|
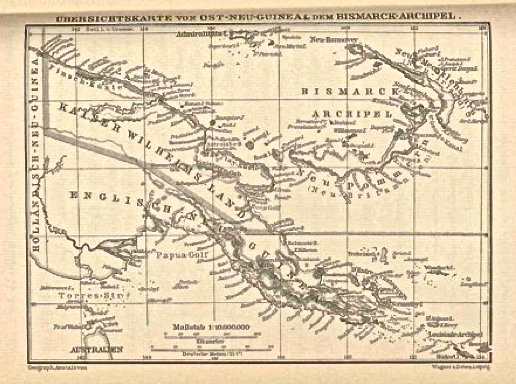
Markham Valley
The Markham Valley is a geographical area in Papua New Guinea. The name "Markham" commemorates Sir Clements Markham, Secretary of the British Royal Geographical Society - Captain John Moresby of the Royal Navy named the Markham River after Sir Clements in the course of his voyage of exploration in HMS Basilisk (1848), HMS ''Basilisk'' in 1873. The valley contains two districts of Morobe Province: Huon District, Huon Gulf district on the east and Markham District, Markham district on the west. The inhabitants of the valley are of Oceanic (Austronesian) descent and live in large villages under a chieftain political system. The valley is described as "Flatter than a pancake for miles and miles in all directions, until it runs into the mountains that surround it on three sides" and "always hot, and usually bone dry". The Highlands Highway runs through the valley. The Markham River runs through the valley. According to one visitor, about once a year, the local Papua New Guineans burn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chieftain
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom. Tribe The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia. Tribal societies are sometimes categorized as an intermediate stage between the band society of the Paleolithic stage and civilization with centralized, super-regional government based in Cities of the Ancient Near East, cities. Anthropologist Elman Service distinguishes two stages of tribal societies: simple societies organized by limited instances of social rank and prestige, and more stratified society, stratified societies led by chieftains or tribal kings (chiefdoms). Stratified tribal societies led by tribal kings are thought to have flourished from the Neolithic stage into the Iron Age, albeit in competition with Urban area, urban civilisations and empires beginning in the Bronze Age. In the case of tribal societies of indigenous peoples existing within larger colonial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markham Languages
The Markham languages form a family of the Huon Gulf languages. It consists of a dozen languages spoken in the Ramu Valley, Markham Valley and associated valley systems in the lowlands of the Madang and Morobe Provinces of Papua New Guinea. Unlike almost other Western Oceanic languages of New Guinea, which are spoken exclusively in coastal areas, many Markham languages are spoken in the mountainous interior of Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea, where they are in heavy contact with Trans-New Guinea languages. Although the Markham languages are Austronesian, they have had much contact with neighboring Papuan languages. A phonological reconstruction of Proto-Markham is presented in Holzknecht (1989) and is summarized below. Languages Labu (= Hapa) ;Lower Markham: Aribwaung (= Aribwaungg, Yalu), Aribwatsa† (= Lae, Lahe), Musom, Nafi (= Sirak), Duwet (= Guwot, Waing), Wampar, Silisili (Middle Watut), Maralango (South Watut), Dangal (South Watut) ;Upper Markham: Adzera ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1993 Finisterre Earthquakes
The 1993 Finisterre Range earthquakes occurred in October 1993, beneath the Finisterre Range, north of Markham Valley in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. The earthquake sequence began on October 13 with a 6.9 mainshock, followed by 6.5 and 6.7 mainshocks. The complex earthquake sequence seriously damaged many villages in the rural Eastern Papua New Guinea region, generating landslides and killing at least 60 people. Tectonic setting Papua New Guinea is situated in a region where the Pacific, Australian, Caroline and several microplates are converging. At the Huon Peninsula, the Woodlark Plate is moving north, converging beneath the South Bismarck Plate along the Markham Valley. The tectonic motion forms a complex zone of subduction and continental collision zones which affect the region. Due to the location at a major plate boundary zone, Papua New Guinea is struck by earthquakes and tsunamis frequently and is one of the world's most seismically active regions. The Finiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landslide Dam
A landslide dam or barrier lake is the natural damming of a river by some kind of landslide, such as a debris flow, rock avalanche or volcanic eruption. If the damming landslide is caused by an earthquake, it may also be called a quake lake. Some landslide dams are as high as the largest existing artificial dam.Robert B. Jansen (1988) "Advanced Dam Engineering for Design, Construction, and Rehabilitation", Causes The major causes for landslide dams investigated by 1986 are landslides from excessive precipitation and earthquakes, which account for 84%. Volcanic eruptions account for a further 7% of dams. Other causes of landslides account for the remaining 9%. Consequences The water impounded by a landslide dam may create a dam reservoir (lake) that may last for a short time, to several thousand years. Because of their rather loose nature and absence of controlled spillway, landslide dams frequently fail catastrophically and lead to downstream flooding, often with high casualti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madang
Madang (old German name: ''Friedrich-Wilhelmshafen'') is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 (in 2005) on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century. History Russian biologist Nicholai Miklukho-Maklai was probably the first European to visit the area. In 1871 he stayed at Astrolabe Bay south of present-day Madang for 15 months. He had a good relationship with the local communities before leaving, suffering from malaria. In April 1884 an expedition by the German New Guinea Company led by Otto Finsch and Eduard Dallmann arrived and named the landing point "Friedrich Wilhelmshafen"; however, they felt that the area was unsuitable for a settlement. A subsequent survey in 1888 mentioned good soil conditions that would make a coffee plantation possible. In the summer of 1891 a station was built and by September 1892 was the seat of the provincial administration; however, the Imperial Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highlands Highway
The Highlands Highway, sometimes known as the Okuk Highway, is the main land highway in Papua New Guinea. It connects several major cities and is vital for the movement of people and goods between the populous Highlands region and the coast. For most of its length the Highlands Highway is no more than a single carriageway two-lane road which is often hindered by potholes and land slips. It is also notorious, particularly in the Highlands region, for being the place of numerous armed hold-ups and robberies committed by local bandits called raskols. Description The highway begins in Lae and travels through the Markham Valley and the province of Morobe. From the Markham Valley the Highlands Highway turns left and climbs up and over the approximately 1,500 metre high Kassam Pass and into the Eastern Highlands Province. It passes over the wall of Yonki Dam and then travels through the towns of Kainantu and Henganofi to the provincial capital, Goroka. From here it travels up an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markham District . The population of the district was 62,495 at the 2011 census.Markham District is a district of the Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Kaiapit Kaiapit is a town in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. at statoids.com References Districts of Papua New Guinea Morobe Province {{MorobeProvince-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clements Markham
Sir Clements Robert Markham (20 July 1830 – 30 January 1916) was an English geographer, explorer and writer. He was secretary of the Royal Geographical Society (RGS) between 1863 and 1888, and later served as the Society's president for a further 12 years. In the latter capacity he was mainly responsible for organising the British National Antarctic Expedition of 1901–1904, and for launching the polar career of Robert Falcon Scott. Markham began his career as a Royal Navy cadet and midshipman, during which time he went to the Arctic with in one of the many searches for Franklin's lost expedition. Later, Markham served as a geographer to the India Office, and was responsible for the collection of cinchona plants from their native Peruvian forests, and their transplantation in India. By this means, the Indian government acquired a home source from which quinine could be extracted. Markham also served as geographer to Sir Robert Napier, 1st Baron Napier of Magdala, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huon District
Huon District (alternatively Huon Gulf District) is a district of the Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Salamaua Salamaua () was a small town situated on the northeastern coastline of Papua New Guinea, in Salamaua Rural LLG, Morobe province. The settlement was built on a minor isthmus between the coast with mountains on the inland side and a headland. The c .... The population of the district was 77,564 at the 2011 census. at statoids.com References Districts of Papua New Guinea Morobe Province {{MorobeProvince-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morobe Province
Morobe Province is a province on the northern coast of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital and largest city is Lae. The province covers 33,705 km2, with a population of 674,810 (2011 census), and since the division of Southern Highlands Province in May 2012 it is the most populous province. It includes the Huon Peninsula, the Markham River, and delta, and coastal territories along the Huon Gulf. The province has nine administrative districts. At least 101 languages are spoken, including Kâte and Yabem language. English language, English and Tok Pisin are common languages in the urban areas, and in some areas pidgin forms of German are mixed with the native language. History Nomenclature The Morobe Province takes its name from former German administration center of ''Morobe'' southeast of the Lae. Under German administration, Morobe (meaning post) was named Adolfhafen for the German Deutsch Neuguinea-Kompagnie's Adolf von Hansemann and German word ''hafen'' (''heɪfən' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)