|
Marinids
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) around Gibraltar. It was named after the Banu Marin (, Berber: ''Ayt Mrin''), a Zenata Berber tribe. The sultanate was ruled by the Marinid dynasty ( ar, المرينيون ), founded by Abd al-Haqq I.C.E. Bosworth, ''The New Islamic Dynasties'', (Columbia University Press, 1996), 41-42. In 1244, after being at their service for several years, the Marinids overthrew the Almohads which had controlled Morocco. At the height of their power in the mid-14th century, during the reigns of Abu al-Hasan and his son Abu Inan, the Marinid dynasty briefly held sway over most of the Maghreb including large parts of modern-day Algeria and Tunisia. The Marinids supported the Emirate of Granada in al-Andalus in the 13th and 14th centuries and made an att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marinid Emblem Of Morocco
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) around Gibraltar. It was named after the Banu Marin (, Berber: ''Ayt Mrin''), a Zenata Berber tribe. The sultanate was ruled by the Marinid dynasty ( ar, المرينيون ), founded by Abd al-Haqq I.C.E. Bosworth, ''The New Islamic Dynasties'', (Columbia University Press, 1996), 41-42. In 1244, after being at their service for several years, the Marinids overthrew the Almohads which had controlled Morocco. At the height of their power in the mid-14th century, during the reigns of Abu al-Hasan and his son Abu Inan, the Marinid dynasty briefly held sway over most of the Maghreb including large parts of modern-day Algeria and Tunisia. The Marinids supported the Emirate of Granada in al-Andalus in the 13th and 14th centuries and made an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenata
The Zenata (Berber language: Iznaten) are a group of Amazigh (Berber) tribes, historically one of the largest Berber confederations along with the Sanhaja and Masmuda. Their lifestyle was either nomadic or semi-nomadic. Etymology ''Iznaten (ⵉⵣⵏⴰⵜⵏ)'' come from his singular ''Aznat (ⴰⵣⵏⴰⵜ)''. ''Aznat'' is composed by ''Azn'' ''(ⴰⵣⵏ)'' and ''At (ⴰⵜ)''. In Berber language, ''Azn'' means ''Send'' and ''At'' means ''Sons'' in zenati berber. For the word ''Sons'', ''At'' in berber is only used in zenati berber. In the others berber dialects, the word for ''Sons'' is ''Ayt (ⴰⵢⵜ)'' or ''Ag (ⴰⴳ)''. Society The 14th-century historiographer Ibn Khaldun reports that the Zenata were divided into three large tribes: Jarawa, Maghrawa, and Banu Ifran. Formerly occupying a large portion of the Maghreb (Tamazgha), they were displaced to the south and west in conflicts with the more powerful Kutama and Houara. The Zenata adopted Islam early, in the 7t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Haqq I
Abu Muhammad Abd al-Haqq I (died 1217) was the first leader of the Marinid dynasty of the Maghreb. - The History Files (African Kingdoms) History The "Banu Marin" (Marinids) were a semi-nomadic Berber tribe who in the 12th century were practising in the region between and the |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The term is used by modern historians for the former Islamic states in modern Spain and Portugal. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula and a part of present-day southern France, Septimania (8th century). For nearly a hundred years, from the 9th century to the 10th, al-Andalus extended its presence from Fraxinetum into the Alps with a series of organized raids and chronic banditry. The name describes the different Arab and Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. These boundaries changed constantly as the Christian Reconquista progressed,"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fes, Morocco
Fez or Fes (; ar, فاس, fās; zgh, ⴼⵉⵣⴰⵣ, fizaz; french: Fès) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fès-Meknès administrative region. It is the second largest city in Morocco, with a population of 1.11 million according to the 2014 census. Located to the north west of the Atlas Mountains, Fez is linked to several important cities of different regions; it is from Tangier to the northwest, from Casablanca, from Rabat to the west, and from Marrakesh to the southwest. It is surrounded by hills and the old city is centered around the Fez River (''Oued Fes'') flowing from west to east. Fez was founded under Idrisid rule during the 8th-9th centuries CE. It initially consisted of two autonomous and competing settlements. Successive waves of mainly Arab immigrants from Ifriqiya (Tunisia) and al-Andalus (Spain/Portugal) in the early 9th century gave the nascent city its Arab character. After the downfall of the Idrisid dynasty, other empires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-Hasan Ali Ibn Othman
Abu Al-Hasan 'Ali ibn 'Othman (c. 1297 – 24 May 1351), () was a sultan of the Marinid dynasty who reigned in Morocco between 1331 and 1348. In 1333 he captured Gibraltar from the Castilians, although a later attempt to take Tarifa in 1339 ended in fiasco. In North Africa he extended his rule over Tlemcen and Hafsid Ifriqiya, which together covered the north of what is now Algeria and Tunisia. Under him the Marinid realms in the Maghreb briefly covered an area that rivaled that of the preceding Almohad Caliphate. However, he was forced to retreat due to a revolt of the Arab tribes, was shipwrecked, and lost many of his supporters. His son Abu Inan Faris seized power in Fez. Abu Al-Hasan died in exile in the High Atlas mountains. Early years Abu al-Hassan was the son of Marinid ruler Abu Sa'id Uthman II and an Abyssinian mother. He had a dark complexion, and was known as the 'Black Sultan' of Morocco. He succeeded his father Abu Sa'id Uthman II in 1331. Abu al-Hassan married Fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg , caption = The Berber ethnic flag , population = 36 million , region1 = Morocco , pop1 = 14 million to 18 million , region2 = Algeria , pop2 = 9 million to ~13 million , region3 = Mauritania , pop3 = 2.9 million , region4 = Niger , pop4 = 2.6 million, Niger: 11% of 23.6 million , region5 = France , pop5 = 2 million , region6 = Mali , pop6 = 850,000 , region7 = Libya , pop7 = 600,000 , region8 = Belgium , pop8 = 500,000 (including descendants) , region9 = Netherlands , pop9 = 467,455 (including descendants) , region10 = Burkina Faso , pop10 = 406,271, Burkina Faso: 1.9% of 21.4 million , region11 = Egypt , pop11 = 23,000 or 1,826,580 , region12 = Tunisia , pop12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Debdou
The Principality of Debdou was an autonomous hereditary viceroyalty that existed in eastern Morocco from 1430 to 1563, with its capital at Debdou. It was governed by the Ouartajin, a dynasty of Berber descent, related to the Marinids and the Wattasids.Louis Massignon, ''Le Maroc dans les premières années du XVIe siècle : Tableau géographique d'après Léon L'Africain'', in: Mémoires de la Société Historique Algérienne I, Éd. Adolphe Jourdan, 1906, p.266 History The Principality of Debdou was first established in 1430 as a governorate of Morocco, then ruled by the Marinid dynasty. By the second half of the 15th century, the Ouartajin gained more autonomy towards Fez as Marinids lost their prestige and most of their power to Wattasid viziers. The principality became fully autonomous when Muhammad ibn Ahmed was appointed viceroy of Debdou by Wattasid sultan Muhammad ibn Yahya (r. 1472-1504). During the last years of the reign of Muhammad II, the Principality of Debdou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattasid Dynasty
The Wattasid dynasty ( ber, Iweṭṭasen; ar, الوطاسيون, ''al-waṭṭāsīyūn'') was a ruling dynasty of Morocco. Like the Marinid dynasty, its rulers were of Zenata Berber descent. The two families were related, and the Marinids recruited many viziers from the Wattasids. These viziers assumed the powers of the Sultans, seizing control of the Marinid dynasty's realm when the last Marinid, Abu Muhammad Abd al-Haqq, who had massacred many of the Wattasids in 1459, was murdered during a popular revolt in Fez in 1465. Abu Abd Allah al-Sheikh Muhammad ibn Yahya was the first Sultan of the Wattasid Dynasty. He controlled only the northern part of Morocco, the south being divided into several principalities. The Wattasids were finally supplanted in 1554, after the Battle of Tadla, by the Saadi dynasty princes of Tagmadert who had ruled all of southern Morocco since 1511. Overview Morocco endured a prolonged multifaceted crisis in the 15th and early 16th centuries brought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almohad Caliphate
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the Tawhid, unity of God) was a North African Berbers, Berber Muslim empire founded in the 12th century. At its height, it controlled much of the Iberian Peninsula (Al Andalus) and North Africa (the Maghreb). The Almohad movement was founded by Ibn Tumart among the Berber Masmuda tribes, but the Almohad caliphate and its ruling dynasty were founded after his death by Abd al-Mu'min, Abd al-Mu'min al-Gumi. Around 1120, Ibn Tumart first established a Berber state in Tinmel in the Atlas Mountains. Under Abd al-Mu'min (r. 1130–1163) they succeeded in overthrowing the ruling Almoravid dynasty governing Morocco in 1147, when he conquered Marrakesh and declared himself caliph. They then extended their power over all of the Maghreb by 1159. Al-Andalus soon followed, and all of Muslim Iberia was under Almohad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Inan Faris
Abu Inan Faris (1329 – 10 January 1358) ( ar, أبو عنان فارس بن علي) was a Marinid ruler of Morocco. He succeeded his father Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn Othman in 1348. He extended his rule over Tlemcen and Ifriqiya, which covered the north of what is now Algeria and Tunisia, but was forced to retreat due to a revolt of Arab tribes there. He died strangled by his vizier in 1358. History Abu Inan's father Abu'l Hasan had taken the town of Tlemcen in 1337. In 1347 Abu'l Hasan annexed Ifriqiya, briefly reuniting the Maghrib territories as they had been under the Almohads. However, Abu'l Hasan went too far in attempting to impose more authority over the Arab tribes, who revolted and in April 1348 defeated his army near Kairouan. Abu Inan Faris, who had been serving as governor of Tlemcen, returned to Fez and declared that he was sultan. Tlemcen and the central Maghreb revolted. Abu Inan took the title of ''Amir al-Mu'minin'' ("commander of the believers"). Abu'l Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
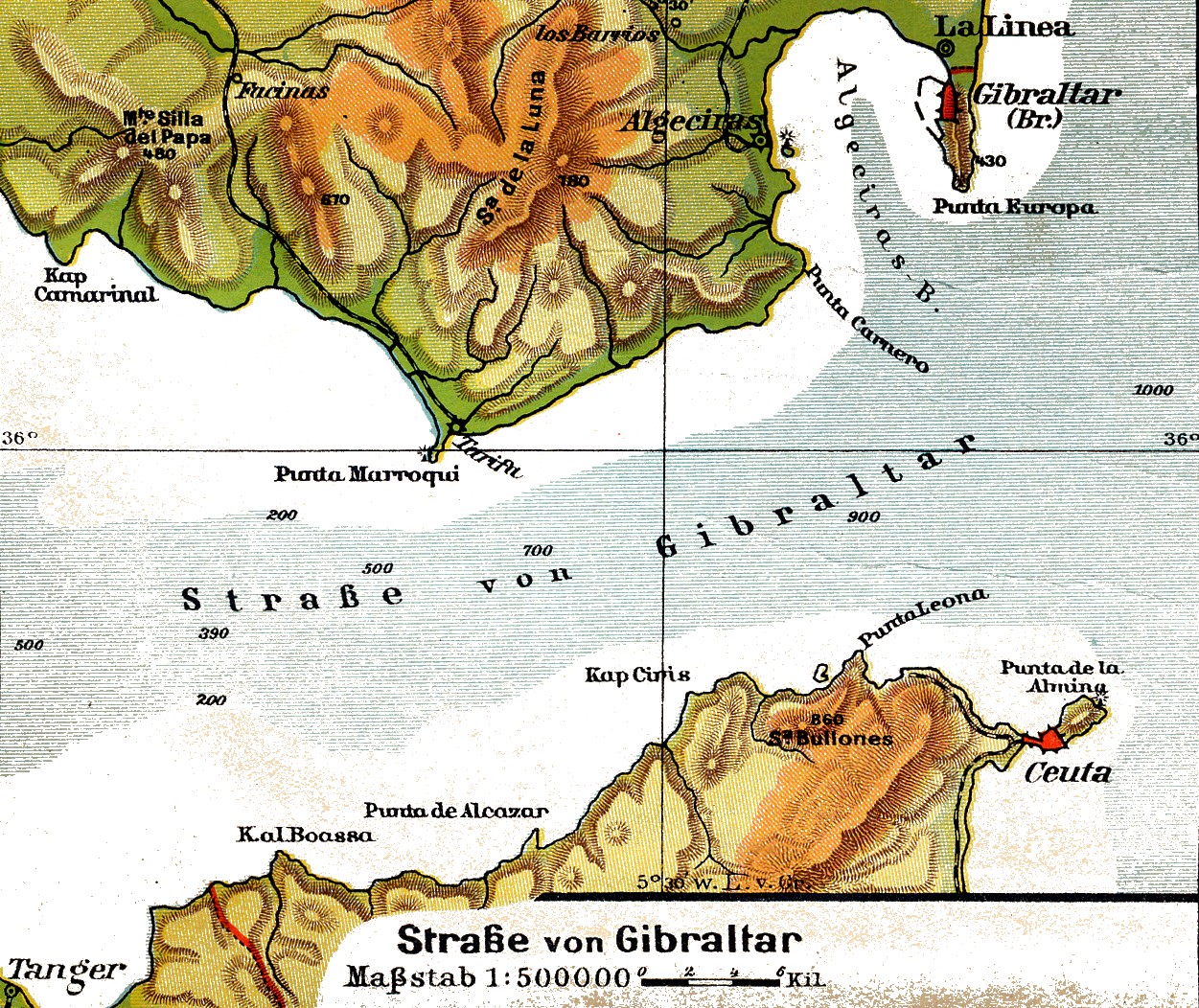
Gibraltar
) , anthem = " God Save the King" , song = " Gibraltar Anthem" , image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg , map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe , map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green , mapsize = , image_map2 = Gibraltar map-en-edit2.svg , map_alt2 = Map of Gibraltar , map_caption2 = Map of Gibraltar , mapsize2 = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = British capture , established_date = 4 August 1704 , established_title2 = , established_date2 = 11 April 1713 , established_title3 = National Day , established_date3 = 10 September 1967 , established_title4 = Accession to EEC , established_date4 = 1 January 1973 , established_title5 = Withdrawal from the EU , established_date5 = 31 January 2020 , official_languages = English , languages_type = Spoken languages , languages = , capital = Westside, Gibraltar (de facto) , coordinates = , largest_settlement_type = largest district , l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |