|
University Of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the world's second-oldest university in continuous operation. It grew rapidly from 1167 when Henry II banned English students from attending the University of Paris. After disputes between students and Oxford townsfolk in 1209, some academics fled north-east to Cambridge where they established what became the University of Cambridge. The two English ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. Both are ranked among the most prestigious universities in the world. The university is made up of thirty-nine semi-autonomous constituent colleges, five permanent private halls, and a range of academic departments which are organised into four divisions. All the colleges are self-governing institutions within the university, each controlling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public University
A public university or public college is a university or college that is in state ownership, owned by the state or receives significant government spending, public funds through a national or subnational government, as opposed to a private university. Whether a national university is considered public varies from one country (or region) to another, largely depending on the specific education landscape. Africa Egypt In Egypt, Al-Azhar University was founded in 970 AD as a madrasa; it formally became a public university in 1961 and is one of the oldest institutions of higher education in the world. In the 20th century, Egypt opened many other public universities with government-subsidized tuition fees, including Cairo University in 1908, Alexandria University in 1912, Assiut University in 1928, Ain Shams University in 1957, Helwan University in 1959, Beni-Suef University in 1963, Zagazig University in 1974, Benha University in 1976, and Suez Canal University in 1989. Kenya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G5 (universities)
The golden triangle refers to the triangle formed by the university cities of Cambridge, London and Oxford in the southeast of England. The triangle is occasionally referred to as the Loxbridge triangle, a portmanteau of London and Oxbridge or, when limited to five members, the G5. The golden triangle universities are: * University of Oxford * University of Cambridge * University College London (UCL) * Imperial College London (ICL) * King's College London (KCL) * London School of Economics (LSE) The list of universities considered to be members of the golden triangle varies between sources, but typically comprises the University of Cambridge, the University of Oxford, Imperial College London, University College London, King's College London, and the London School of Economics. Some sources omit either or both of King's College London and the London School of Economics. while occasionally other universities are included, e.g. the London Business School and the London School o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colleges Of The University Of Oxford
The University of Oxford has thirty-nine colleges, and five permanent private halls (PPHs) of religious foundation. Colleges and PPHs are autonomous self-governing corporations within the university. These colleges are not only houses of residence, but have substantial responsibility for teaching undergraduate students. Generally tutorials (one of the main methods of teaching in Oxford) and classes are the responsibility of colleges, while lectures, examinations, laboratories, and the central library are run by the university. Students normally have most of their tutorials in their own college, but often have a couple of modules taught at other colleges or even at faculties and departments. Most colleges take both graduates and undergraduates, but several are for graduates only. Undergraduate and graduate students may name preferred colleges in their applications. For undergraduate students, an increasing number of departments practise reallocation to ensure that the ratios bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxbridge
Oxbridge is a portmanteau of Oxford and Cambridge, the two oldest, wealthiest, and most famous universities in the United Kingdom. The term is used to refer to them collectively, in contrast to other British universities, and more broadly to describe characteristics reminiscent of them, often with implications of superior social or intellectual status or elitism. Origins Although both universities were founded more than eight centuries ago, the term ''Oxbridge'' is relatively recent. In William Makepeace Thackeray's novel '' Pendennis'', published in 1850, the main character attends the fictional Boniface College, Oxbridge. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', this is the first recorded instance of the word. Virginia Woolf used it, citing Thackeray, in her 1929 essay '' A Room of One's Own''. The term was used in the '' Times Educational Supplement'' in 1957, and the following year in ''Universities Quarterly''. When expanded, the universities are almost always r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient University
The ancient universities are British and Irish medieval universities and early modern universities founded before the year 1600. Four of these are located in Scotland, two in England, and one in Ireland. The ancient universities in Britain and Ireland are amongst the oldest extant universities in the world. Foundation The surviving ancient universities in England, Scotland and Ireland are, in order of formation: These universities are often governed in a quite different fashion to more recent foundations. The ancient universities of Scotland also share several distinctive features and are governed by arrangements laid down by the ''Universities (Scotland) Acts''. In addition to these universities, some now-defunct institutions were founded during this period, including the University of Northampton (1261–1265), the university or college at Stamford, Lincolnshire (1331?–1335), the university or college at Fraserburgh, Aberdeenshire (1592–1605), and the college in Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Marty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
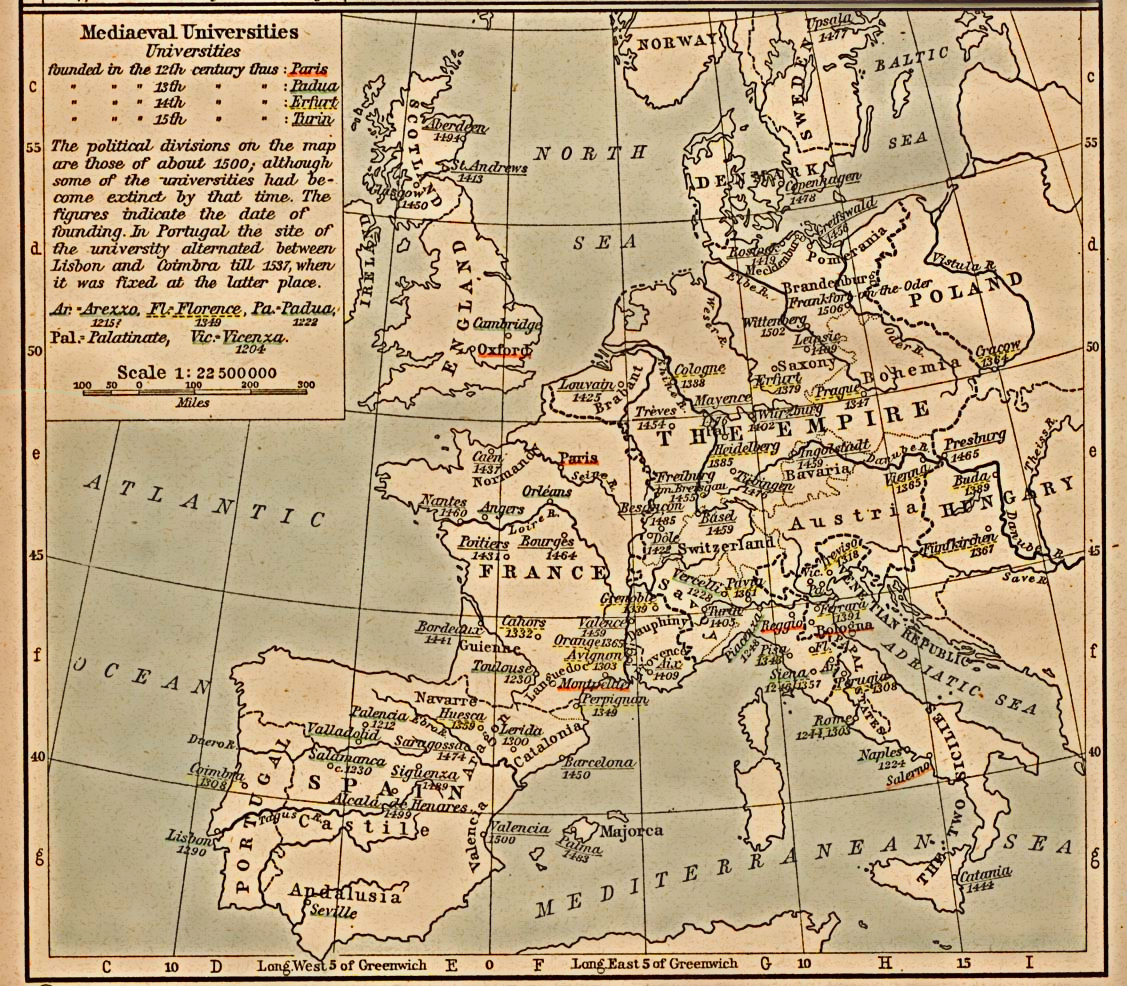
University Of Paris
The University of Paris (french: link=no, Université de Paris), Metonymy, metonymically known as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, active from 1150 to 1970, with the exception between 1793 and 1806 under the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated with the cathedral school of Notre Dame de Paris, it was considered the List of medieval universities, second-oldest university in Europe.Charles Homer Haskins, Haskins, C. H.: ''The Rise of Universities'', Henry Holt and Company, 1923, p. 292. Officially chartered in 1200 by King Philip II of France and recognised in 1215 by Pope Innocent III, it was later often nicknamed after its theological College of Sorbonne, in turn founded by Robert de Sorbon and chartered by List of French monarchs, French King Louis IX, Saint Louis around 1257. Internationally highly reputed for its academic performance in the humanities ever since the Middle Ages – notably in theology and philosophy – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin king of England. King Louis VII of France made him Duke of Normandy in 1150. Henry became Count of Anjou and Count of Maine, Maine upon the death of his father, Count Geoffrey V, in 1151. His marriage in 1152 to Eleanor of Aquitaine, former spouse of Louis VII, made him Duke of Aquitaine. He became Count of Nantes by treaty in 1158. Before he was 40, he controlled England; large parts of Wales; the eastern half of Ireland; and the western half of France, an area that was later called the Angevin Empire. At various times, Henry also partially controlled Scotland and the Duchy of Brittany. Henry became politically involved by the age of 14 in the efforts of his mother Empress Matilda, Matilda, daughter of Henry I of England, to the Anarchy, claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Oldest Universities In Continuous Operation
This article contains a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world. Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a university used by academic historians although it may have existed as a different kind of institution before that time. This definition limits the term "university" to institutions with distinctive structural and legal features that developed in Europe, and which make the university form different from other institutions of higher learning in the pre-modern world, even though these may sometimes now be referred to popularly as universities. Thus, to be included in the list below, the university must have been founded before 1500 in Europe or be the oldest university derived from the medieval European model in a country or region. It must also be still in operation, with institutional continuity retained throughout its history. So some early universities, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-speaking World
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language by number of speakers, and the third largest language by number of native speakers. England and the Scottish Lowlands, countries of the United Kingdom, are the birthplace of the English language, and the modern form of the language has been being spread around the world since the 17th century, first by the worldwide influence of England and later the United Kingdom, and then by that of the United States. Through all types of printed and electronic media of these countries, English has become the leading language of international discourse and the lingua franca in many regions and professional contexts such as science, navigation and law. The United Kingdom remains the largest English-speaking country in Europe. The United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collegiate University
A collegiate university is a university in which functions are divided between a central administration and a number of constituent colleges. Historically, the first collegiate university was the University of Paris and its first college was the Collège des Dix-Huit. The two principal forms are residential college universities, where the central university is responsible for teaching and colleges may deliver some teaching but are primarily residential communities, and federal universities where the central university has an administrative (and sometimes examining) role and the colleges may be residential but are primarily teaching institutions. The larger colleges or campuses of federal universities, such as University College London and University of California, Berkeley, may be effectively universities in their own right and often have their own student unions. For universities with residential colleges, the principal difference between these and non-collegiate halls of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)