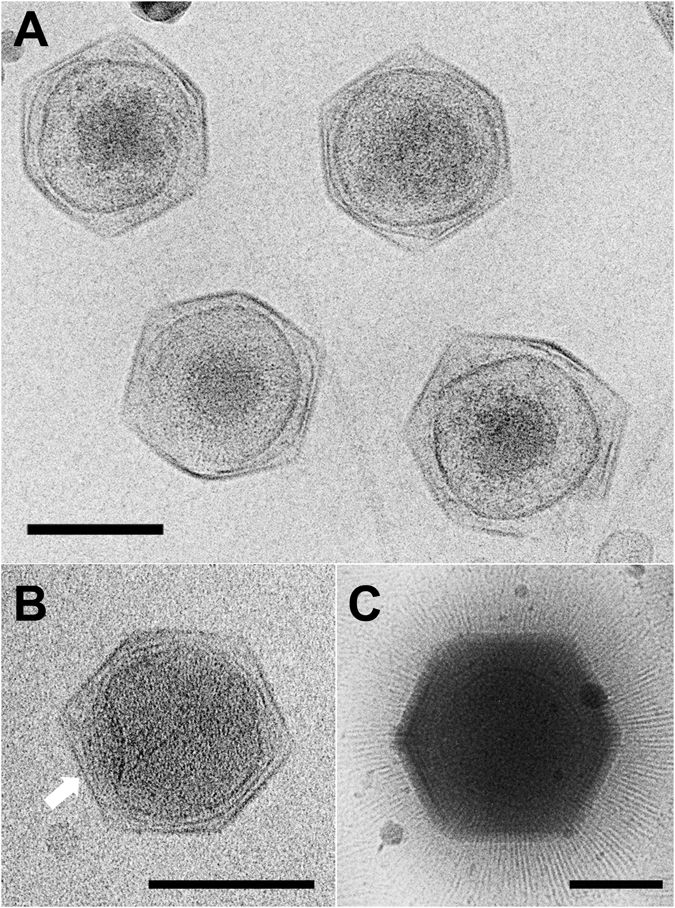
|
Maveriviricetes
Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for their own replication. One of the characteristics of virophages is that they have a parasitic relationship with the co-infecting virus. Their dependence upon the giant virus for replication often results in the deactivation of the giant viruses. The virophage may improve the recovery and survival of the host organism. Unlike satellite viruses, virophages have a parasitic effect on their co-infecting virus. Virophages have been observed to render a giant virus inactive and thereby improve the condition of the host organism. All known virophages are grouped into the family ''Lavidaviridae'' (from "large virus dependent or associated" + -viridae). Discovery The first virophage was discovered in a cooling tower in Paris, France in 2008. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sputnik Virophage
''Mimivirus-dependent virus Sputnik'' (from Russian "satellite") is a subviral agent that reproduces in amoeba cells that are already infected by a certain helper virus; Sputnik uses the helper virus's machinery for reproduction and inhibits replication of the helper virus. It is known as a virophage, in analogy to the term ''bacteriophage''. Viruses like Sputnik that depend on co-infection of the host cell by helper viruses are known as satellite viruses. At its discovery in a Paris water-cooling tower in 2008, Sputnik was the first known satellite virus that inhibited replication of its helper virus and thus acted as a parasite of that virus. In analogy, it was called a ''virophage''. Sputnik virophages were found infecting giant viruses of ''Mimiviridae'' group A. However, they are able to grow in amoebae infected by ''Mimiviridae'' of any of the groups A, B, and C. Virology Sputnik was first isolated in 2008 from a sample obtained from humans; it was harvested from the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee On Taxonomy Of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus that affects living organisms. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as delimiting the boundaries of species within a family, typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families. History The International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses (ICNV) was established in 1966, at the International Congress for Microbiology in Moscow, to standardize the naming of viruses. The ICVN published its first report in 1971. For viruses infecting vertebrates, the first report included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamfordvirae
''Bamfordvirae'' is a kingdom of viruses. This kingdom is recognized for its use of double jelly roll major capsid proteins. It was formerly known as the PRD1-adenovirus lineage. The kingdom is named after Dennis H. Bamford who first promoted the evolutionary unity of all viruses encoding double jelly-roll major capsid proteins. Taxonomy The following phyla are recognized: *''Nucleocytoviricota'' *''Preplasmiviricota ''Preplasmiviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Taxonomy The phylum contains the following classes: * ''Maveriviricetes Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting v ...'' References {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
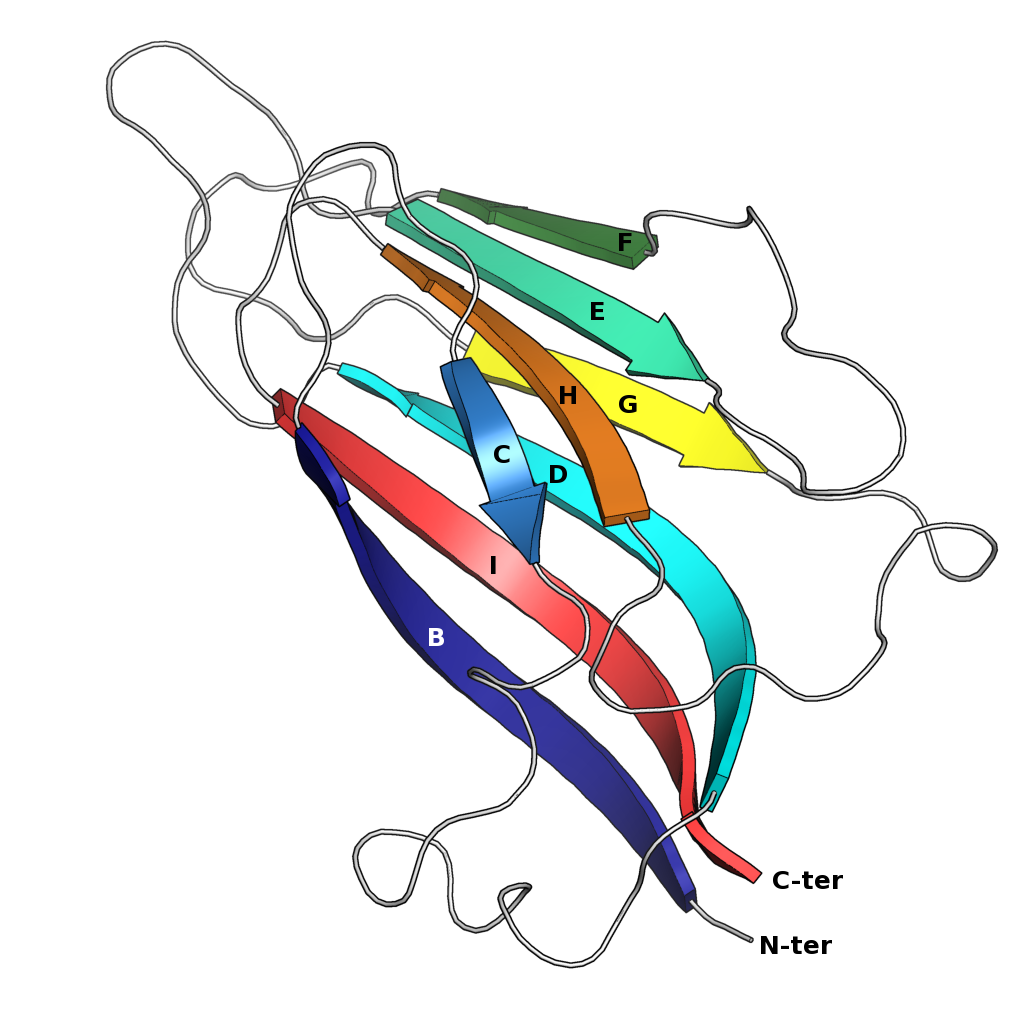
Jelly Roll Fold
The jelly roll or Swiss roll fold is a protein fold or supersecondary structure composed of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded sheets. The name of the structure was introduced by Jane S. Richardson in 1981, reflecting its resemblance to the jelly or Swiss roll cake. The fold is an elaboration on the Greek key motif and is sometimes considered a form of beta barrel. It is very common in viral proteins, particularly viral capsid proteins. Taken together, the jelly roll and Greek key structures comprise around 30% of the all-beta proteins annotated in the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database. Structure The basic jelly roll structure consists of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded antiparallel beta sheets which pack together across a hydrophobic interface here citation... uniprot The strands are traditionally labeled B through I for the historical reason that the first solved structure, of a jelly roll capsid protein from the tomato bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life. Some such enzymes are integral membrane proteins (anchored within biological membranes), and move solutes across the membrane, typically against their concentration gradient. These are called transmembrane ATPases. Functions Transmembrane ATPases import metabolites necessary for cell metabolism and export toxins, wastes, and solutes that can hinder cellular processes. An important example is the sodium-potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Protease
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad. Discovered by Gopal Chunder Roy in 1873, the first cysteine protease to be isolated and characterized was papain, obtained from ''Carica papaya''. Cysteine proteases are commonly encountered in fruits including the papaya, pineapple, fig and kiwifruit. The proportion of protease tends to be higher when the fruit is unripe. In fact, the latex of dozens of different plant families are known to contain cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases are used as an ingredient in meat tenderizers. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 14 superfamilies plus several currently unassigned families (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid Protein
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid. Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the helical shape resembles the shape of a spring, taking the space of a cylinder but not being a cylinder itself. The capsid faces may consist of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. This genus contains a single identified species named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses. In colloquial speech, APMV is more commonly referred to as just "mimivirus". Mimivirus, short for "mimicking microbe", is so called to reflect its large size and apparent Gram-staining properties. Mimivirus has a large and complex genome compared with most other viruses. Until 2013, when a larger virus ''Pandoravirus'' was described, it had the largest capsid diameter of all known viruses. History APMV was discovered accidentally in 1992 within the amoeba '' Acanthamoeba polyphaga'', after which it is named, during research into legionellosis by researchers from Marseille and Leeds. The virus was observed in a Gram stain and mistakenly thought to be a Gram-positive bacterium. As a consequence it was nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cafeteria Roenbergensis Virus
''Cafeteria roenbergensis virus'' (CroV) is a giant virus that infects the marine bicosoecid flagellate ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'', a member of the microzooplankton community. History The virus was isolated from seawater samples collected from the Gulf of Mexico during 1989 to 1991, on a flagellate host that was misidentified as belonging to the genus ''Bodo''; hence the original designation of the virus as BV-PW1. The virus was shown to be about 300 nm in diameter and have a complex internal structure, as well as evidence of a putative tail-like structure Further work on the virus indicated that the host was an isolate of the genus ''Cafeteria'' and that the genome had a G+C content of ~34%. Further analysis suggested that the helicase of the virus was phylogenetically related to those found in the family '' Asfarviridae'', and that the virus shared properties with members of the Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses group. CroV has one of the largest genomes of all marine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoviridae
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (known as the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genera: * '' Atadenovirus'' * '' Aviadenovirus'' * '' Ichtadenovirus'' * '' Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * '' Siadenovirus'' * '' Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (Human adenovirus A to G): * A: 12, 18, 31 * B: 3, 7, 11, 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poliovirus
A poliovirus, the causative agent of polio (also known as poliomyelitis), is a serotype of the species ''Enterovirus C'', in the family of ''Picornaviridae''. There are three poliovirus serotypes: types 1, 2, and 3. Poliovirus is composed of an RNA genome and a protein capsid. The genome is a single-stranded positive-sense RNA (+ssRNA) genome that is about 7500 nucleotides long. The viral particle is about 30 nm in diameter with icosahedral symmetry. Because of its short genome and its simple composition—only RNA and a nonenveloped icosahedral protein coat that encapsulates it—poliovirus is widely regarded as the simplest significant virus. Poliovirus was first isolated in 1909 by Karl Landsteiner and Erwin Popper. The structure of the virus was first elucidated in 1958 using X-ray diffraction by a team at Birkbeck College led by Rosalind Franklin, showing the polio virus to have icosahedral symmetry. In 1981, the poliovirus genome was published by two different teams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


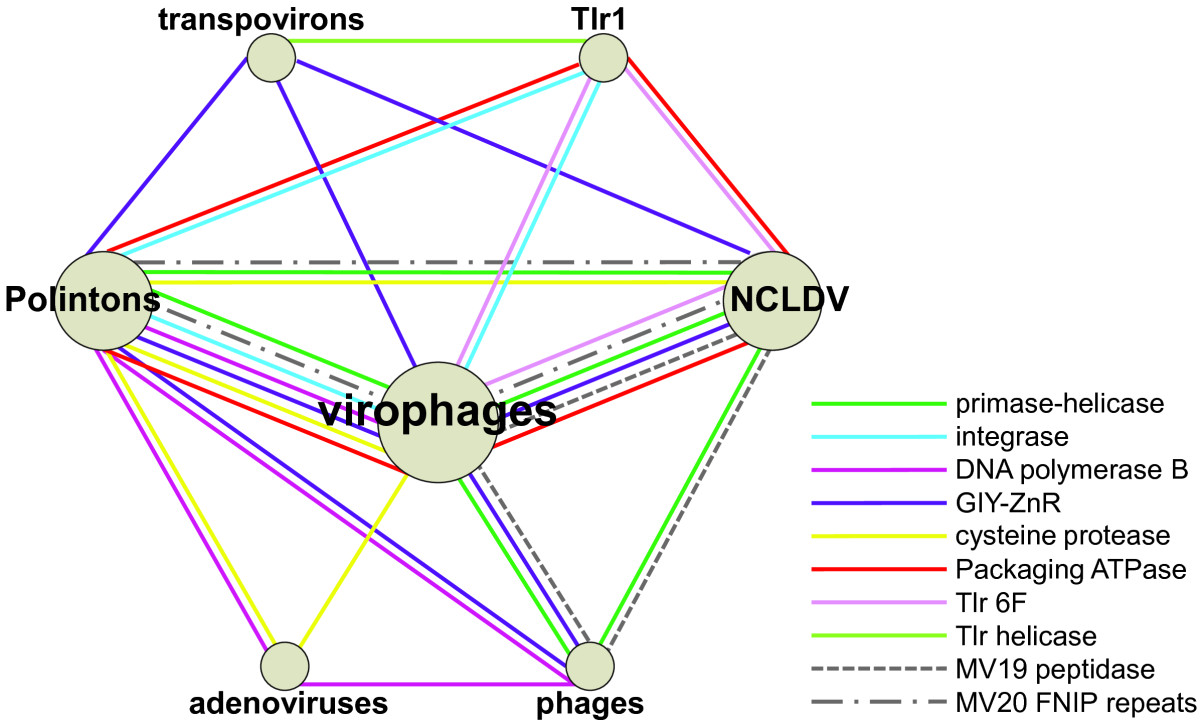
.gif)