|
Marie-Angélique Memmie Le Blanc
Marie-Angélique Memmie Le Blanc (1712 in Wisconsin?, French Louisiana – 15 December 1775 in Paris, France) was a famous feral child of the 18th century in France who was known as The Wild Girl of Champagne, The Maid of Châlons, or The Wild Child of Songy. Her case is more controversial than that of some other feral children because a few modern-day scholars have regarded it as either wholly or partly fictional. However, in 2004, the French author Serge Aroles argued that it was indeed authentic, after spending ten years carrying out archival research into French and American history. Aroles speculates that Marie-Angélique had survived for ten years living wild in the forests of France, between the ages of nine and 19, before she was captured by villagers in Songy in Champagne in September 1731. He claims that she was born in 1712 as a Native American of the Meskwaki (or "Fox") people in what today is the Midwestern U.S. state of Wisconsin and that she died in Paris i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana refers to two distinct regions: * first, to Louisiana (New France), colonial French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by Early Modern France, France during the 17th and 18th centuries; and, * second, to modern French Louisiana, which stretches across the southern extreme of the present-day State of Louisiana. Each term has been in use for many years. Colonial French Louisiana Colonial French Louisiana was a part of New France. Beginning in 1682 this region, known in French as ''Louisiana (New France), la Louisiane française'', The contemporary French term for the U.S. state of Louisiana is ''"Louisiane"'', with the larger colonial region called ''"la Louisiane française"''. However, in colonial writings the colony would be called "La Louisiane" (before the state was created from the lower portion of the region), just as English used "Louisiana" for both the region/state names, rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
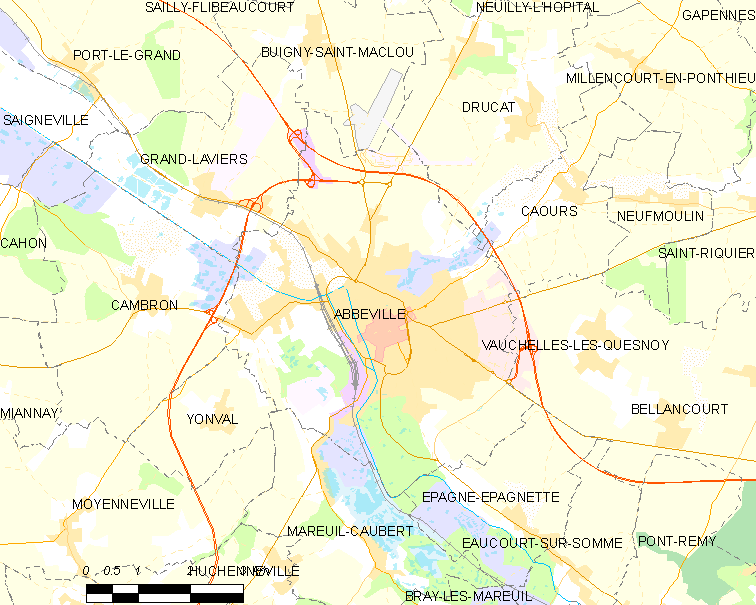
Abbeville
Abbeville (, vls, Abbekerke, pcd, Advile) is a commune in the Somme department and in Hauts-de-France region in northern France. It is the chef-lieu of one of the arrondissements of Somme. Located on the river Somme, it was the capital of Ponthieu. Its inhabitants are called the ''Abbevillois''. Geography Location Abbeville is located on the river Somme, from its modern mouth in the English Channel. The majority of the town is located on the east bank of the Somme, as well as on an island. It is located at the head of the Abbeville Canal, and is northwest of Amiens and approximately from Paris. It is also as the crow flies from the and the English Channel. In the medieval period, it was the lowest crossing point on the Somme and it was nearby that Edward III's army crossed shortly before the Battle of Crécy in 1346. Just halfway between Rouen and Lille, it is the historical capital of the County of Ponthieu and maritime Picardy. Quarters, hamlets and local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Author
An author is the writer of a book, article, play, mostly written work. A broader definition of the word "author" states: "''An author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility for what was created''." Typically, the first owner of a copyright is the person who created the work, i.e. the author. If more than one person created the work (i.e., multiple authors), then a case of joint authorship takes place. The copyright laws are have minor differences in various jurisdictions across the United States. The United States Copyright Office, for example, defines copyright as "a form of protection provided by the laws of the United States (title 17, U.S. Code) to authors of 'original works of authorship.'" Legal significance of authorship Holding the title of "author" over any "literary, dramatic, musical, artistic, rcertain other intellectual works" gives rights to this person, the owner of the copyright, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abel Hugo
Abel Joseph Hugo (15 November 1798, Paris - 7 February 1855, Paris) was a French military officer, essayist, and historian. His younger brother was the novelist Victor Hugo. Biography He was the eldest son of General Joseph Léopold Sigisbert Hugo and his wife, the artist Sophie Trébuchet. He attended the Lycée Impérial in Paris. At the age of thirteen, he was the only son of the General who followed him to Spain. There, he entered the school for pages of Joseph Bonaparte, who was then King of Spain. He would be the only French page at the Spanish Court. While serving in that capacity, he began to practice his writing skills. He took part in the French retreat of 1812, and served as a Second Lieutenant.Jacques Hantraye, "Abel Hugo, de l’expérience à l’écriture de la guerre", In: ''Hugo et la guerre'', Claude Millet (Ed.), Maisonneuve et Larose, 2003 Two years later, the Comte d’Artois (who would later become King Charles X), made him and his brothers Knights in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude-Rémy Buirette De Verrières
Claude Rémy Buirette de Verrières (22 March 1749, Verrières, Marne, France9 January 1793, Brussels) was a lawyer, historian, author and French revolutionary. He was the author of four books about the history and antiquities of the city of Châlons-en-Champagne and the region of Champagne (historical province) in north-eastern France. An early supporter of the French Revolution, Buirette, despite being a hunchback, was put in command of revolutionary troops in Paris and later became military governor of the Belgian seaport of Antwerp. He is said to have been a friend of the prominent French revolutionary Jean-Paul Marat Jean-Paul Marat (; born Mara; 24 May 1743 – 13 July 1793) was a French political theorist, physician, and scientist. A journalist and politician during the French Revolution, he was a vigorous defender of the ''sans-culottes'', a radical ....Jean-Paul Barbier ''Des Châlonnais célèbres illustres et mémorables'', 2000 References {{DEFAULTSORT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Monboddo
James Burnett, Lord Monboddo (baptised 25 October 1714; died 26 May 1799) was a Scottish judge, scholar of linguistic evolution, philosopher and deist. He is most famous today as a founder of modern comparative historical linguistics. In 1767 he became a judge in the Court of Session. As such, Burnett adopted an honorary title based on the name of his father's estate and family seat, Monboddo House. Monboddo was one of a number of scholars involved at the time in development of early concepts of biological evolution. Some credit him with anticipating in principle the idea of natural selection that was read by (and acknowledged in the writings of) Erasmus Darwin. Charles Darwin read the works of his grandfather Erasmus and later developed the ideas into a scientific theory. Early years James Burnett was born in 1714 at Monboddo House in Kincardineshire, Scotland. After his primary education at the parish school of Laurencekirk, he studied at Marischal College, Aberdeen, fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques-Christophe Valmont De Bomare
Jacques-Christophe Valmont de Bomare (born 17 September 1731, Rouen; died 24 August 1807, Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...) was a French botanist and naturalist. He wrote an influential encyclopedia of natural history in the 1760s: ''Dictionnaire raisonné universel d’histoire naturelle'' (6 volumes, Paris, Chez Lacombe, 1764–1768). Works * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** References 1731 births 1807 deaths 19th-century French botanists French naturalists Scientists from Rouen Burials at Père Lachaise Cemetery 18th-century French botanists {{France-scientist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte De Buffon
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (; 7 September 1707 – 16 April 1788) was a French naturalist, mathematician, cosmologist, and encyclopédiste. His works influenced the next two generations of naturalists, including two prominent French scientists Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Georges Cuvier. Buffon published thirty-six quarto volumes of his ''Histoire Naturelle'' during his lifetime, with additional volumes based on his notes and further research being published in the two decades following his death. Ernst Mayr wrote that "Truly, Buffon was the father of all thought in natural history in the second half of the 18th century".Mayr, Ernst 1981. ''The Growth of Biological Thought''. Cambridge: Harvard. p 330 Credited with being one of the first naturalists to recognize ecological succession, he was later forced by the theology committee at the University of Paris to recant his theories about geological history and animal evolution because they contradicted the Biblical na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Burnett, Lord Monboddo
James Burnett, Lord Monboddo (baptised 25 October 1714; died 26 May 1799) was a Scottish judge, scholar of linguistic evolution, philosopher and deist. He is most famous today as a founder of modern comparative historical linguistics. In 1767 he became a judge in the Court of Session. As such, Burnett adopted an honorary title based on the name of his father's estate and family seat, Monboddo House. Monboddo was one of a number of scholars involved at the time in development of early concepts of biological evolution. Some credit him with anticipating in principle the idea of natural selection that was read by (and acknowledged in the writings of) Erasmus Darwin. Charles Darwin read the works of his grandfather Erasmus and later developed the ideas into a scientific theory. Early years James Burnett was born in 1714 at Monboddo House in Kincardineshire, Scotland. After his primary education at the parish school of Laurencekirk, he studied at Marischal College, Aberdeen, fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Racine
Louis Racine (born 6 November 1692, Paris; died 29 January 1763, Paris) was a French poet of the Age of the Enlightenment. The second son and the seventh and last child of the celebrated tragic dramatist Jean Racine, he was interested in poetry from childhood but was dissuaded from trying to make it his career by the poet Boileau on the grounds that the gift never existed in two successive generations. However, in 1719 Racine became a member of the Académie des Inscriptions and published his first major poem, ''La Grâce'', in 1722. But, because of the poem's Jansenist inspiration, Cardinal de Fleury, chief minister of Louis XV, blocked the poet's admission to the Académie Française, and instead Racine was induced to accept the post of inspector-general of taxes at Marseille in Provence. For the next 24 years, although he continued to write poetry, Racine worked as a tax inspector in various provincial towns and cities, marrying in 1728. His most important poem, ''La Religion' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

