|
Maritime Central Airways
Maritime Central Airways was a predecessor of Eastern Provincial Airways and was founded by Prince Edward Island native Carl Burke and Josiah Anderson in 1941 out of Moncton, New Brunswick and provided standard passenger, cargo, and charter flights throughout the Maritimes and Newfoundland and Labrador - at the time not yet part of Canada. This early fleet consisted of a Boeing 247 and a Fairchild 24. Wartime operations MCA participated in the Second World War effort with various projects, including a search and rescue mission for the U.S. government in Greenland in 1942 that caused the loss of one Barkley-Grow T8P-1. This charter was typical of the mixed-bag operations that most Canadian carriers, including MCA, survived on: in addition to the scheduled passenger runs we are familiar with today. Early postwar history By 1946, the fleet had grown to include a Douglas DC-3, de Havilland Rapide, Lockheed Model 10 Electra, Cessna Crane, and PBY Canso. In addition to passenger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II. It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper version of the Douglas DC-2. It is a low-wing metal monoplane with conventional landing gear, powered by two radial piston engines of . (Although most DC-3s flying today use Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp engines, many DC-3s built for civil service originally had the Wright R-1820 Cyclone.) The DC-3 has a cruising speed of , a capacity of 21 to 32 passengers or 6,000 lbs (2,700 kg) of cargo, and a range of , and can operate from short runways. The DC-3 had many exceptional qualities compared to previous aircraft. It was fast, had a good range, was more reliable, and carried passengers in greater comfort. Before the war, it pioneered many air travel routes. It was able to cross the continental United States from New York to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Central Airways Flight 315
Maritime Central Airways Flight 315 was an international charter flight from London, England to Toronto, Ontario, Canada, with refueling stops in Reykjavík, Iceland, and Goose Bay, Labrador. On 11 August 1957, the aircraft operating this flight, a Douglas DC-4, crashed in bad weather west of Issoudun, Quebec, killing all 79 people on board. At the time, it was the deadliest aviation accident in Canadian history, and as of 2020 is still the fifth-deadliest. It is also the second-deadliest crash involving a DC-4, behind another in 1967. Accident Flight 315 departed London Heathrow International Airport for Reykjavík at 21:48 GMT. Then, after stopping in Reykjavík for 66 minutes to refuel, it proceeded on the next leg of its route to Canada. After entering Canadian airspace, the flight crew radioed that they wished to bypass Goose Bay and proceed to Montreal instead. At 18:10, Quebec Radio Range Station relayed a message to the aircraft, requesting it to con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas DC-6
The Douglas DC-6 is a piston-powered airliner and cargo aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company from 1946 to 1958. Originally intended as a military transport near the end of World War II, it was reworked after the war to compete with the Lockheed Constellation in the long-range commercial transport market. More than 700 were built and many still fly in cargo, military, and wildfire control roles. The DC-6 was known as the C-118 Liftmaster in United States Air Force service and as the R6D in United States Navy service prior to 1962, after which all U.S. Navy variants were also designated as the C-118. Design and development The United States Army Air Forces commissioned the DC-6 project as the XC-112 in 1944. The Army Air Forces wanted a lengthened, pressurized version of the DC-4-based C-54 Skymaster transport with more powerful engines. By the time the prototype XC-112A flew on 15 February 1946, the war was over, the USAAF had rescinded its requirement, and the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas DC-4
The Douglas DC-4 is an American four-engined (piston), propeller-driven airliner developed by the Douglas Aircraft Company. Military versions of the plane, the C-54 and R5D, served during World War II, in the Berlin Airlift and into the 1960s. From 1945, many civil airlines operated the DC-4 worldwide. Design and development Following proving flights by United Airlines of the DC-4E, it became obvious that the 52-seat airliner was too inefficient and unreliable to operate economically and the partner airlines, American Airlines, Eastern, Pan American, Trans World and United, recommended a lengthy list of changes to the design. Douglas took the new requirements and produced an entirely new, much smaller design, the DC-4A, with a simpler, still unpressurized fuselage, Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp engines, and a single fin and rudder. A tricycle landing gear was retained. With the entry of the United States into World War II, in December 1941, the United States Army Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro York
The Avro York was a British transport aircraft developed by Avro during the Second World War. The design was derived from the Avro Lancaster heavy bomber, several sections of the York and Lancaster being identical. Due to the importance of Lancaster production, York output proceeded slowly until 1944, after which a higher priority was placed upon transport aircraft. The York saw service in military and civilian roles with various operators between 1943 and 1964. In civilian service, British South American Airways (BSAA) and British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) were the largest users of the type. In military service, large numbers of Yorks were used for air-supply missions during the Berlin Blockade 1948–49. A number of the type were used as air transports of heads of state and government; VIPs who flew on Yorks included British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, French General Charles de Gaulle, Indian Governor-General Lord Mountbatten and South African Prime M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Viscount
The Vickers Viscount is a British medium-range turboprop airliner first flown in 1948 by Vickers-Armstrongs. A design requirement from the Brabazon Committee, it entered service in 1953 and was the first turboprop-powered airliner. The Viscount was well received by the public for its cabin conditions, which included pressurisation, reductions in vibration and noise, and panoramic windows. It became one of the most successful and profitable of the first post-war transport aircraft; 445 Viscounts were built for a range of international customers, including in North America. Development Origins The Viscount was a response to the 1943 Brabazon Committee's proposed Type II design for a post-war small medium-range pressurised aircraft to fly less-travelled routes, carrying 24 passengers up to 1,750 mi (2,816 km) at 200 mph (320 km/h).Cacutt 1989, pp. 323–333. During discussions between the committee and Vickers' chief designer, Rex Pierson, Vickers advoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
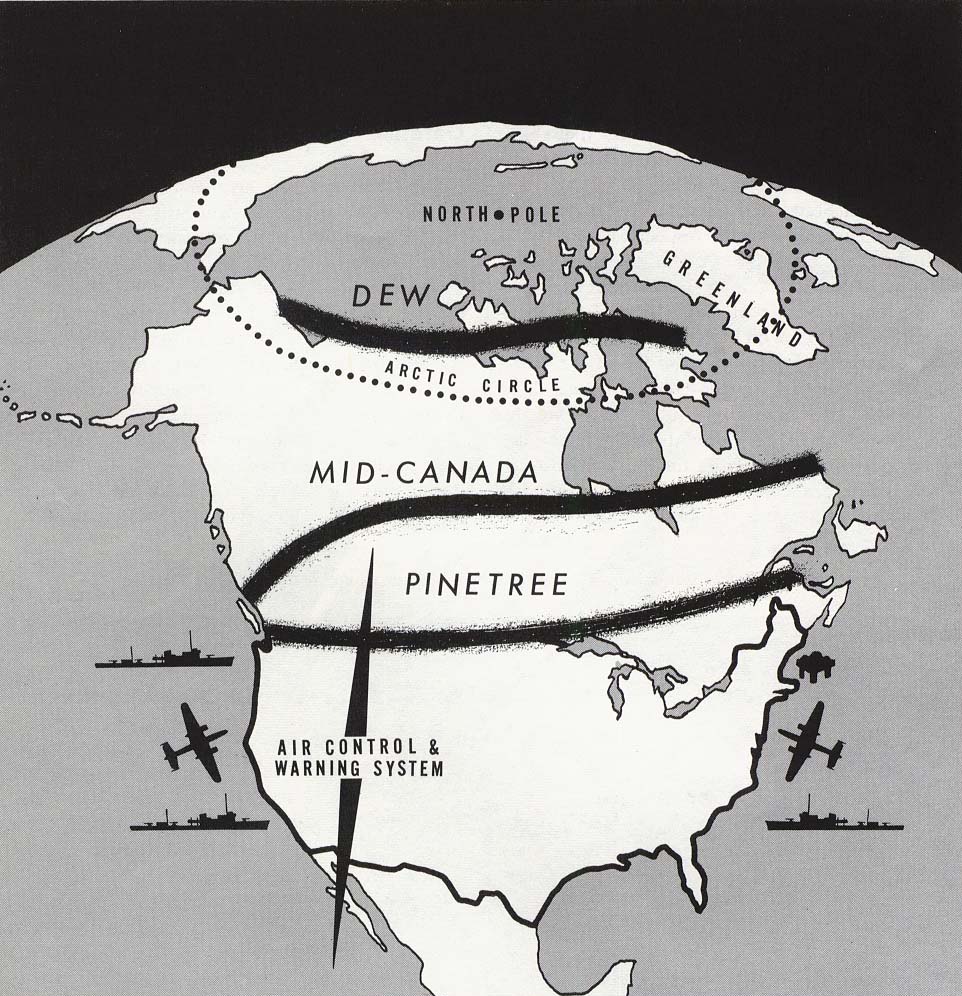
Distant Early Warning Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see Project Stretchout and Project Bluegrass), in addition to the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. It was set up to detect incoming bombers of the Soviet Union during the Cold War, and provide early warning of any sea-and-land invasion. The DEW Line was the northernmost and most capable of three radar lines in Canada and Alaska. The first of these was the joint Canadian-United States Pinetree Line, which ran from Newfoundland to Vancouver Island just north of the Canada–United States border, but even while it was being built there were concerns that it would not provide enough warning time to launch an effective counterattack. The Mid-Canada Line (MCL) was proposed as an inexpensive solution using bistatic radar. This provided a "t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PBY Catalina
The Consolidated PBY Catalina is a flying boat and amphibious aircraft that was produced in the 1930s and 1940s. In Canadian service it was known as the Canso. It was one of the most widely used seaplanes of World War II. Catalinas served with every branch of the United States Armed Forces and in the air forces and navies of many other nations. The last military PBYs served until the 1980s. As of 2021, 86 years after its first flight, the aircraft continues to fly as a waterbomber (or airtanker) in aerial firefighting operations in some parts of the world. None remain in military service. Design and development Background The PBY was originally designed to be a patrol bomber, an aircraft with a long operational range intended to locate and attack enemy transport ships at sea in order to disrupt enemy supply lines. With a mind to a potential conflict in the Pacific Ocean, where troops would require resupply over great distances, the U.S. Navy in the 1930s invested mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_5.jpg)