|
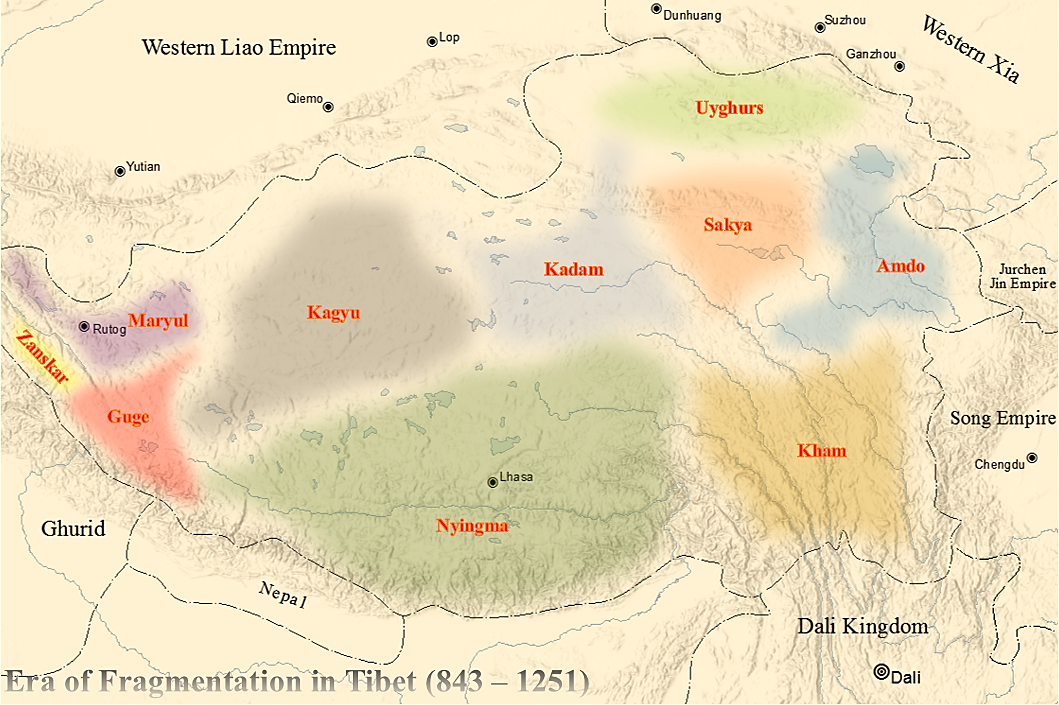
Mauyul
Maryul (also called ''Mar-yul'' of ''mNgah-ris''), later the Kingdom of Ladakh, was a west Tibetan kingdom based in modern-day Ladakh and Tibet. The kingdom had its capital at Shey. The kingdom was founded by Lhachen Palgyigon, during the rule of his father Kyide Nyimagon, in .: "it seems that his father bequeathed him a theoretical right of sovereignty, but the actual conquest was effected by dPal-gyi-mgon himself." It stretched from the Zoji La at the border of Kashmir to Demchok in the southeast, and included Rudok and other areas presently in Tibet. The kingdom came under the control of the Namgyal dynasty in 1460, eventually acquiring the name "Ladakh", and lasted until 1842. In that year, the Dogra general Zorawar Singh, having conquered it, made it part of the would-be princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. Etymology ''Mar-yul'' has been interpreted in Tibetan sources as lowland (of Ngari),. Scholars suspect that it was a proper name that was in use earlier, even before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Shahis
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details regarding past rulers can only be assembled from disparate chronicles, coins and stone inscriptions. Scholarship Scholarship on Hindu Shahis remain scarce. Colonial scholars— James Prinsep, Alexander Cunningham, Henry Miers Elliot, Edward Thomas et al.—had published on the Hindu Shahis, primarily from a numismatic perspective. The first comprehensive volume on the subject appeared in 1972 by Yogendra Mishra, a professor in the Department of History of Patna University; he explored the Rajatarangini meticulously but lacked in numismatics and paleography. The next year, Deena Bandhu Pandey—Professor of Art History at Banaras Hindu University—published his doctoral dissertation but his handling of Muslim sources, coins etc. were la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a Provinces of China, province-level Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of Ü-Tsang and Kham. It was formally established in 1965 to replace the Tibet Area (administrative division), Tibet Area, the former Administrative divisions of China, administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC) established after the annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, annexation of Tibet. The establishment was about five years after the 1959 Tibetan uprising and the dismissal of the Kashag, and about 13 years after the original annexation. The current borders of the Tibet Autonomous Region were generally established in the 18th century and include about half of historic Tibet, or the Tibet, ethno-cultural Tibet. The Tibet Autonomous Region spans ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zan-zun
Zhangzhung or Shangshung was an ancient culture and kingdom in western and northwestern Tibet, which pre-dates the culture of Tibetan Buddhism in Tibet. Zhangzhung culture is associated with the Bon religion, which has influenced the philosophies and practices of Tibetan Buddhism. Zhangzhung people are mentioned frequently in ancient Tibetan texts as the original rulers of today's western Tibet. Only in the last two decades have archaeologists been given access to do archaeological work in the areas once ruled by the Zhangzhung. Extent of the Zhangzhung kingdoms Tradition has it that Zhangzhung consisted "of three different regions: sGob-ba, the outer; Phug-pa, the inner; and Bar-ba, the middle. The outer is what we might call Western Tibet, from Gilgit in the west to Dangs-ra khyung-rdzong in the east, next to lake gNam-mtsho, and from Khotan in the north to Chu-mig brgyad-cu rtsa-gnyis in the south. Ladakh, including lahaul and spiti, was part of sGob-ba. The inner region is sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of his journey to India in 629–645 CE, his efforts to bring over 657 Indian texts to China, and his translations of some of these texts.Li Rongxi (1996), ''The Great Tang Dynasty Record of the Western Regions'', Bukkyo Dendo Kyokai and Numata Center for Buddhist Translation and Research, Berkeley, , pp. xiii-xiv Xuanzang was born on 6 April 602 in Chenliu, what is now Kaifeng municipality in Henan province. As a boy, he took to reading religious books, and studying the ideas therein with his father. Like his elder brother, he became a student of Buddhist studies at Jingtu monastery. Xuanzang was ordained as a ''śrāmaṇera'' (novice monk) at the age of thirteen. Due to the political and social unrest caused by the fall of the Sui dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetic after the Old Tibetan period. Though it extends from the 12th century until the modern day, it particularly refers to the language of early canonical texts translated from other languages, especially Sanskrit. The phonology implied by Classical Tibetan orthography is very similar to the phonology of Old Tibetan, but the grammar varies greatly depending on period and geographic origin of the author. Such variation is an under-researched topic. In 816, during the reign of King Sadnalegs, literary Tibetan underwent a thorough reform aimed at standardizing the language and vocabulary of the translations being made from Sanskrit, which was one of the main influences for literary standards in what is now called Classical Tibetan. Nouns Structure of the noun phrase Nominalizing suffixes — ''pa'' or ''ba'' and ''ma'' — are required by the noun or adjective that is to be singled out; * ''po'' or ''bo'' (ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jammu And Kashmir (princely State)
Jammu and Kashmir, officially known as the Princely State of Kashmir and Jammu, was a princely state during the Company rule in India from 1757 to 1858 as well as the British Raj in India from 1846 to 1952. The princely state was created after the First Anglo-Sikh War, from the territories that had earlier been in the Sikh Empire. At the time of the partition of India and the political integration of India, Hari Singh, the ruler of the state, delayed making a decision about the future of his state. However, an uprising in the western districts of the state followed by an attack by raiders from the neighbouring Northwest Frontier Province, supported by Pakistan, forced his hand. On 26 October 1947, Hari Singh acceded to India in return for the Indian military being airlifted to Kashmir to engage the Pakistan-supported forces, starting the Kashmir conflict. The western and northern districts presently known as Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan passed to the control of Pakistan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zorawar Singh Kahluria
Zorawar Singh Kahluria (1784–12 December 1841) was a military general of the Dogra Rajput ruler, Gulab Singh of Jammu. He served as the governor (''wazir-e-wazarat'') of Kishtwar and extended the territories of the kingdom by conquering Ladakh and Baltistan. He also boldly attempted the conquest of Western Tibet (''Ngari Khorsum'') but was killed in battle of To-yo during the Dogra-Tibetan war. In reference to his legacy of conquests in the Himalaya Mountains including Ladakh, Tibet, Baltistan and Iskardu as General and Wazir, Zorowar Singh has been referred to as the "Napoleon of India", and "Conqueror of Ladakh". Early life and career He was born in September 1784 in a Kahluria Rajput family in the princely state of Kahlur (Bilaspur) state, in present-day Himachal Pradesh. His family migrated to the Jammu region where, on coming of age, Zorawar took up service under Raja Jaswant Singh of Marmathi (modern Doda district). Zorawar Singh was employed by the ambitious Raja G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogra
The Dogras or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group in India and Pakistan consisting of the Dogri language speakers. They live predominantly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, and in adjoining areas of Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, and northeastern Pakistan. Their historical homeland is known as Duggar. Dogra Rajputs ruled Jammu from the 19th century, when Gulab Singh was made a hereditary Raja of Jammu by Ranjit Singh, whilst his brother Dhian Singh was the empire's prime minister of Punjab, until October 1947. Through the Treaty of Amritsar (1846), they acquired Kashmir as well. The Dogra Regiment of the Indian Army primarily consists of Dogras from the Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Jammu region. Etymology The term Dogra is thought to derive from ''Durgara'', the name of a kingdom mentioned in an eleventh century copper-plate inscription in Chamba. The inscription mentions the Raja of Chamba facing an attack by Kiras aided by the Lord of Durgara (''durg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namgyal Dynasty Of Ladakh
The Namgyal dynasty was a dynasty whose rulers were the monarchs of the former kingdom of Ladakh that lasted from 1460 to 1842 and were titled the Gyalpo of Ladakh. The Namgyal dynasty succeeded the first dynasty of Maryul and had several conflicts with the neighboring Mughal Empire and various dynasties of Tibet, including the Tibet–Ladakh–Mughal War. The dynasty eventually fell to the Sikh Empire and Dogras of Jammu and Kashmir. Most of its known history is written in the ''Ladakh Chronicles''. History Founding According to the ''Ladakh Chronicles'', the Namgyal dynasty was founded by Bhagan, the son of Bhara in the kingdom of Maryul. Bhagan was described as warlike, and established the Namgyal dynasty in 1460 after he formed an alliance with the people of Leh and dethroned the Maryul king Blo-gros-mc-og-ldan and his brothers drun-pa A-li and Slab-bstan-dar-rgyas. He took the surname Namgyal (meaning victorious) and founded a new dynasty which still survives today. Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutog County
Rutog County (), (in ) is a county in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. The county seat is the new Rutog Town, located some or 700 miles west-northwest of the Tibetan capital, Lhasa. Rutog County shares a border with India. The county has a rich history of folk tales, myths, legends, proverbs and folk songs and has many caves, rock paintings and other relics. The Xinjiang-Tibet Highway runs through the Rutog County for . The modern county established in March 1961 covers . It has a very low population density with a population of just over 10,000. Name 'Rutog' is Tibetan for "mountain shaped like a spear and fork". Geography and climate Rutog County is located in northwestern Tibet, Ngari northwest with a number of territorial borders. It is divided into 12 townships and 30 village committees. The Karakoram Mountains go through the county. The average altitude of with a maximum altitude of . Lakes in Rutog County include Bangda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demchok (historical Village)
Demchok (), KNAB Place Name Databse, retrieved 27 July 2021. was described by a British boundary commission in 1847 as a village lying on the border between the and the . It was a "hamlet of half a dozen huts and tents", divided into two parts by a rivulet which formed the boundary between the two states. The rivulet, a tributary of the variously called the |
Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompasses a larger area that includes the Indian-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |