|
Mataī
''Prumnopitys taxifolia'', the mataī ( mi, mataī) or black pine, is an endemic (ecology), endemic New Zealand coniferous tree that grows on the North Island and South Island. It also occurs on Stewart Island/Rakiura (47 °S) but is uncommon there. It grows up to 40 m high, with a trunk up to 2 m diameter. The leaf, leaves are linear to sickle-shaped, 10–15 mm long and 1.5–2 mm broad. The conifer cone, seed cones are highly modified, reduced to a central stem 3–4 cm long bearing 1-6 scales, each scale maturing berry-like, 10–15 mm long, violet-purple with a soft edible pulp covering the single seed. The seeds are dispersed by the New Zealand pigeon (kererū), which eats the 'berries' and passes the seeds in its droppings. Classification The scientific name ''taxifolia'' derives from the resemblance of the leaves to those of the Taxus, yew (''Taxus''). In the past the species, like the other species of ''Prumnopitys'', was often included in ''Podoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocrossa Iophaea
''Heterocrossa iophaea'' is a species of moth in the family Carposinidae. It is Endemism, endemic to New Zealand. Taxonomy This species was described by Edward Meyrick in 1907 using material collected by Alfred Philpott in Invercargill. In 1922 Meyrick classified ''Heterocrossa'' as a synonym of the genus ''Carposina''. George Hudson (entomologist), George Hudson discussed and illustrated this species under the name ''Carposina iophaea'' in his 1928 publication ''The Butterflies and Moths of New Zealand.'' In 1978 Elwood Zimmerman argued that the genus ''Heterocrassa'' should not be a synonym of ''Carposina'' as the genitalia of the species within the genus ''Heterocrassa'' are distinctive. In 1988 John S. Dugdale assigned the species back to the genus ''Heterocrossa''. He also synonymised ''Heterocrossa thalamota'' with ''Heterocrossa iophaea''. The Type (biology), lectotype specimen is held at the Natural History Museum, London. Description This species was described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences. Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James Cook's first great voyage (1768–1771), visiting Brazil, Tahiti, and after 6 months in New Zealand, Australia, returning to immediate fame. He held the position of president of the Royal Society for over 41 years. He advised King George III on the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and by sending botanists around the world to collect plants, he made Kew the world's leading botanical garden. He is credited for bringing 30,000 plant specimens home with him; amongst them, he was the first European to document 1,400. Banks advocated British settlement in New South Wales and the colonisation of Australia, as well as the establishment of Botany Bay as a place for the reception of convicts, and advised the British government on all Australian matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prumnopitys
''Prumnopitys'' is a genus of conifers belonging to the family Podocarpaceae. The nine recognized species of ''Prumnopitys'' are densely branched, dioecious evergreen trees up to 40 metres in height. Etymology The name ''Prumnopitys'' comes from the Ancient Greek ' ( ‘hindmost’) and ' ( ‘pine’), referring to the resin duct being behind the midrib. Description The leaves are similar to those of the yew, strap-shaped, 1–4 cm long and 2–3 mm broad, with a soft texture; they are green above, and with two blue-green stomatal bands below. The seed cones are highly modified, reduced to a central stem 1–5 cm long bearing several scales; from one to five scales are fertile, each with a single seed surrounded by fleshy scale tissue, resembling a drupe. These berry-like cone scales are eaten by birds which then disperse the seeds in their droppings. Distribution The species are distributed on both sides of the Pacific, in eastern Australia, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Concern Plants
Comparison is a feature in the morphology or syntax of some languages whereby adjectives and adverbs are inflected to indicate the relative degree of the property they define exhibited by the word or phrase they modify or describe. In languages that have it, the comparative construction expresses quality, quantity, or degree relative to ''some'' other comparator(s). The superlative construction expresses the greatest quality, quantity, or degree—i.e. relative to ''all'' other comparators. The associated grammatical category is degree of comparison. The usual degrees of comparison are the ''positive'', which simply denotes a property (as with the English words ''big'' and ''fully''); the ''comparative'', which indicates ''greater'' degree (as ''bigger'' and ''more fully''); and the ''superlative'', which indicates ''greatest'' degree (as ''biggest'' and ''most fully''). Some languages have forms indicating a very large degree of a particular quality (called ''elative'' in Semit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of Mild Maritime Climate
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are usable as lumber or plants above a specified height. In wider definitions, the taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos are also trees. Trees are not a taxonomic group but include a variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some reaching several thousand years old. Trees have been in existence for 370 million years. It is estimated that there are some three trillion mature trees in the world. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground by the trunk. This trunk typically c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of New Zealand
New Zealand's long geological isolation means that most of its flora is unique, with many durable hard woods. There is a wide variety of native trees, adapted to all the various micro-climates in New Zealand. The native bush (forest) ranges from the subtropical kauri forests of the northern North Island, temperate rainforests of the West Coast, the alpine forests of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana and Fiordland to the coastal forests of the Abel Tasman National Park and the Catlins. In the early period of British colonisation, many New Zealand trees were known by names derived from the names of unrelated European trees, but more recently the trend has been to adopt the native Māori language names into English. For a listing in order of Māori name, with species names for most, see the ''Flora of New Zealand'' list overnacular names The New Zealand Plant Conservation Network has published a list of New Zealand indigenous vascular plants including all 574 native tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
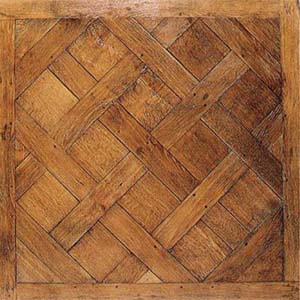
Parquetry
Parquet (; French for "a small compartment") is a geometric mosaic of wood pieces used for decorative effect in flooring. Parquet patterns are often entirely geometrical and angular—squares, triangles, lozenges—but may contain curves. The most popular parquet flooring pattern is herringbone. Etymology The word derives from the Old French ''parchet'' (the diminutive of ''parc''), literally meaning "''a small enclosed space''". History Large diagonal squares known as ''parquet de Versailles'' were introduced in 1684 as ''parquet de menuiserie'' ("woodwork parquet") to replace the marble flooring that required constant washing, which tended to rot the joists beneath the floors. Such ''parquets en losange'' were noted by the Swedish architect Daniel Cronström at Versailles and at the Grand Trianon in 1693. Materials Timber contrasting in color and grain, such as oak, walnut, cherry, lime, pine, maple etc. are sometimes employed, and in the more expensive kinds the ric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrgotis Zygiana
''Pyrgotis zygiana'' is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. ''P. zygiana'' was first described by Edward Meyrick in 1882 from a specimen obtained in Canterbury. This species has also been recorded in Titirangi. The wingspan is about 14 mm. The forewings are dark reddish ochreous fuscous, mixed with dark fuscous and strigulated (finely streaked) with leaden grey. The hindwings are grey. The larvae feed exclusively on ''Prumnopitys taxifolia ''Prumnopitys taxifolia'', the mataī ( mi, mataī) or black pine, is an endemic New Zealand coniferous tree that grows on the North Island and South Island. It also occurs on Stewart Island/Rakiura (47 °S) but is uncommon there. It grows up ...''. References Moths described in 1882 Archipini Moths of New Zealand Endemic fauna of New Zealand Endemic moths of New Zealand {{Archipini-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prumnopitys Ferruginea
''Prumnopitys ferruginea'', commonly called miro, is an evergreen coniferous tree which is endemic to New Zealand. Before the genus ''Prumnopitys'' was distinguished, it was treated in the related genus ''Podocarpus'' as ''Podocarpus ferrugineus''. It grows up to 25 m high, with a trunk up to 1.3 m diameter. The leaves are linear to sickle-shaped, 15–25 mm long and 2–3 mm broad, with downcurved margins. The plants are dioecious with pollen cones being solitary while those of female plants hang from a curved, scaly stalk. The seed cones are highly modified, reduced to a central stem 2–3 cm long bearing 1-3 scales, each scale maturing berry-like, oval, about 20 mm long and 10–15 mm broad, red to purple-red with a soft edible pulp covering the single seed. The seeds are dispersed by the New Zealand pigeon, which eats the very conspicuous 'berries' and passes the seeds in its droppings. It is found growing on both lowland terrain and on hill slopes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |