his daughter and his followers to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Csák
Michael from the kindred Csák ( hu, Csák nembeli Mihály; died after 1277) was a Hungarian nobleman and soldier in the 13th century, who served as ''ispán'' of Veszprém County in 1272. He actively participated in various military conflicts in the 1260s and 1270s. Family Michael was born into the Dobóc (or Orbova) branch of the ''gens'' (clan) Csák as the son of Peter.Engel: ''Genealógia'' (Genus Csák 2., Dobóc rbovabranch) He had three brothers, Dominic, who pursued career in politics resulting the ascendance of their branch, Simon and possibly Beers. Michael had no known descendants. Career While Dominic entered court service and was involved in national governance, Michael excelled in a military career since the 1260s. Both of them belonged to the accompaniment of Duke Stephen, who governed Transylvania since 1260. When the tense relationship between Stephen and his father King Béla IV of Hungary sparked into a civil war at the turn of 1264 into 1265, Michael was ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław The Pious
Bolesław the Pious (1224/27 – 14 April 1279) was a Duke of Greater Poland during 1239–1247 (according to some historians during 1239–1241 sole Duke of Ujście), Duke of Kalisz during 1247–1249, Duke of Gniezno during 1249–1250, Duke of Gniezno-Kalisz during 1253–1257, Duke of whole Greater Poland and Poznań during 1257–1273, in 1261 ruler over Ląd, regent of the Duchies of Mazovia, Płock and Czersk during 1262–1264, ruler over Bydgoszcz during 1268–1273, Duke of Inowrocław during 1271–1273, and Duke of Gniezno-Kalisz from 1273 until his death. He was the second son of Władysław Odonic, Duke of Greater Poland by his wife Jadwiga, who was probably the daughter of Mestwin I, Duke of Pomerania, or a member of the Přemyslid dynasty. His name was very popular in the Piast dynasty, so it's unknown exactly after whom he was named. Very soon Bolesław received the nickname of "the Pious" ( Latin: ''Pius''), given to him during his lifetime by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo I Of Galicia
Leo I of Galicia ( ua, Лев Дани́лович, translit=Lev Danylovych) (c. 1228 – c. 1301) was a king of Ruthenia, prince (Kniaz) of Belz (1245–1264), Peremyshl, Halych (1264–1269), and grand prince of Kiev (Kyiv, 1271–1301). He was a son of King Daniel of Galicia and his first wife, Anna Mstislavna Smolenskaia (daughter of Mstislav Mstislavich the Bold). As his father, Lev was a member of the senior branch of Vladimir II Monomakh descendants. Reign Leo (also known as Lev) moved his father's capital from Halych to the newly founded city of Lviv. This city was named after him by its founder, Lev's father, King Daniel of Galicia. In 1247, Leo married Constance, the daughter of Béla IV of Hungary. Unlike his father, who pursued a western political course, Leo worked closely with the Mongols and together with them invaded Poland. However, although his troops plundered territory as far west as Racibórz in Silesia, sending many captives and much booty back to Galici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław V The Chaste
Bolesław V the Chaste ( pl, Bolesław Wstydliwy; 21 June 1226 – 7 December 1279) was Duke of Sandomierz in Lesser Poland from 1232 and High Duke of Poland from 1243 until his death, as the last male representative of the Lesser Polish branch of Piasts. Birth and nickname Bolesław V was born on 21 June 1226 at Stary Korczyn, as the third child and only son of Leszek I the White by his wife Grzymisława, a Rurikid princess of disputed parentage. Named after his great-grandfather Bolesław Wrymouth, the numeral V was assigned to him in the ''Poczet królów Polskich''. His nickname of "Chaste" (Latin: ''Pudicus''), appeared relatively early and was already mentioned in the ''Rocznik franciszkański krakowski''. It was given to him by his subjects because of the vows of chastity that Bolesław V and his wife Kinga of Hungary had jointly taken; for this reason, their marriage was never consummated. Youth Father's death On 24 November 1227, during the Congress of Gąsaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czech Republic. It was an Imperial State in the Holy Roman Empire, and the Bohemian king was a prince-elector of the empire. The kings of Bohemia, besides the region of Bohemia proper itself, also ruled other lands belonging to the Bohemian Crown, which at various times included Moravia, Silesia, Lusatia, and parts of Saxony, Brandenburg, and Bavaria. The kingdom was established by the Přemyslid dynasty in the 12th century from the Duchy of Bohemia, later ruled by the House of Luxembourg, the Jagiellonian dynasty, and from 1526 the House of Habsburg and its successor, the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. Numerous kings of Bohemia were also elected Holy Roman Emperors, and the capital, Prague, was the imperial seat in the late 14th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. France originated as West Francia (''Francia Occidentalis''), the western half of the Carolingian Empire, with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ''rex Francorum'' ("king of the Franks") well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ''rex Francie'' ("King of France") was Philip II, in 1190, and officially from 1204. From then, France was continuously ruled by the Capetians and their cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmentation of the Mongol Empire after 1259 it became a functionally separate khanate. It is also known as the Kipchak Khanate or as the Ulus of Jochi, and replaced the earlier less organized Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the death of Batu Khan (the founder of the Golden Horde) in 1255, his dynasty flourished for a full century, until 1359, though the intrigues of Nogai instigated a partial civil war in the late 1290s. The Horde's military power peaked during the reign of Uzbeg Khan (1312–1341), who adopted Islam. The territory of the Golden Horde at its peak extended from Siberia and Central Asia to parts of Eastern Europe from the Urals to the Danube in the west, and from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea in the south, while b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szepes County
Szepes ( sk, Spiš; la, Scepusium, pl, Spisz, german: link=no, Zips) was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary, called Scepusium before the late 19th century. Its territory today lies in northeastern Slovakia, with a very small area in southeastern Poland. For the current region, see Spiš. Geography Szepes county shared borders with Poland and with the counties as follows: Liptó, Gömör-Kishont, Abaúj-Torna and Sáros. After the late 18th century dismemberment of Poland, the border was with the Austrian province of Galicia. Its area was 3,668 km2 in 1910. The county became part of Czechoslovakia, apart from a very small area now in Poland, after World War I, and is now part of Slovakia (and Poland). Capitals The original seat of government of Szepes county was Spiš Castle ( hu, Szepesi vár), which was constructed in the 12th century. Unofficially from the 14th century, and officially from the 16th century, until 1920 the capital of the county was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_Tafel_03.png)

