|
Mayatskoye
Mayatskoye, also known as Mayatskoe or Mayaki, is a ''gorodishche'' (hill fort) and historical settlement located in the Divnogorye museum-reserve area of Liskinsky District in Voronezh Oblast, Russia. Along with Verkhnii Saltiv, it gives its name to the Saltovo-Mayaki culture, which is the main archaeological culture of the Khazars. Mayatskoye is the northernmost site associated with the Khazars, and was probably near the frontier with Slavic tribes. It is also one of the best-preserved and best-studied Khazar sites. The Mayatskoye site consists of a hill fort surrounded by a settlement with an adjacent burial ground. The overall settlement area is 30 hectares, of which 6,000 square meters have been excavated. Remains of pottery workshops have been identified in this area. The fortress itself covers 1.1 hectare, and about 30% of the area enclosed by its walls has been excavated. The walls themselves have been only been excavated in small portions; most of their circuit remains bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divnogorye
Divnogorye — (russian: Музей-заповедник «Дивногорье», ''Muzej-zapovednik Divnogor'e'') is a plateau and open-air museum in Liskinsky District, Voronezh Oblast, Russia. It is located 10 km to the west from district administrative center on the right bank of Don River, 80 km to the south from Voronezh, not far from khutor Divnogorye. Museum was established in 1988 and received official status of nature reserve museum in 1991. Divnogorye remains of the most popular and recognizable tourist attractions of Voronezh Oblast. More than 60,000 visitors are attracted every season (from May to October), mostly from Voronezh and Oblast. Description Nature reserve museum Divnogorye occupies of limestone outcrops. Maximum altitude above sea level is 181 m or 103 m relative to the mouth of the Tikhaya Sosna River at the confluence with Don River (which flows at the foot of the plateau). Due to rather significant difference in altitude betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verkhnii Saltiv (museum-reserve)
Verkhnii Saltiv is a historic-archaeological museum-reserve that is located near the village of Verkhnii Saltiv in Chuhuiv Raion, Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. The reserve covers one of the type sites of the Saltovo-Mayaki culture, the main archaeological culture of the Khazars, with the other type site being Mayatskoye. Findings from the Verkhnii Saltiv archaeological complex are mostly displayed in museums of Kyiv, Kharkiv, Odesa, Moscow, Saint Petersburg, and Sofia, while only a small portion of them was kept in the museum in Verkhnii Saltiv. History The settlement with traces of fortifications that is located near the village of Verkhnii Saltiv was first mentioned in "Book to the Bolshoy Chertezh" (17th century) as Saltanovskoye. It is located on the high right bank of Pechenih Reservoir on Siverskyi Donets River that rises above the floodplain by 35 m. The area has several defensive lines. The main fortification has the shape of an irregular trapezoid with dimensions 180 × 135 × ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
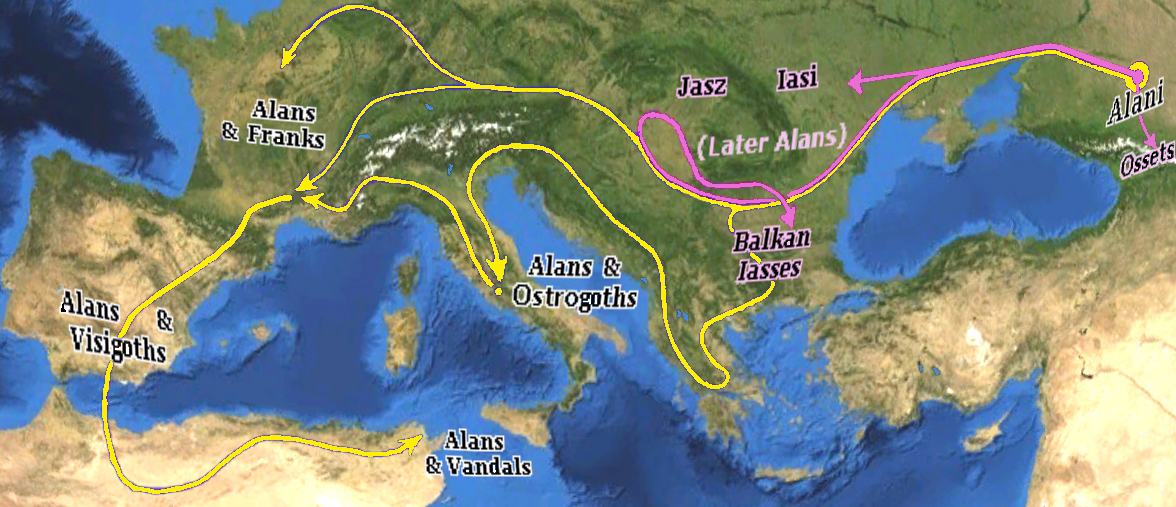
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Russia
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khazar Towns
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (c. 650–965) the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazaria long served as a buffer state between the Byzantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Russia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Voronezh Oblast
Voronezh Oblast (russian: Воронежская область, Voronezhskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Voronezh. Its population was 2,308,792 as of the 2021 Census. Geography Voronezh Oblast borders internally with Belgorod Oblast, Kursk Oblast, Lipetsk Oblast, Tambov Oblast, Saratov Oblast, Volgograd Oblast and Rostov Oblast and internationally with Ukraine. Voronezh Oblast is located in the central belt of the European part of Russia, in a very advantageous strategic location, transport links to the site going to the industrial regions of Russia. Within the radius (12 hours of driving 80 km/h) 960 kilometers around Voronezh more than 50% of the population Russia, and 40% in Ukraine live. The area of the region - 52.4 thousand km2, which is about one third of the whole area of Central Black Earth Region. The length of the region from north to south - 277.5 km, and from west to east - 352 km. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth-longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Canal to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don (river)
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half ribbles (meanders subtly) south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabir People
The Sabirs (Savirs, Suars, Sawar, Sawirk among others; el, Σάβιροι) were nomadic people who lived in the north of the Caucasus beginning in the late-5th -7th century, on the eastern shores of the Black Sea, in the Kuban area, and possibly came from Western Siberia. They were skilled in warfare, used siege machinery, had a large army (including women) and were boat-builders. They were also referred to as Huns, a title applied to various Eurasian nomadic tribes in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe during late antiquity. Sabirs led incursions into Transcaucasia in the , but quickly began serving as soldiers and mercenaries during the Byzantine-Sasanian Wars on both sides. Their alliance with the Byzantines laid the basis for the later Khazar-Byzantine alliance. Etymology Gyula Németh and Paul Pelliot considered Turkic etymology for Säbir/Sabïr/Sabar/Säβir/Sävir/Savar/Sävär/Sawār/Säwēr from the root *''sap-'' 'to go astray', i.e. the 'wanderers, nomads', placed in a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Turkic Languages
Common Turkic, or Shaz Turkic, is a taxon in some classifications of the Turkic languages that includes all of them except the Oghuric languages. Classification Lars Johanson's proposal contains the following subgroups: * Southwestern Common Turkic (Oghuz) * Northwestern Common Turkic (Kipchak) * Southeastern Common Turkic (Karluk) * Northeastern Common Turkic (Siberian) * Arghu Common Turkic (Khalaj) In that classification scheme, Common Turkic is opposed to Oghur Turkic (Lir-Turkic). The Common Turkic languages are characterized by sound correspondences such as Common Turkic ''š'' versus Oghuric ''l'' and Common Turkic ''z'' versus Oghuric ''r''. In other classification schemes (such as those of Alexander Samoylovich Alexander Nikolaevich Samoylovich (russian: Алекса́ндр Никола́евич Самойло́вич, 1880–1938) was a Russian Orientalist-Turkologist who served as a member of the USSR Academy of Sciences (1929), Rector of the Lening ... an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)

