|
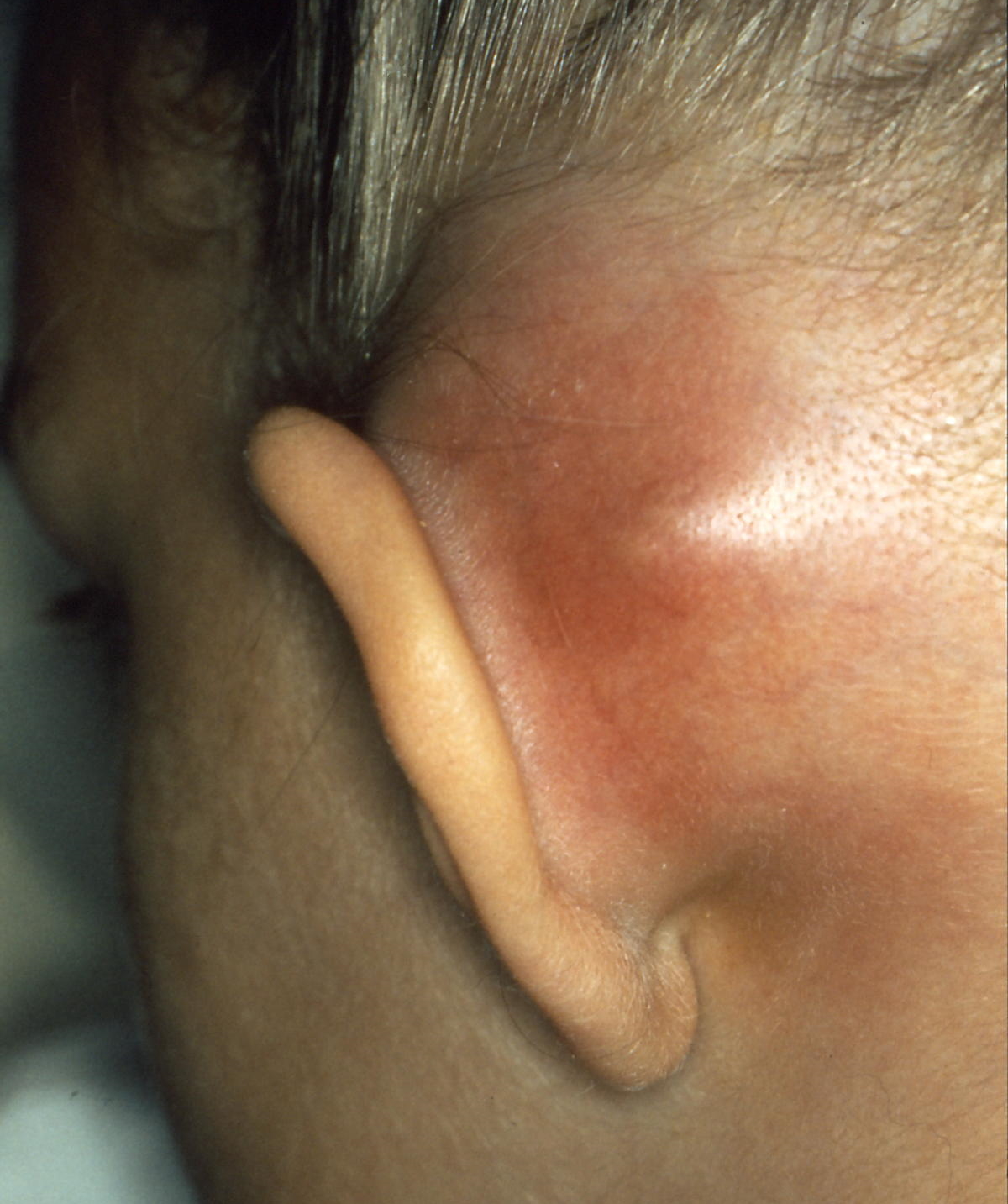
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is the result of an infection that extends to the air cells of the skull behind the ear. Specifically, it is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the mastoid antrum and mastoid air cell system inside the mastoid process. The mastoid process is the portion of the temporal bone of the skull that is behind the ear. The mastoid process contains open, air-containing spaces. Mastoiditis is usually caused by untreated acute otitis media (middle ear infection) and used to be a leading cause of child mortality. With the development of antibiotics, however, mastoiditis has become quite rare in developed countries where surgical treatment is now much less frequent and more conservative, unlike former times. There is no evidence that the drop in antibiotic prescribing for otitis media has increased the incidence of mastoiditis, raising the possibility that the drop in reported cases is due to a confounding factor such as childhood immunizations against ''Haemophilus'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otalgia
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is felt. Most causes of ear pain are non-life-threatening. Primary ear pain is more common than secondary ear pain, and it is often due to infection or injury. The conditions that cause secondary (referred) ear pain are broad and range from temporomandibular joint syndrome to inflammation of the throat. In general, the reason for ear pain can be discovered by taking a thorough history of all symptoms and performing a physical examination, without need for imaging tools like a CT scan. However, further testing may be needed if red flags are present like hearing loss, dizziness, ringing in the ear or unexpected weight loss. Management of ear pain depends on the cause. If there is a bacterial infection, antibiotics are sometimes recommended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Air Cell
The mastoid cells (also called air cells of Lenoir or mastoid cells of Lenoir) are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium. The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells is called mastoiditis. The term "cells" refers to enclosed spaces, not cell (biology), cells as living, biological units. Anatomy A section of the mastoid process will show it to be hollowed out into a number of spaces which exhibit great variety in their size and number. At the upper and front part of the process they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequently quite small and contain Bone marrow, marrow. Occasionally they are entirely absent and the mastoid is solid throughout. Development At birth, the mastoid is not pneumatized, but becomes aerated before age six. Function The air cells are hypothesised to protect the temporal bone a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Air Cell
The mastoid cells (also called air cells of Lenoir or mastoid cells of Lenoir) are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium. The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells is called mastoiditis. The term "cells" refers to enclosed spaces, not cell (biology), cells as living, biological units. Anatomy A section of the mastoid process will show it to be hollowed out into a number of spaces which exhibit great variety in their size and number. At the upper and front part of the process they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequently quite small and contain Bone marrow, marrow. Occasionally they are entirely absent and the mastoid is solid throughout. Development At birth, the mastoid is not pneumatized, but becomes aerated before age six. Function The air cells are hypothesised to protect the temporal bone a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Cells
The mastoid cells (also called air cells of Lenoir or mastoid cells of Lenoir) are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, .... The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells is called mastoiditis. The term "cells" refers to enclosed spaces, not cells as living, biological units. Anatomy A section of the mastoid process will show it to be hollowed out into a number of spaces which exhibit great variety in their size and number. At the upper and front part of the process they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequently quite small and contain marrow. Occasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + '' rhino- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Antrum
The mastoid antrum (tympanic antrum, antrum mastoideum, Valsalva's antrum) is an air space in the petrous portion of the temporal bone, communicating posteriorly with the mastoid cells and anteriorly with the epitympanic recess of the middle ear via the aditus to mastoid antrum (entrance to the mastoid antrum). These air spaces function as sound receptors, provide voice resonance, act as acoustic insulation and dissipation, provide protection from physical damage and reduce the mass of the cranium. The roof is formed by the tegmen antri which is a continuation of the tegmen tympani and separates it from the middle cranial fossa. The lateral wall of the antrum is formed by a plate of bone which is an average of 1.5 cm in adults. The mastoid air cell system is a major contributor to middle ear inflammatory diseases. Additional images File:Gray1209.png, Left temporal bone showing surface markings for the tympanic antrum (red), transverse sinus (blue), and facial nerve T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusobacterium
''Fusobacterium'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-sporeforming bacteria belonging to Gracilicutes. Individual cells are slender, rod-shaped bacilli with pointed ends. Strains of ''Fusobacterium'' cause several human diseases, including periodontal diseases, Lemierre's syndrome, and topical skin ulcers. Although older sources state that ''Fusobacterium'' is part of the normal flora of the human oropharynx, the current consensus is that ''Fusobacterium'' should always be treated as a pathogen. ''F. prausnitzii'', a gut commensal associated with healthy patients, was completely reclassified as '' Faecalibacterium'' (''Clostridiales'':''Ruminococcaceae'') in 2002. Clinical relevance ''Fusobacterium'' is often associated with ulcerative colitis. Research of colon cancer has also shown an overrepresentation of ''Fusobacterium'', both in feces of patients and tumor issue itself. Whether ''Fusobacterium'' causes these diseases or only colonizes existing tumours, remains unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides
''Bacteroides'' is a genus of Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacteria. ''Bacteroides'' species are non endospore-forming bacilli, and may be either motile or nonmotile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40–48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, ''Bacteroides'' membranes contain sphingolipids. They also contain meso-diaminopimelic acid in their peptidoglycan layer. ''Bacteroides'' species are normally mutualistic, making up the most substantial portion of the mammalian gastrointestinal microbiota, where they play a fundamental role in processing of complex molecules to simpler ones in the host intestine. As many as 1010–1011 cells per gram of human feces have been reported. They can use simple sugars when available; however, the main sources of energy for ''Bacteroides'' species in the gut are complex host-derived and plant glycans. Studies indicate that long-term diet is strongly associated with the gut microbiome composition—those who eat ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevotella
''Prevotella'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. ''Prevotella'' spp. are members of the oral, vaginal, and gut microbiota and are often recovered from anaerobic infections of the respiratory tract. These infections include aspiration pneumonia, lung abscess, pulmonary empyema, and chronic otitis media and sinusitis. They have been isolated from abscesses and burns in the vicinity of the mouth, bites, paronychia, urinary tract infection, brain abscesses, osteomyelitis, and bacteremia associated with upper respiratory tract infections. ''Prevotella'' spp. predominate in periodontal disease and periodontal abscesses. Role in gut microbiota Human gut is mainly inhabited by two phyla of bacteria—''Bacillota'' and ''Bacteroidota'', the latter mostly dominated by '' Bacteroides'' and '' Prevotella'' genera. ''Prevotella'' and ''Bacteroides'' are thought to have had a common ancestor. Formally, the two genera were differentiated in 1990. However classification is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Infection
Anaerobic infections are caused by anaerobic bacteria. Obligately anaerobic bacteria do not grow on solid media in room air (0.04% carbon dioxide and 21% oxygen); facultatively anaerobic bacteria can grow in the presence or absence of air. Microaerophilic bacteria do not grow at all aerobically or grow poorly, but grow better under 10% carbon dioxide or anaerobically. Anaerobic bacteria can be divided into strict anaerobes that can not grow in the presence of more than 0.5% oxygen and moderate anaerobic bacteria that are able of growing between 2 and 8% oxygen.Jousimies-Somer HR, Summanen P, Baron EJ, Citron DM, Wexler HM, Finegold SM. Wadsworth-KTL anaerobic bacteriology manual. 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Star Publishing, 2002. Anaerobic bacteria usually do not possess catalase, but some can generate superoxide dismutase which protects them from oxygen. The clinically important anaerobes in decreasing frequency are:Brook, I.: "Anaerobic Infections Diagnosis and Management". A Textbook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraxella Catarrhalis
''Moraxella catarrhalis'' is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system, middle ear, eye, central nervous system, and joints of humans. It causes the infection of the host cell by sticking to the host cell using trimeric autotransporter adhesins. Epidemiology ''Moraxella catarrhalis'' is a human pathogen with an affinity for the human upper respiratory tract. Other primates, such as macaques, might become infected by this bacterium. History ''Moraxella catarrhalis'' was previously placed in a separate genus named '' Branhamella''. The rationale for this was that other members of the genus '' Moraxella'' are rod-shaped and rarely caused infections in humans. However, results from DNA hybridization studies and 16S rRNA sequence comparisons were used to justify inclusion of the species ''M. catarrhalis'' in the genus ''Moraxella''. As a consequence, the name ''Moraxella catarrhal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |