|
Marktsackpfeife
The term „Marktsackpfeife“ (literally „market bagpipes“, also known as „German Pipes“, often abbreviated as MSP) commonly refers to a type of bagpipe which has been developed in East Germany at the beginning of 1980s for the specific purpose to be played at faires and markets as a modern interpretation of a certain type of Medieval bapipes. Depictions of such bagpipes are found in Medieval sources and are characterized by specific features like wide flaring bells atop the chanter and drones, apparent conical shape of the chanter and reportedly substantial volume of their sound. Since no actual chanters of this type of bagpipe have survived and/or have been recovered so far, the MSP has to be classified as a purely modern musical instrument having a historically informed exterior. MSP chanters typically use double reeds made of plastic or Arundo donax cane and drones usually work with single reeds made of same materials. Chanter bores are conical with a pronounced flare a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are based on the ratio 3:2.Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh edition, 2 vols. (Boston: McGraw-Hill). Vol. I: p. 56. . This ratio, also known as the "pure" perfect fifth, is chosen because it is one of the most consonant and easiest to tune by ear and because of importance attributed to the integer 3. As Novalis put it, "The musical proportions seem to me to be particularly correct natural proportions." Alternatively, it can be described as the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the generator is the ratio 3:2 (i.e., the untempered perfect fifth), which is ≈702 cents wide. The system dates to Ancient Mesopotamia; see . The system is named, and has been widely misattributed, to Ancient Greeks, notably Pythagoras (sixth century BC) by modern authors of music theory, while Ptolemy, and later Boethius, ascribed the divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltatio Mortis
Saltatio Mortis is a German medieval metal group. The Latin name means "dance of death". It is an allusion to the Danse Macabre, and a motto of the band is: "He who dances does not die." Members Current * Alea der Bescheidene - vocals, bagpipes, didgeridoo, guitar, Irish bouzouki, shawms * Falk Irmenfried von Hasen-Mümmelstein - bagpipes, vocals, hurdy-gurdy, shawms * El Silbador (since 2006) - bagpipes, shawms, smallpipes, uilleann pipes and other pipes * Bruder Frank (since 2006) - bass guitars, electric upright Chapman Stick, guitar * Till Promill (since 2012) - guitars * Jean Mechant der Tambour (since 2009) - drums, piano, guitar, vocals * Luzi das L (since 2011) - pipes, shawms, flutes Past * Lasterbalk der Lästerliche (up to 2021) - drums, davul and other percussion * Dominor der Filigrane (2000 to 2009) - guitars, German bagpipes, shawms * Die Fackel (2000 to 2006) - bass guitars, mandola, harp, German bagpipes, shawms * Ungemach der Missgestimmte (2000 to 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Extremo
In Extremo (Latin for ''At the Edge''; abbreviated InEx or IE) is a German Medieval metal band originating from Berlin. The band's musical style combines metal with Medieval traditional songs, blending the sound of the standard rock/metal instruments with historical instruments (such as bagpipes, harp, hurdy-gurdy and shawm). Versions of well-known traditional/Medieval ballads make up the main part of their repertoire, but the band has written an increasing share of original material in recent years. Their own material is written in German, whilst the traditional songs and cover songs are in a variety of languages. History In Extremo began as two projects: a nameless, purely Medieval band, and a rock band. They became known at that time through frequent appearances at Medieval market meetings, at which they performed their acoustic pieces and sold CDs of their renditions of traditional songs. On 11 April 1995, during the recording for that year's season, Michael Rhein (alias "D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvus Corax (band)
Corvus Corax is a German band known for playing neo-Medieval music using authentic instruments. Their name is the Latin name for the common raven. The band was formed in 1989 by Castus Rabensang, Wim (Venustus) and Meister Selbfried ("Master Selfpeace") in East Germany. The band often uses bagpipes as the solo instrument; their live performances attract attention with the bizarre look of the musicians being reminiscent of ancient Greek myths: half-naked, dressed in unusual clothes, wearing primitive tribal decorations, often tattooed. Today the band consists of seven members: Castus Rabensang ("Castus Ravensong"), Xandru, Norri (formerly known as Harmann der Drescher), Hatz ("hunt"), Vit and Victorius. In May 2005 Meister Selbfried, one of the Corvus Corax founders and the researcher of medieval music, decided to cease his active musicianship and to dedicate himself mostly to managing Corvus Corax's own label Pica Records. His place in the line-up was taken by Jordon Finus in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Medieval Music
Neo-Medieval music is a modern popular music characterized by elements of Medieval music and early music in general. Music styles within neo-Medieval music vary from authentic performance interpretations of Medieval music (understood as Classical music) to crossover genres that blend Medieval instruments, such as bagpipe, shawm and hurdy-gurdy with electronic music and rock. In many cases, it is more or less overlapping with styles such as folk rock, British folk rock and neofolk. Bands specializing in neo-Medieval music are particularly plentiful in Germany, although the genre also enjoys some popularity in North America, the Czech Republic, the Netherlands, France, United Kingdom, Italy and the Scandinavian countries. History It is difficult to point to the exact origins of neo-Medieval music. One could argue that all Medieval-sounding tunes written after the Middle Ages are in some way neo-Medieval music; this definition would include music from as early as the Renaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingering (music)
In music, fingering, or on stringed instruments sometimes also called stopping, is the choice of which fingers and hand positions to use when playing certain musical instruments. Fingering typically changes throughout a piece; the challenge of choosing good fingering for a piece is to make the hand movements as comfortable as possible without changing hand position too often. A fingering can be the result of the working process of the composer, who puts it into the manuscript, an editor, who adds it into the printed score, or the performer, who puts his or her own fingering in the score or in performance. A substitute fingering is an alternative to the indicated fingering, not to be confused with finger substitution. Depending on the instrument, not all the fingers may be used. For example, saxophonists do not use the right thumb and string instruments (usually) only use the fingers. Instruments Brass instruments Fingering applies to the rotary and piston valves employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pitch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
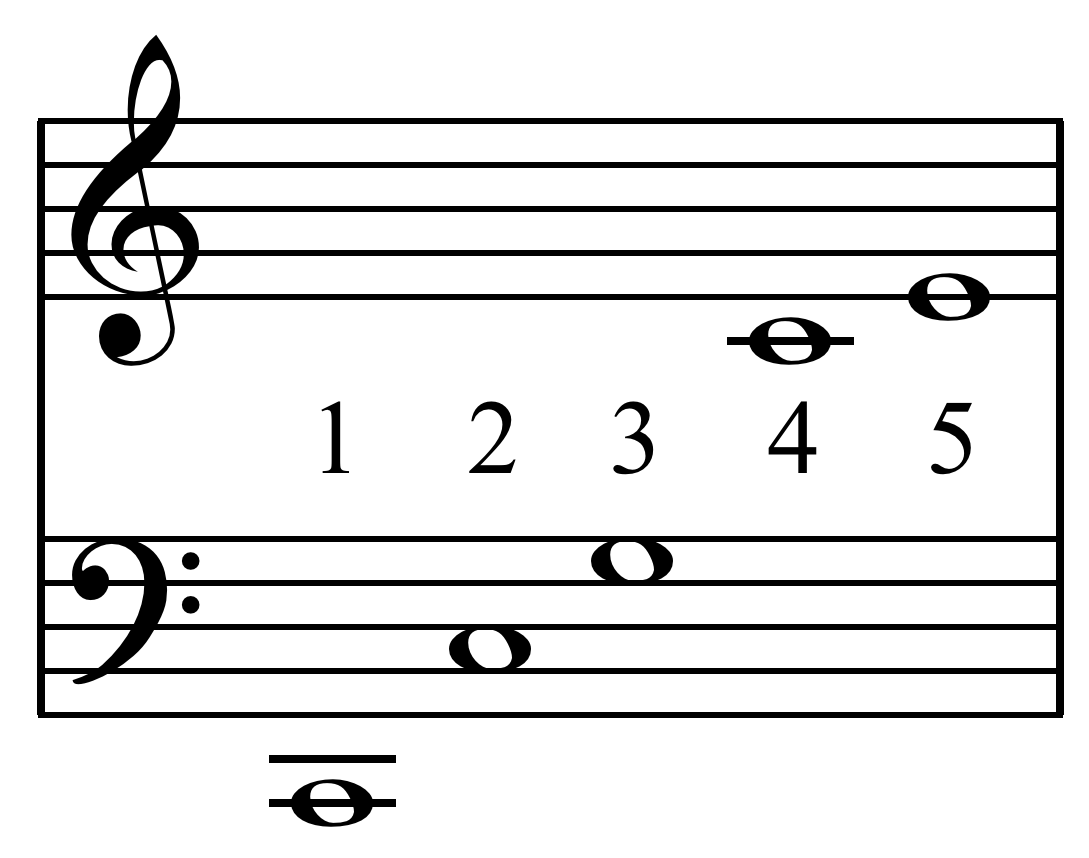
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals Interval may refer to: Mathematics and physics * Interval (mathematics), a range of numbers ** Partially ordered set#Intervals, its generalization from numbers to arbitrary partially ordered sets * A statistical level of measurement * Interval e ... as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of Frequency, frequencies. An interval (music), interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorian Mode
Dorian mode or Doric mode can refer to three very different but interrelated subjects: one of the Ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' (characteristic melodic behaviour, or the scale structure associated with it); one of the medieval musical modes; or—most commonly—one of the modern modal diatonic scales, corresponding to the piano keyboard's white notes from D to D, or any transposition of itself. : Greek Dorian mode The Dorian mode (properly ''harmonia'' or ''tonos'') is named after the Dorian Greeks. Applied to a whole octave, the Dorian octave species was built upon two tetrachords (four-note segments) separated by a whole tone, running from the ''hypate meson'' to the ''nete diezeugmenon''. In the enharmonic genus, the intervals in each tetrachord are quarter tone–quarter tone–major third. : In the chromatic genus, they are semitone–semitone–minor third. : In the diatonic genus, they are semitone–tone–tone. : In the diatonic genus, the sequence over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |