|
Massacre In The Mokotów Prison
The Massacre in the Mokotów prison - mass murder of residents of the Mokotów prison in Warsaw by the Germans on the second day of the Warsaw Uprising. On August 2, 1944, soldiers of the Waffen- SS - SS-Pz. Gren. Ausb.-und Ers. Btl. 3 (of SS-Panzer Division "Totenkopf") shot about 600 Poles on the premises of the prison at 37 Rakowiecka Street. It was one of the biggest crimes committed by the Germans in Mokotów during the suppression of the Warsaw Uprising. During the massacre, some prisoners actively resisted the Nazis, which allowed several hundred people to escape to the area controlled by the insurgents. Before the outbreak of the Uprising Soon after the Germans entered Warsaw (28 September 1939), the former Polish penitentiary at 37 Rakowiecka Street was adapted for the needs of the occupying forces. The Gerichtsgefängnis in der Rakowieckastrasse 37 was henceforth a prison under the authority of the German special courts ( Sondergericht), and its residents remained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
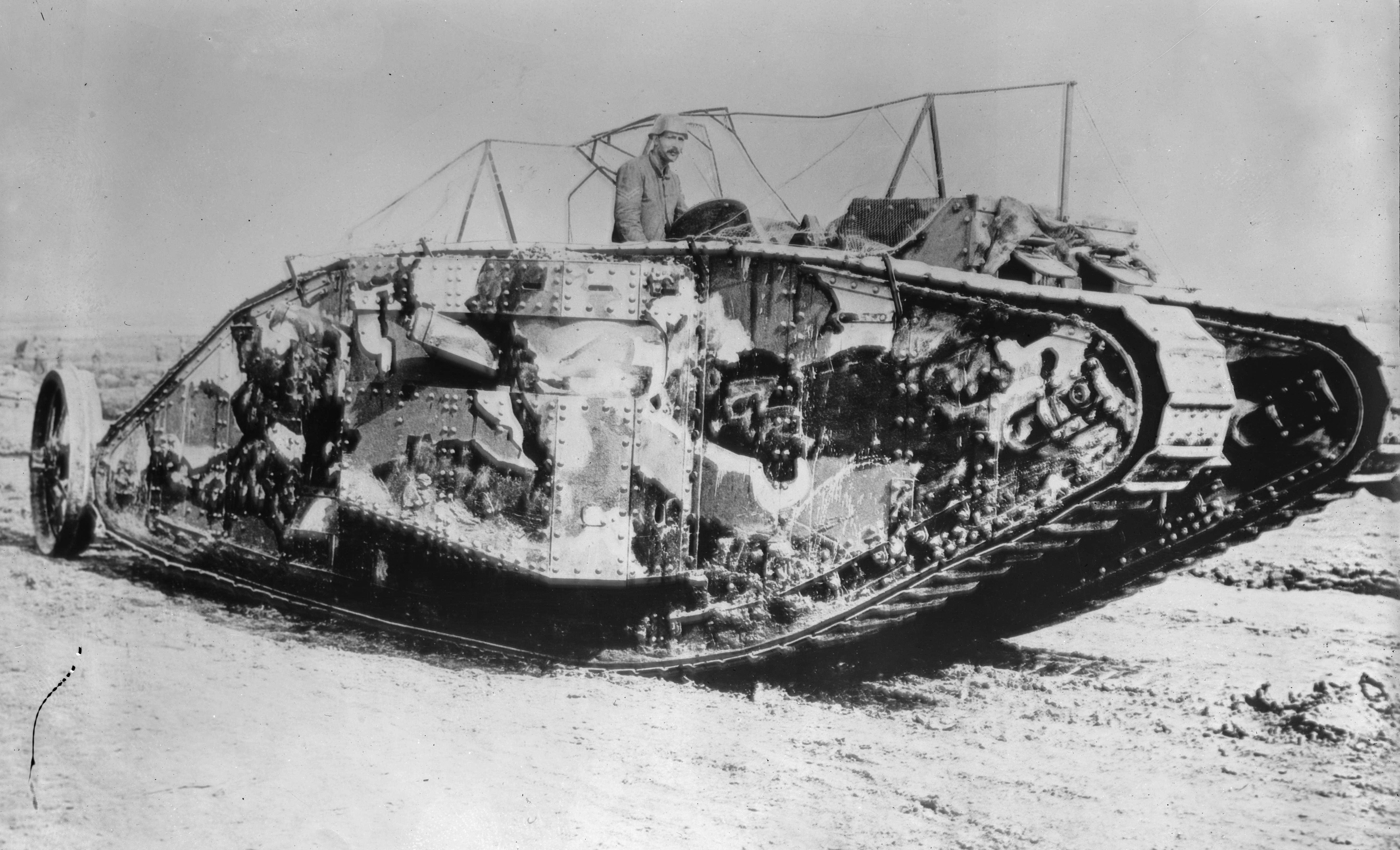
Tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; usually their main armament is mounted in a turret. They are a mainstay of modern 20th and 21st century ground forces and a key part of combined arms combat. Modern tanks are versatile mobile land weapons platforms whose main armament is a large-caliber tank gun mounted in a rotating gun turret, supplemented by machine guns or other ranged weapons such as anti-tank guided missiles or rocket launchers. They have heavy vehicle armour which provides protection for the crew, the vehicle's munition storage, fuel tank and propulsion systems. The use of tracks rather than wheels provides improved operational mobility which allows the tank to overcome rugged terrain and adverse conditions such as mud and ice/snow better than wheeled vehicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
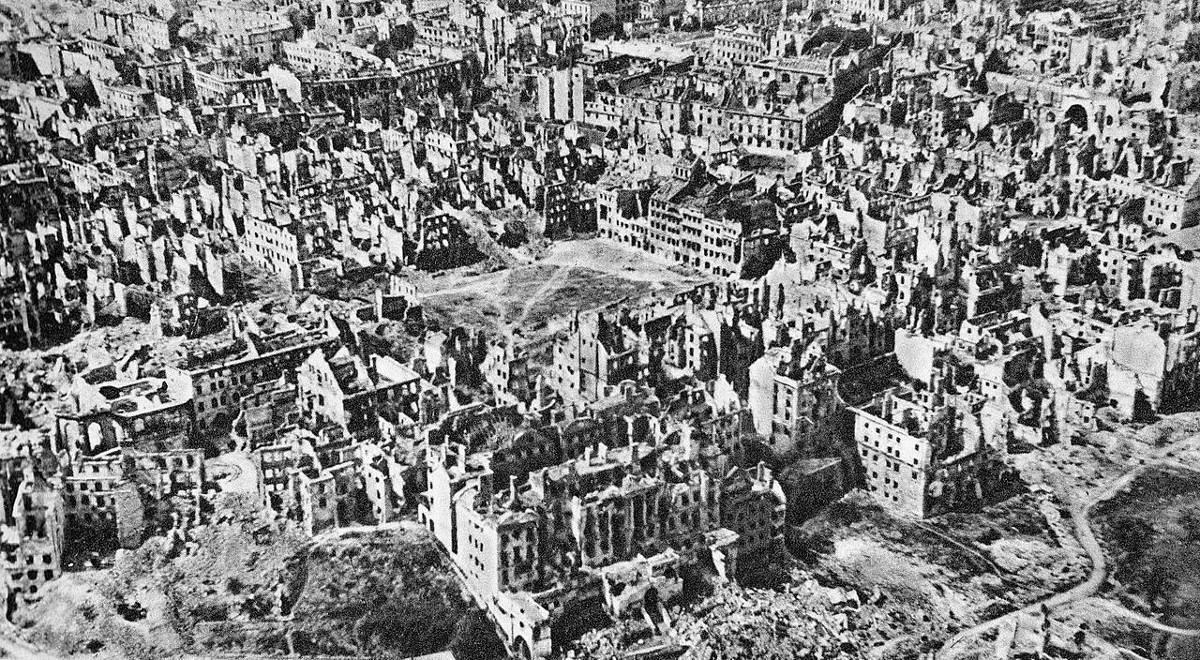
Nazi War Crimes During The Warsaw Uprising
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly influenced by the paramilitary groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the Cologne Bonn Region, urban region. Centered on the left bank of the Rhine, left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powązki Military Cemetery
Powązki Military Cemetery (; pl, Cmentarz Wojskowy na Powązkach) is an old military cemetery located in the Żoliborz district, western part of Warsaw, Poland. The cemetery is often confused with the older Powązki Cemetery, known colloquially as "Old Powązki". The Old Powązki cemetery is located to the south-east of the military cemetery. The military cemetery holds the graves of many who have fought and died for their country since the early 19th century, including a large number involved in the 1920 Battle of Warsaw, the September 1939 Campaign, and the ill-fated 1944 Warsaw Uprising against Nazi Germany. History It was founded in 1912 as an annex to the Catholic cemetery, but after Poland regained independence in 1918, it became the state cemetery, where some of the most notable people of the period were buried, regardless of their faith. A large part of the cemetery is occupied by graves of Polish soldiers who died in the Warsaw Uprising. Most of the graves were exh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison In Stauferkaserne Barracks
Stauferkaserne prison was a provisional prison, and at the same time a gathering point for expelled Warsaw residents, established by the Germans during the first days of the Warsaw Uprising on the grounds of the SS-Stauferkaserne barracks at 4 Rakowiecka Street. In August and September 1944 over a thousand residents of the district passed through the SS barracks in Mokotów. They were detained there in harsh conditions and were subjected to extremely brutal treatment. During the Warsaw Uprising, the Stauferkaserne area was the scene of numerous executions, the victims of which were at least 100 people. Establishment of the prison During the German occupation, the complex of buildings of the Main Staff of the Polish Army, located at 4 Rakowiecka Street in Warsaw's Mokotów, was transformed into SS barracks - the so-called SS-Stauferkaserne. When the Warsaw Uprising broke out, it housed the 3rd SS Grenadier Reserve Battalion,Maja Motyl, Stanisław Rutkowski: ''Powstanie Wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vodka
Vodka ( pl, wódka , russian: водка , sv, vodka ) is a clear distilled alcoholic beverage. Different varieties originated in Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impurities and flavourings. Traditionally, it is made by distilling liquid from fermented cereal grains, and potatoes since introduced in Europe in the 1700's. Some modern brands use fruits, honey, or maple sap as the base. Since the 1890s, standard vodkas have been 40% alcohol by volume (ABV) (80 U.S. proof). The European Union has established a minimum alcohol content of 37.5% for vodka. Vodka in the United States must have a minimum alcohol content of 40%. Vodka is traditionally drunk "neat" (not mixed with water, ice, or other mixers), and it is often served ''freezer chilled'' in the vodka belt of Belarus, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and Ukraine. It is also used in cocktails and mixed dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Otto Geibel
Paul Otto Geibel (10 June 1898 – 12 November 1966) was a German SS-''Brigadeführer'' and ''Generalmajor'' of police who served as the last SS and Police Leader (SSPF) "Warsaw" during the Second World War. He was involved in suppressing the Warsaw Uprising and in the subsequent destruction of the city. At the end of the war, he was convicted of war crimes and committed suicide while serving a life sentence in Poland. Early life Geibel was born in Dortmund, the son of a school director. On the outbreak of the First World War, he left school and joined the Imperial German Navy. He served at sea and in the coastal artillery, finishing his service aboard the battlecruiser ''SMS Hindenburg'', and rising to the rank of ''Leutnant zur see''. After the war, he returned to civilian life and worked as an insurance salesman from 1920 to 1933. He joined the Nazi Party (membership number 761,353) and its paramilitary wing, the SA, in December 1931. He was commissioned an SA-''Sturmführ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberführer
__NOTOC__ ''Oberführer'' (short: ''Oberf'', , ) was an early paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) dating back to 1921. An ''Oberführer'' was typically a NSDAP member in charge of a group of paramilitary units in a particular geographical region. From 1921 to 1925, the phrase ''Oberführer'' was used as a title in the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), but became an actual SA rank after 1926. ''Oberführer'' was also a rank of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS, at that time a branch of the SA), established in 1925 as ''Gauführer'', a rank for SS officers in charge of SS personnel in the several ''Gaue'' throughout Germany; in 1928 the rank was renamed ''Oberführer'', and used of the commanders of the three regional ''SS-Oberführerbereiche''. In 1930, the SS was reorganized into ''SS-Gruppen'' and ''Brigaden'', at which time ''Oberführer'' became subordinate to the higher rank of ''Brigadeführer''. By 1932, ''Oberführer'' was an established rank of the SA, SS and NSKK. ''Oberführ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reiner Stahel
Reiner Stahel (15 January 1892 – 30 November 1955) was a German officer. He is best known for his retreat from Vilna and the command of the garrison of Warsaw during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944. Arrested by the NKVD in Romania, he spent the rest of his life in Soviet captivity. Early life Stahel was born in Bielefeld. World War I He joined the German Army during World War I. By the end of the war, he had moved to Finland and joined the Finnish Army participating in the Finnish Civil War. Interwar In 1933 he went to Nazi Germany where he worked at the Ministry of Aviation. World War II Stahel participated in the German invasion of the Soviet Union as commander of Flakregiments 34 (June 1941), Flakregiment 99 (April 1942) and 4th Luftwaffe Field Division (September 1942). During the Battle of Stalingrad, Stahel conducted defensive actions at the head of ''Kampfgruppe Stahel''. On 21 January 1943, he was promoted to Major General and then transferred to Air Fleet 4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |