|
Mary Ann Angell
Mary Ann Angell Young (June 8, 1803 – June 27, 1882) was the second woman married to Brigham Young, who served as president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). Young's first wife had died in 1832, leaving Young a widower. Angell and Young were married on March 31, 1834 in Kirtland, Ohio. In 1842, Angell gave her consent to the practice of plural marriage upon Young's marriage to Lucy Ann Decker, his first plural wife. Angell remained married to Young until his death in 1877, and together they had six children. Early life and conversion Angell was born in Seneca, New York to James and Phoebe Morton Angell on June 8, 1803. Her parents moved to Providence, Rhode Island when she was young, where Mary Ann later became a Free Will Baptist and worked as a Sunday School teacher. Deeply religious and studious of the Hebrew and Christian scriptures, she vowed never to marry until she met "a man of God" in whom she could confide her spirituality and with who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneca, New York
Seneca is a town in Ontario County, New York, United States. The population was 2,658 at the 2020 census. The town is named after a group of local natives. The Town of Seneca is on the southern border of the county and is southwest of the City of Geneva. The Town of West Seneca in Erie County added "west" to its name to avoid confusion with the Town of Seneca. History The region was the locale of the Seneca tribe, a member of the Iroquois, and the sites of many important villages are in the town or the surrounding area; Kanadaseaga is one. The area was part of the Phelps and Gorham Purchase. Settlement commenced around 1790, the year after the county was formed. A "District of Seneca" was created judicially in 1789 at the time the county was established, but its extent and subdivisions are not clearly known. The town was finally organized in 1793. In 1872, the northeast part of the town was used to form the Town of Geneva, taking with it most of the historic Seneca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China, New York
China is a hamlet in Delaware County, New York Delaware County is a county located in the US state of New York. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 44,308. The county seat is Delhi. The county is named after the Delaware River, which was named in honor of Thomas West, ..., United States. It is located north-northeast of Deposit on China Road at its intersection with Schofield Road. Cold Spring Creek flows south through the hamlet. References {{DelawareCountyNY-geo-stub Geography of Delaware County, New York Hamlets in Delaware County, New York Hamlets in New York (state) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostle (Latter Day Saints)
In the Latter Day Saint movement, an apostle is a "special witness of the name of Jesus Christ who is sent to teach the principles of salvation to others." In many Latter Day Saint churches, an apostle is a priesthood office of high authority within the church hierarchy. In many churches, apostles may be members of the Quorum of the Twelve and First Presidency of the church. In most Latter Day Saint churches, modern-day apostles are considered to have the same status and authority as the Biblical apostles. In the Latter Day Saint tradition, apostles and prophets are believed to be the foundation of the church, Jesus Christ himself being the chief cornerstone. The "Articles of Faith", written by Joseph Smith, mentions apostles: "We believe in the same organization that existed in the Primitive Church, namely, apostles, prophets, pastors, teachers, evangelists, and so forth." History Joseph Smith and Oliver Cowdery were both designated apostles by 1830. The founding articles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake Temple
The Salt Lake Temple is a temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints on Temple Square in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. At , it is the largest Latter-day Saint temple by floor area. Dedicated in 1893, it is the sixth temple completed by the church, requiring 40 years to complete, and the fourth temple built since the Mormon exodus from Nauvoo, Illinois, in 1846. The temple was closed in December 2019 for a general remodelling and seismic renovations that are anticipated to take approximately four years. Details The Salt Lake Temple is the centerpiece of the Temple Square in Salt Lake City, Utah. Like other Latter-day Saint temples, the church and its members consider it sacred and a temple recommend is required to enter, so there are no public tours inside the temple as there are for other adjacent buildings on Temple Square. In 1912, the first public photographs of the interior were published in the book ''The House of the Lord'', by James E. Talmage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Utah, most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the county seat, seat of Salt Lake County, Utah, Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, the city is the core of the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, which had a population of 1,257,936 at the 2020 census. Salt Lake City is further situated within a larger metropolis known as the Salt Lake City–Provo–Orem Combined Statistical Area, Salt Lake City–Ogden–Provo Combined Statistical Area, a corridor of contiguous urban and suburban development stretched along a segment of the Wasatch Front, comprising a population of 2,746,164 (as of 2021 estimates), making it the 22nd largest in the nation. It is also the central core of the larger of only two major urban areas located within the Great Basin (the other being Reno, Nevada). Salt Lake C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
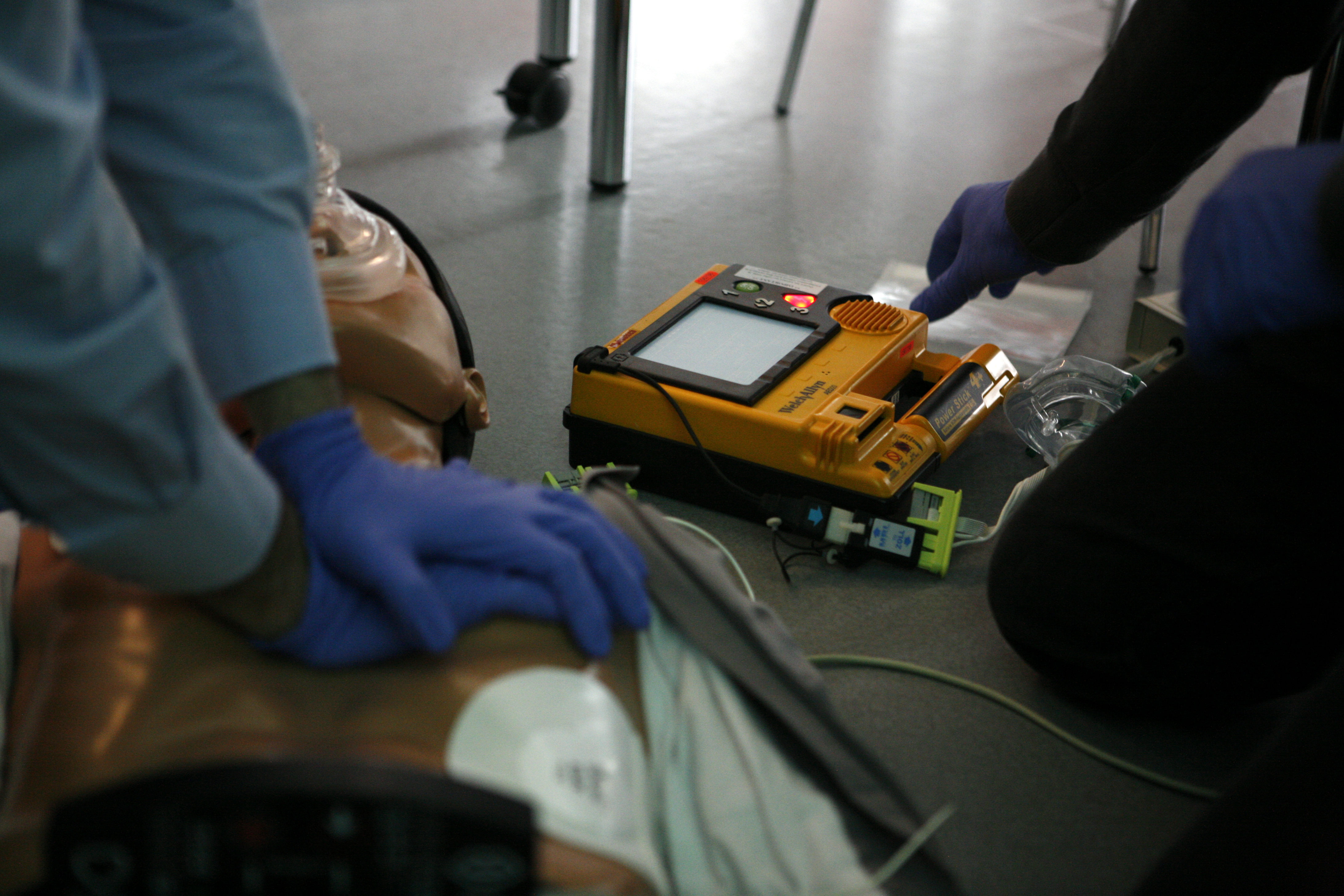
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations. CPR involves chest compressions for adults between and deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations place emphasis on early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for untrained rescuers. Wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camphor
Camphor () is a waxy, colorless solid with a strong aroma. It is classified as a terpenoid and a cyclic ketone. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel ('' Cinnamomum camphora''), a large evergreen tree found in East Asia; and in the kapur tree ( ''Dryobalanops'' sp.), a tall timber tree from South East Asia. It also occurs in some other related trees in the laurel family, notably '' Ocotea usambarensis''. Rosemary leaves (''Rosmarinus officinalis'') contain 0.05 to 0.5% camphor, while camphorweed (''Heterotheca'') contains some 5%. A major source of camphor in Asia is camphor basil (the parent of African blue basil). Camphor can also be synthetically produced from oil of turpentine. The compound is chiral, existing in two possible enantiomers as shown in the structural diagrams. The structure on the left is the naturally occurring (+)-camphor ((1''R'',4''R'')-bornan-2-one), while its mirror image shown on the right is the (−)-camphor ((1''S'',4''S'')-bornan-2-one). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormon Pioneer Memorial Monument
The Mormon Pioneer Memorial Monument (also known as the Brigham Young Family Cemetery) is a private cemetery and memorial. It is the burial site of Brigham Young, and his legal, non-plural wife, Mary Ann Angell, along with other wives and family members. Part of the property was dedicated to the Mormon pioneers who died making the journey to Utah from Illinois and other parts of the world between 1847 and 1869. Burial site The majority of graves in the cemetery are unmarked and prior to restoration work that began in the early 2020s, ground-penetrating radar was used, and 40-plus graves were discovered. The marked graves include: # Brigham Young — an American leader in the Latter Day Saint movement and a settler of the Western United States. He was the President of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) from 1847 until his death in 1877, he founded Salt Lake City, and he served as the first governor of the Utah Territory, United States. Young also led t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beehive House
A beehive house is a building made from a circle of stones topped with a domed roof. The name comes from the similarity in shape to a straw beehive. Occurrences The ancient Bantu used this type of house, which was made with mud, poles, and cow dung. Early European settlers in the Karoo region of South Africa built similar structures known as corbelled houses. These white-washed structures are described as coursed rubble on a circular plan, with each successive course smaller and slightly corbelled over the course below so that a conical shape is achieved as each course is completed. Beehive houses are some of the oldest known structures in Ireland and Scotland, dating from as far back as around 2000 BC. Bee houses have also been built in the Italian peninsula, with some still being built as late as the 19th century in Apulia (south-eastern Italy). In Southern Italy, these houses are called '' trulli'' while its prehistoric Sardinian versions were referred to as ''nuraghi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lion House (Salt Lake City)
The Lion House is a large residence built in 1856 by Brigham Young, second president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), in Salt Lake City, Utah. History Truman O. Angell, Young's brother-in-law, by his first wife Mary Ann Angell, and designer of the Salt Lake City Temple, was also involved in the design of this home. The house got its name from the statue of a lion, sculpted by the craftsman William F. Ward, above the front entrance. ''Lion of the Lord'' was a nickname of Young. The design is a Gothic Revival mansion with 20 gables for 20 small bedrooms. The house is situated at 63 East South Temple, near the corner of South Temple and State Street, just one block east of Temple Square. It is adjacent to Young's other official residence, the Beehive House, to which it is connected by a series of rooms used as offices. A polygamist, Young ultimately fathered 57 children by more than two dozen wives, and also had many adopted, foster, and stepchild ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, he had attracted tens of thousands of followers and founded a religion that continues to the present with millions of global adherents. Smith was born in Sharon, Vermont. By 1817, he had moved with his family to Western New York, the site of intense religious revivalism during the Second Great Awakening. Smith said he experienced a series of visions, including one in 1820 during which he saw "two personages" (whom he eventually described as God the Father and Jesus Christ), and another in 1823 in which an angel directed him to a buried book of golden plates inscribed with a Judeo-Christian history of an ancient American civilization. In 1830, Smith published what he said was an English translation of these plates called the ''Book of Mormo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The face is flushed and the rash is red and blanching. It typically feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. The rash occurs as a result of capillary damage by exotoxins produced by ''S.pyogenes''. On darker pigmented skin the rash may be hard to discern. Scarlet fever affects a small number of people who have strep throat or streptococcal skin infections. The bacteria are usually spread by people coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread when a person touches an object that has the bacteria on it and then touches their mouth or nose. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |