|
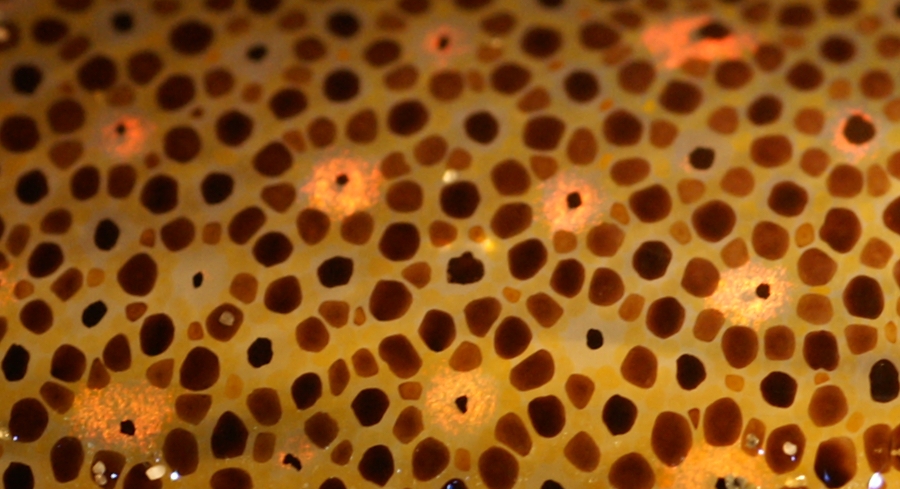
Mastigoteuthis Magna
''Mastigoteuthis magna'' is a species of whip-lash squid, characterised by a lack of photophores. The skin is heavily pigmented a deep red by a numerous chromatophore Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, ...s. Image:Mastigoteuthis magna2.jpg, Side view of a club sucker Image:Mastigoteuthis magna3.jpg, Funnel component of the funnel locking apparatus Mastigoteuthis magna.jpg, ''M. magna'' References *Joubin, L. 1920. ''Céphalopodes provenant des Campagnes de la Princesse Alice (1898-1910)''. 3e Serie. Monaco. External links Tree of Life web project: ''Mastigoteuthis magna'' Mastigoteuthis Molluscs described in 1913 {{Squid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joubin
Louis Marie Adolphe Olivier Édouard Joubin (27 February 1861 in Épinal – 24 April 1935 in Paris) was a professor at the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle in Paris. He published works on nemerteans, chaetognatha, cephalopods, and other Mollusk, molluscs. He served as an assistant to Henri de Lacaze-Duthiers, subsequently becoming director of the laboratories at Banyuls-sur-Mer (1882) and Station biologique de Roscoff, Roscoff (1884). Later on, he became an instructor at the University of Rennes,Prosopo Sociétés savantes and in 1903 succeeded Edmond Perrier as ''chaire des mollusques, des vers et des zoophytes'' at the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle (from 1917 onward his title was ''chaire des mollusques''). In 1906 he was chosen by Albert I, Prince of Monaco to be in charge of instruction at the Institut océanographique. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whip-lash Squid
The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally described by Verill in 1881, it was later lowered by Chun (1920) to a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of the Chiroteuthidae. However, Roper et al. (1969) raised it back to the family level, and this has not been changed since. The taxonomy of this family is extremely unstable, and there have been at times one genus (Young, Lindgren, & Vecchione, 2008), two genera and four subgenera(Salcedo-Vargas & Okutani, 1994), two genera and several 'groups' (Salcedo-Vargas, 1997), five genera (Braid, McBride, & Bolstad, 2014) and one species with an uncertain placement, or six genera (Young, Vecchione, & Braid, 2014). Description Mastigoteuthids range in size from quite small species in the genus '' Mastigoteuthis'', to relatively gigantic sizes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, however unlike an eye it is optimized to produce light, not absorb it. The bioluminescence can variously be produced from compounds during the digestion of prey, from specialized mitochondrial cells in the organism called photocytes ("light producing" cells), or, similarly, associated with symbiotic bacteria in the organism that are cultured. The character of photophores is important in the identification of deep sea fishes. Photophores on fish are used for attracting food or for camouflage from predators by counter-illumination. Photophores are found on some cephalopods including the firefly squid, which can create impressive light displays, as well as numerous other deep sea organisms such as the pocket shark Mollisquama mississippien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. Estimated at around US$14.86 billion in 2018 and will rise at over 4.9% CAGR from 2019 to 2026. The global demand for pigments was roughly US$20.5 billion in 2009. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each year. Physical principles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are Biological pigment, pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for animal coloration, coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye color, eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly "hue") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescence, iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funnel–mantle Locking Apparatus
The funnel–mantle locking apparatus is a structure found in many cephalopods that connects the mantle and hyponome (funnel) and restricts their movement relative to each other.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold (1999)Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Life Web Project. It consists of two interlocking components: one located on the mantle (often fibrous) and the other on the funnel (often cartilaginous). The apparatus may permit some anterior–posterior displacement or prevent movement altogether. Function Variability Funnel component Six major forms of the funnel locking apparatus are recognised among teuthids (lazy-T shape, inverted-T shape, straight shape, triangular shape, oval with tragus and/or antitragus, and oval shape) and several more are found in the sepioids (including the boomerang shape and keyhole shape).Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold (1997)Cephalopod Funnel Locking-Apparatus Tree of Life Web Project The Tree of Life Web Project is an Interne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastigoteuthis
''Mastigoteuthis'' is a genus of whip-lash squid containing at least seven valid species. Some teuthologists consider ''Idioteuthis'' synonymous with this taxon. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Species *Genus ''Mastigoteuthis'' **'' Mastigoteuthis agassizii'' Verrill, 1881 **'' Mastigoteuthis dentata'' Hoyle, 1904 **''Mastigoteuthis flammea'' Chun, 1908 **'' Mastigoteuthis glaukopis'' Chun, 1908 **'' Mastigoteuthis grimaldii'' ( Joubin, 1895) **'' Mastigoteuthis psychrophila'' Nesis, 1977 **'' Mastigoteuthis schmidti'' Degner, 1925 **'' Mastigoteuthis hastula'' * ( Berry, 1920) **''Mastigoteuthis inermis'' * Rancurel, 1972 **'' Mastigoteuthis iselini'' * MacDonald & Clench, 1934 **'' Mastigoteuthis okutanii'' * Salcedo-Vargas, 1997 **'' Mastigoteuthis tyroi'' * Salcedo-Vargas, 1997 '' Magnapinna talismani'' was previously placed in this genus, but is now considered a species of bigfin squid. The taxa listed above with an asterisk (*) are ''taxon inquirendum In bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |