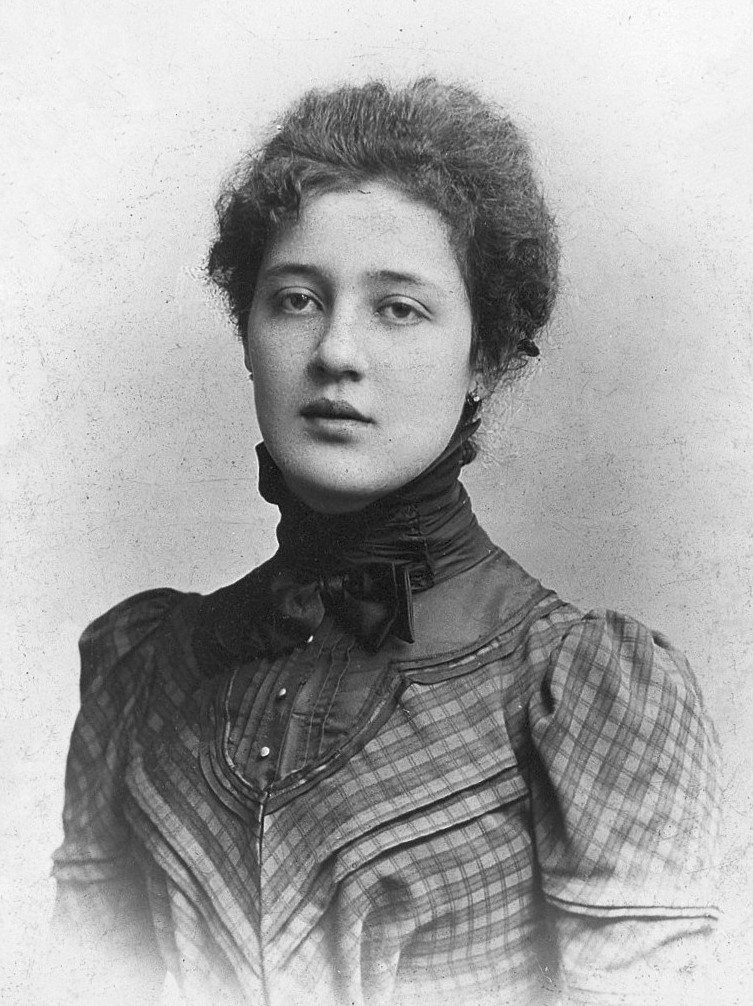|
Martha Harris
Martha Harris, née Dunlop (13 April 1919 – November 1987) was a British Kleinian psychoanalyst of children and adults. From 1960 to 1980 she was head of the Child Psychotherapy service at the Tavistock Clinic, taking over from Esther Bick, who had established a foundational method of disciplined infant observation. Harris was responsible for the subsequent expansion in the number of English and international trainees at the Tavistock, and for laterally developing the training into what became known as the Tavi Model. This model, in which infant observation continues to play a pre-eminent role, has been adopted, with modifications, in other European countries and in South America: such as the GERPEN in France, the six Martha Harris Study Centres in Italy, and the São Paulo Mother-Baby Study Centre in Brazil. Life and work Martha Gemmell Dunlop was the eldest of four children born to Gabriel Dunlop, a farmer, and Margaret McLure, who had run her own tailoring company. She wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavistock Clinic
The Tavistock and Portman NHS Foundation Trust is a specialist mental health trust based in north London. The Trust specialises in talking therapies. The education and training department caters for 2,000 students a year from the United Kingdom and abroad. The Trust is based at the Tavistock Centre in Swiss Cottage. The founding organisation was the Tavistock institute of medical psychology founded in 1920 by Dr. Hugh Crichton-Miller. The Tavistock and Portman NHS Trust was formed in 1994, when the Tavistock Clinic merged with the neighbouring Portman Clinic in Fitzjohn's Avenue. The Portman specialises in areas of forensic psychiatry, including the treatment of addictive, sociopathic and criminal behaviours and tendencies. It has developed as a centre of excellence for psychoanalysis within the NHS since being included at its founding in 1948. The Trust and predecessor organisations have been influential beyond medicine, including in the British Army, management consultanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy's Hospital
Guy's Hospital is an NHS hospital in the borough of Southwark in central London. It is part of Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and one of the institutions that comprise the King's Health Partners, an academic health science centre. It is a large teaching hospital and is, with St Thomas' Hospital and King's College Hospital, the location of King's College London GKT School of Medical Education. The hospital's Tower Wing (originally known as Guy's Tower) was, when built in 1974, the tallest hospital building in the world, standing at with 34 floors. The tower was overtaken as the world's tallest healthcare-related building by The Belaire in New York City in 1988. As of June 2019, the Tower Wing, which remains one of the tallest buildings in London, is the world's fifth-tallest hospital building. History The hospital dates from 1721, when it was founded by philanthropist Thomas Guy, who had made a fortune as a printer of Bibles and greatly increased it by speculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1919 Births
Events January * January 1 ** The Czechoslovak Legions occupy much of the self-proclaimed "free city" of Pressburg (now Bratislava), enforcing its incorporation into the new republic of Czechoslovakia. ** HMY ''Iolaire'' sinks off the coast of the Hebrides; 201 people, mostly servicemen returning home to Lewis and Harris, are killed. * January 2– 22 – Russian Civil War: The Red Army's Caspian-Caucasian Front begins the Northern Caucasus Operation against the White Army, but fails to make progress. * January 3 – The Faisal–Weizmann Agreement is signed by Emir Faisal (representing the Arab Kingdom of Hejaz) and Zionist leader Chaim Weizmann, for Arab–Jewish cooperation in the development of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, and an Arab nation in a large part of the Middle East. * January 5 – In Germany: ** Spartacist uprising in Berlin: The Marxist Spartacus League, with the newly formed Communist Party of Germany and the Independent Social De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organisation For Economic Co-operation And Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a Forum (legal), forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are High income economy, high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index, Human Development Index (HDI), and are regarded as Developed country, developed countries. Their collective population is 1.38 billion. , the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of List of countries by GDP (nominal), global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Meltzer
Donald Meltzer (1922–2004) was a Kleinian psychoanalyst whose teaching made him influential in many countries. He became known for making clinical headway with difficult childhood conditions such as autism, and also for his theoretical innovations and developments. His focus on the role of emotionality and aesthetics in promoting mental health has led to his being considered a key figure in the "post-Kleinian" movement associated with the psychoanalytic theory of thinking created by Wilfred Bion. Life and work Meltzer was born in New York City and studied medicine at Yale University. He practised in St. Louis as a psychiatrist, before moving to England in 1954 to have analysis with Melanie Klein. He joined the "Kleinian group", became a teaching analyst of the British Psychoanalytical Society (BPS) and took on British citizenship. In the early 1980s disagreements about the mode of training led him to withdraw from the BPS.Meltzer, “A review of my writings”, in Cohen and Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Rosenfeld
Herbert Alexander Rosenfeld (2 July 1910 – 29 November 1986) was a German-British psychoanalyst. Rosenfeld made seminal contributions to Kleinian thinking on psychotic and other very ill patients; while his emphasis on the role of the analyst in contributing to potential impasses in the analytic encounter has had a wide impact on analysts both in Britain and internationally. Among his most significant contributions were his groundbreaking exploration of projective identification; the development of the concept of "confusion"; and the foundation of a theory of destructive narcissism, since taken up and developed by André Green and Otto Kernberg. Life Rosenfeld was born in Nuremberg in 1910, received his medical diploma from Munich in 1934, and emigrated to Britain one year later due to the Nuremberg laws prohibiting him from working with non-Aryan patients. He retook his medical in degree, and went on to undergo a teaching analysis with Melanie Klein. He eventually became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfred Bion
Wilfred Ruprecht Bion DSO (; 8 September 1897 – 8 November 1979) was an influential English psychoanalyst, who became president of the British Psychoanalytical Society from 1962 to 1965. Early life and military service Bion was born in Mathura, North-Western Provinces, India, and educated at Bishop's Stortford College in England.Malcolm Pines'Bion, Wilfred Ruprecht (1897–1979)' ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, September 2004; online edition, May 2007. . Retrieved 2008-09-10. After the outbreak of the First World War, he served in the Tank Corps as a tank commander in France, and was awarded both the Distinguished Service Order (DSO) (on 18 February 1918, for his actions at the Battle of Cambrai), and the Croix de Chevalier of the Légion d'honneur. He first entered the war zone on 26 June 1917, and was promoted to temporary lieutenant on 10 June 1918, and to acting captain on 22 March 1918, when he took command of a tank section, he r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanie Klein
Melanie Klein (née Reizes; 30 March 1882 – 22 September 1960) was an Austrian-British author and psychoanalyst known for her work in child analysis. She was the primary figure in the development of object relations theory. Klein suggested that pre-verbal existential anxiety in infancy catalyzed the formation of the unconscious, resulting in the unconscious splitting of the world into good and bad idealizations. In her theory, how the child resolves that split depends on the constitution of the child and the character of nurturing the child experiences; the quality of resolution can inform the presence, absence, and/or type of distresses a person experiences later in life. Life Melanie Klein was born into a Jewish family and spent most of her early life in Vienna. She was the fourth and final child of parents Moriz, a doctor, and Libussa Reizes. Educated at the Gymnasium, Klein planned to study medicine. Her family's loss of wealth caused her to change her plans. At the age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Psychoanalytical Society
The British Psychoanalytical Society was founded by the British neurologist Ernest Jones as the London Psychoanalytical Society on 30 October 1913. It is one of two organizations in Britain training psychoanalysts, the other being the British Psychoanalytic Association. The society has been home to a number of important psychoanalysts, including Wilfred Bion, Donald Winnicott, Anna Freud and Melanie Klein. Today it has over 400 members and is a member organisation of the International Psychoanalytical Association. Establishment and name Psychoanalysis was founded by Sigmund Freud, and much of the early work on Psychoanalysis was carried out in Freud's home city of Vienna and in central europe. However, in the early 1900's Freud began to spread his theories throughout the English speaking world. Around this time he established a relationship with Ernest Jones, a British neurosurgeon who had read his work in German and met Freud at the inaugural Psychoanalytical Congress in Sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Froebel College
Froebel College is one of the four constituent colleges of the University of Roehampton. History The college was founded as a women's teacher training college in 1892 by followers of Friedrich Fröbel. The Froebel Society had been formed in 1874 and in 1892 Julia Salis Schwabe led an initiative to found a college for training teachers. It was imperative that the trainee teachers should be allowed to practice whilst they were learning so a school/kindergarten was established in parallel. * Margaret Lowenfeld Margaret Frances Jane Lowenfeld (4 February 1890 – 2 February 1973) was a British pioneer of child psychology and play therapy, a medical researcher in paediatric medicine, and an author of several publications and academic papers on the study ... (1890–1973) was a pioneer in child psychology and psychotherapy References External links Froebel College, Roehampton UniversityRoehampton University University of Roehampton Teacher training colleges in the United Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esther Bick
Esther Bick, (1902–1983), born in Przemyśl, Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia, Poland (then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire), was a psychologist and child and adult psychoanalyst who, with Dr. John Bowlby, established the child and adolescent psychotherapy training program at the Tavistock and Portman NHS Foundation Trust, Tavistock Clinic, London, in 1948. Biography Estera Lifsa Wander was born the oldest daughter in an orthodox Jewish family in Poland. She studied in Vienna with Charlotte Bühler and completed her doctorate in 1935. After graduation, she married a medical student Philipp Bick (1904-?); the couple had fled Austria to Switzerland together after the ''Anschluss'', the annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in 1938. Because she could not get a work permit there, she went to England, without her husband, as a refugee. Most of her family that remained in Poland died later in Nazi concentration camps. She settled in Manchester, working in nurseries during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light , established = , endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019) , budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20) , chancellor = The Lord Patten of Barnes , vice_chancellor = Louise Richardson , students = 24,515 (2019) , undergrad = 11,955 , postgrad = 12,010 , other = 541 (2017) , city = Oxford , country = England , coordinates = , campus_type = University town , athletics_affiliations = Blue (university sport) , logo_size = 250px , website = , logo = University of Oxford.svg , colours = Oxford Blue , faculty = 6,995 (2020) , academic_affiliations = , The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |