|
Matupiri State Park
Matupiri State Park ( pt, Parque Estadual do Matupiri) is a state park in the state of Amazonas, Brazil. It protects a rich area of Amazon rainforest and an ecologically important area of woodland savanna along the Matupiri River. Unusually for a state park, it includes an "indigenous special use zone" that allows the Mura people to continue to fish and extract forest products, as they have for many generations. Location Matupiri State Park is divided between the municipalities of Borba (9.95%) and Manicoré (90.05%) in the state of Amazonas. It has an area of . The park is to the south of the BR-319 highway. It is in the Médio Madeira microregion of Amazonas. The park is in the Purus - Madeira inter-fluvial region, in the basins of the Matupiri and Amapá rivers. The Matupiri river runs through the centre of the park from southwest to northeast, and provides the main way to access the interior of the park. To the southeast it adjoins the Rio Madeira Sustainable Development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manicoré
Manicoré is a municipality located in the south-east of the Brazilian state of Amazonas. Location The population of Manicoré was 56,583 (2020) and its area is 48,282 km2. The town is located on the banks of the Madeira River about downstream from where the Manicoré River merges into the Madeira. The city is served by Manicoré Airport. Economy Santo Antônio do Matupí is a major centre of logging in the region. History Manicoré's origins date back to 1637, with the expedition of Pedro Teixeira, a Portuguese explorer and military man. The authorities of Grão-Pará sent an escort to the Madeira River in 1716, commanded by João de Barros e Guerra, an experienced captain. In 1797, the village of Crato was founded, under orders from the Governor of Grão-Pará, with a view to facilitating commercial transactions between Pará, Mato Grosso and Goiás. The village was transferred to a site between the Baetas and Arraias rivers, in 1802. On July 4, 1858, through Law no. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piagaçu-Purus Sustainable Development Reserve
Piagaçu-Purus Sustainable Development Reserve ( pt, Reserva de Desenvolvimento Sustentável Piagaçu-Purus) is a sustainable development reserve in the state of Amazonas, Brazil. Location The Piagaçu-Purus Sustainable Development Reserve (RDS) is divided between the municipalities of Tapauá (30.35%), Coari (1.37%), Anori (40.11%) and Beruri (28.17%) in the state of Amazonas. It covers an area of . The name comes from the Tupi language: ''pi'á'' (guts, heart or stomach) and ''wa'su'' (large, wide), and means "great heart of the Purus". There are about 85 communities of people in the reserve, who live by fishing, agriculture, hunting and extraction of timber and non-timber products. The RDS adjoins the Abufari Biological Reserve to the southwest and the Nascentes do Lago Jari National Park to the south. The southern part of the RDS surrounds the Itixi Mitari Indigenous Territory, and further north the RDS surrounds the Lago Aiapuá Indigenous Territory. The Purus River runs t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andiroba
''Carapa'' is a genus of flowering plants in the mahogany family, Meliaceae. These are trees up to 30 meters tall occurring in tropical South America, Central America,Hogan, C. M. 2008Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests.Encyclopedia of Earth, World Wildlife Fund, National Council of Science and the Environment. and Africa. Common names include andiroba and crabwood. Diversity The list of species within this genus is still under discussion. Generally recognized species are: *'' Carapa guianensis'' (andiroba, crabwood): Amazon Region, Central America, Caribbean *''Carapa megistocarpa'' (tangare): Ecuador *''Carapa procera'' (African crabwood, kowi, okoto): West Africa, the Congos Other proposed species: *'' Carapa akuri'' *'' Carapa alticola'' *'' Carapa longipetala'' *'' Carapa nicaraguensis'' *'' Carapa vasquezii'' Uses The timber is important, and oil is produced from the seeds. The name andiroba is from Nheengatu ''nhandi rob'', meaning "bitter oil". ''Carapa guianensis'' produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copaiba
Copaiba is a stimulant oleoresin obtained from the trunk of several pinnate-leaved South American leguminous trees (genus ''Copaifera''). The thick, transparent exudate varies in color from light gold to dark brown, depending on the ratio of resin to essential oil. Copaiba is used in making varnishes and lacquers. The balsam may be steam distilled to give ''copaiba oil'', a colorless to light yellow liquid with the characteristic odor of the balsam and an aromatic, slightly bitter, pungent taste. The oil consists primarily of sesquiterpene hydrocarbons; its main component is β-caryophyllene. The oil also contains significant amounts of α-bergamotene, α-copaene, and β-bisabolene. Copaiba is also a common name for several species of trees of the legume family native to Tropical Africa and North and South America. Uses Copaiba is particularly interesting as a source of biodiesel, because of the high yield of . The resin is tapped from standing trees, with an individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil Nut
The Brazil nut (''Bertholletia excelsa'') is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and it is also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds. It is one of the largest and longest-lived trees in the Amazon rainforest. The fruit and its nutshell – containing the edible Brazil nut – are relatively large, possibly weighing as much as in total weight. As food, Brazil nuts are notable for diverse content of micronutrients, especially a high amount of selenium. The wood of the Brazil nut tree is prized for its quality in carpentry, flooring, and heavy construction. Common names In various Spanish-speaking countries of South America, Brazil nuts are called , , or . In Brazil, they are more commonly called "" (meaning "chestnuts from Pará" in Portuguese), with other names also used. In North America, as early as 1896, Brazil nuts were sometimes known by the slang term "nigger toes", a vulgarity that gradually fell out of use as the racial slur became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Region Protected Areas Program
The Amazon Region Protected Areas Program (ARPA; pt, Programa Áreas Protegidas da Amazônia) is a joint initiative sponsored by government and non-government agencies to expand protection of the Amazon rainforest in Brazil. Foundation The Amazon Region Protected Areas Program (ARPA) originated in a 1998 promise by the Brazilian government to triple the area of the Amazon that was legally protected. The program was launched in 2003, supported by government agencies, NGOs and major donors. The program is based on a major two-year planning exercise with experts from different disciplines, representatives of the indigenous people and others. This defined a set of priority areas for new parks and reserves throughout the Amazon. Objectives Initial objectives were: * Establish about of new strictly protected conservation units of Brazil * Upgrade about of neglected existing parks to effective standards of management * Establish about of sustainable use reserves supported by local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Woolly Monkey
The gray woolly monkey (''Lagothrix lagothricha cana'') or Geoffroy's woolly monkey is a subspecies of the common woolly monkey from South America. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil and Peru. ''L. l. cana'' gets its common name, gray woolly monkey, from its thick gray coat. Its hands, feet, face and the inside of the arms are dark in color.Rowe, N. (1996) ''The Pictorial Guide to the Living Primates.'' Pogonias Press, Rhode Island. . The gray woolly monkey has been considered endangered by IUCN since 2008. The subspecies is listed as endangered because it suffered a 50% decrease in population over the past 45 years due to deforestation and hunting. Taxonomy Initially thought to be a subspecies of the common woolly monkey (''L. lagothricha''), it was later reclassified as its own species. Two subspecies of ''Lagothrix cana'' were known: ''L. c. cana'' and ''L. c. tschudii''. ''L. c. cana'' in both Brazil and Peru and ''L. c. tschudii'' in southeastern Peru and in the Madidi National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brocket Deer
Brockets or brocket deer are the species of deer in the genus ''Mazama''. They are medium to small in size, and are found in the Yucatán Peninsula, Central and South America, and the island of Trinidad. Most species are primarily found in forests. They are superficially similar to the African duikers and the Asian muntjacs, but only distantly related. About 10 species of brocket deer are described. The genus name ''Mazama'' is derived from Nahuatl ''mazame'', the plural of ''mazatl'' "deer". The common English name "brocket" (from French ''brocart'' < ''broche'', spindle) comes from the word for a stag in its second year, with unbranched antlers. Taxonomy The among ''Mazama'' species has changed significantly in the last decades, and as recently as 1999, some authorities only recognized four species.Now ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collared Peccary
The collared peccary (''Dicotyles tajacu'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed) mammal in the family Tayassuidae found in North, Central, and South America. It is the only member of the genus ''Dicotyles''. They are commonly referred to as ''javelina, saíno'', or ''báquiro'', although these terms are also used to describe other species in the family. The species is also known as the musk hog. In Trinidad, it is colloquially known as ''quenk''. Taxonomy Although somewhat related to true Old World pigs, and frequently referred to as a pig, this species and the other peccaries are no longer classified in the pig family, Suidae. Although formerly classified in the genus ''Pecari'', studies in 2020 placed them in the genus ''Dicotyles'', based on an unequivocal type-species selection; these studies have been accepted by the American Society of Mammalogists. Currently, the IUCN still places them in the genus ''Pecari''. Description The collared peccary stands around tall at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
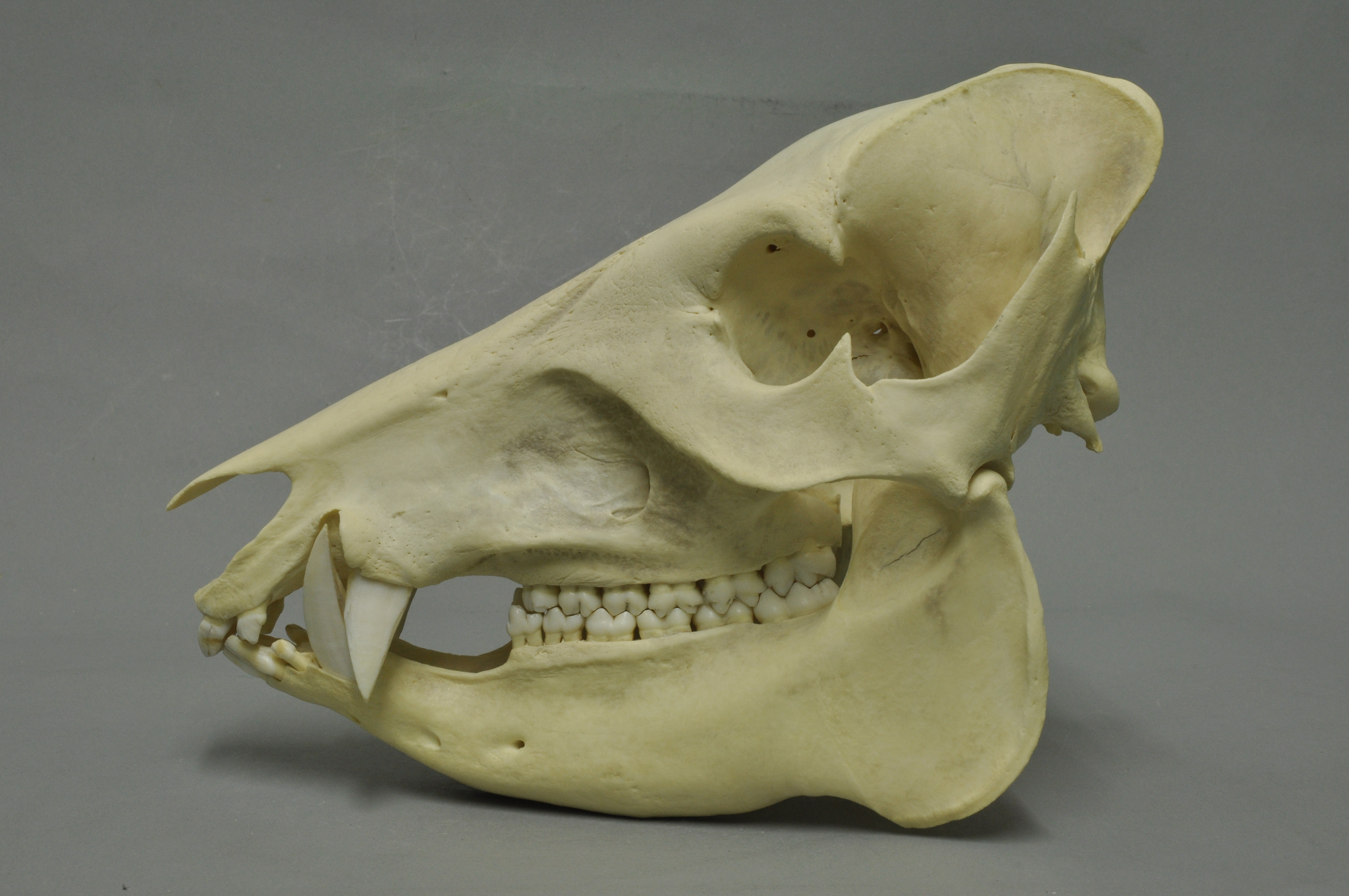
White-lipped Peccary
The white-lipped peccary (''Tayassu pecari'') is a species of peccary found in Central America, Central and South America and the only member of the genus ''Tayassu''. Multiple subspecies have been identified. White-lipped peccaries are similar in appearance to pigs, but covered in dark hair (except on certain regions, such as the throat, where it is cream (color), cream). The range of ''T. pecari'', which extends from Mexico to Argentina, has become fragmented, and the species's population is declining overall (especially in Mexico and Central America). They can be found in a variety of habitats. Social animals, white-lipped peccaries typically forage in large groups, which can have as many as 300 peccaries. They are an important part of their ecosystem and multiple efforts are being made to preserve them in the wild. Not all disappearances are explained, but human activities play a role, with two major threats being deforestation and hunting; the latter is very common in rural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South American Tapir
The South American tapir (''Tapirus terrestris''), also commonly called the Brazilian tapir (from the Tupi ''tapi'ira''), the Amazonian tapir, the maned tapir, the lowland tapir, the ''anta'' (Portuguese), and ''la sachavaca'' (literally "bushcow", in mixed Quechua and Spanish), is one of the four recognized species in the tapir family (of the order '' Perissodactyla'', with the mountain tapir, the Malayan tapir, and the Baird's tapir). It is the largest surviving native terrestrial mammal in the Amazon. Most classification taxons also include ''Tapirus kabomani'' (also known as the little black tapir or kabomani tapir) as also belonging to the species ''Tapirus terrestris'' (Brazilian tapir), despite its questionable existence and the overall lack of information on its habits and distribution. The specific epithet derives from ''arabo kabomani'', the word for tapir in the local Paumarí language. The formal description of this tapir did not suggest a common name for the species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |