|
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. The MPC is higher in the case of poorer people than in rich. According to John Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplier (economics)
In macroeconomics, a multiplier is a factor of proportionality that measures how much an endogenous variable changes in response to a change in some exogenous variable. For example, suppose variable ''x'' changes by ''k'' units, which causes another variable ''y'' to change by ''M'' × ''k'' units. Then the multiplier is ''M''. Common uses Two multipliers are commonly discussed in introductory macroeconomics. Commercial banks create money, especially under the fractional-reserve banking system used throughout the world. In this system, money is created whenever a bank gives out a new loan. This is because the loan, when drawn on and spent, mostly finishes up as a deposit back in the banking system and is counted as part of money supply. After putting aside a part of these deposits as mandated bank reserves, the balance is available for the making of further loans by the bank. This process continues multiple times, and is called the multiplier effect. The multiplier m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Save
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the fraction of an increase in income that is not spent and instead used for saving. It is the slope of the line plotting saving against income. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar, and the marginal propensity to save is 0.35, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Likewise, it is the fractional decrease in saving that results from a decrease in income. The MPS plays a central role in Keynesian economics Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ... as it quantifies the saving-income relation, which is the flip side of the consumption-income relation, and according to Keynes it reflects the fundamental psychological law. The marginal propensity to save is also a key variable in deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Theory
The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves. It analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures, by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint. Factors influencing consumers' evaluation of the utility of goods: income level, cultural factors, product information and physio-psychological factors. Consumption is separated from production, logically, because two different economic agents are involved. In the first case consumption is by the primary individual, individual tastes or preferences determine the amount of pleasure people derive from the goods and services they consume.; in the second case, a producer might make something that he would not consume himself. Therefore, different motivations and abilities are involved. The models that make up consumer theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Propensity To Consume
Average propensity to consume (as well as the marginal propensity to consume) is a concept developed by John Maynard Keynes to analyze the consumption function, which is a formula where total consumption expenditures (C) of a household consist of autonomous consumption (Ca) and income (Y) (or disposable income (YD)) multiplied by marginal propensity to consume (c or MPC). According to Keynes, the individual´s real income determines saving and consumption decisions. Consumption function: C=+cY The average propensity to consume is referred to as the percentage of income spent on goods and services. It is the proportion of income that is consumed and it is calculated by dividing total consumption expenditure (C) by total income (Y): APC=\frac=\frac+c It can be also explained as spending on every monetary unit of income. Moreover Keynes´s theory claims that wealthier people spend less of their income on consumption than less wealthy people. This is caused by autonomous consumptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Propensity To Save
In Keynesian economics, the average propensity to save (APS), also known as the savings ratio, is the proportion of income which is saved, usually expressed for household savings as a fraction of total household disposable income (taxed income). APS=\frac The ratio differs considerably over time and between countries. The savings ratio for an entire economy can be affected by (for example) the proportion of older people (as they have less motivation and capability to save), and the rate of inflation (as expectations of rising prices can encourage people to spend now rather than later) or current interest rates. APS can express the social preference for investing in the future over consuming in the present. The complement (1 minus the APS) is the average propensity to consume (APC). Low average propensity to save might be the indicator of a large percentage of old people or high percentage of irresponsible young people in the population. With income level changes, APS become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Surplus
In mainstream economics, economic surplus, also known as total welfare or total social welfare or Marshallian surplus (after Alfred Marshall), is either of two related quantities: * Consumer surplus, or consumers' surplus, is the monetary gain obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay. * Producer surplus, or producers' surplus, is the amount that producers benefit by selling at a market price that is higher than the least that they would be willing to sell for; this is roughly equal to profit (since producers are not normally willing to sell at a loss and are normally indifferent to selling at a break-even price). Overview In the mid-19th century, engineer Jules Dupuit first propounded the concept of economic surplus, but it was the economist Alfred Marshall who gave the concept its fame in the field of economics. On a standard supply and demand diagram, consumer su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Propensity To Consume
Average propensity to consume (as well as the marginal propensity to consume) is a concept developed by John Maynard Keynes to analyze the consumption function, which is a formula where total consumption expenditures (C) of a household consist of autonomous consumption (Ca) and income (Y) (or disposable income (YD)) multiplied by marginal propensity to consume (c or MPC). According to Keynes, the individual´s real income determines saving and consumption decisions. Consumption function: C=+cY The average propensity to consume is referred to as the percentage of income spent on goods and services. It is the proportion of income that is consumed and it is calculated by dividing total consumption expenditure (C) by total income (Y): APC=\frac=\frac+c It can be also explained as spending on every monetary unit of income. Moreover Keynes´s theory claims that wealthier people spend less of their income on consumption than less wealthy people. This is caused by autonomous consumptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. Instead, it is influenced by a host of factors – sometimes behaving erratically – affecting production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes – a recession, when demand is low, or inflation, when demand is high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between government and central bank. In particular, fiscal policy actions (taken by the government) and monetary policy actio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Consumption
Induced consumption is the portion of consumption that varies with disposable income. When a change in disposable income “induces” a change in consumption on goods and services, then that changed consumption is called “induced consumption”. In contrast, expenditures for autonomous consumption do not vary with income. For instance, expenditure on a consumable that is considered a normal good would be considered to be induced. In the simple linear consumption function, C = a + b \times Y_ induced consumption is represented by the term b \times Y_, where Y_ denotes disposable income and b is called the marginal propensity to consume In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes an .... References * Consumption (macroeconomics) {{Econ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Save
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the fraction of an increase in income that is not spent and instead used for saving. It is the slope of the line plotting saving against income. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar, and the marginal propensity to save is 0.35, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Likewise, it is the fractional decrease in saving that results from a decrease in income. The MPS plays a central role in Keynesian economics Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ... as it quantifies the saving-income relation, which is the flip side of the consumption-income relation, and according to Keynes it reflects the fundamental psychological law. The marginal propensity to save is also a key variable in deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
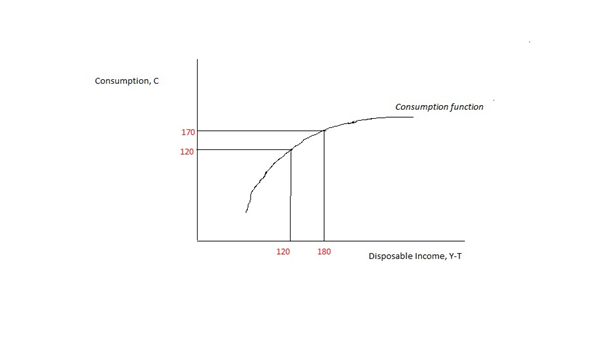
Consumption Function
In economics, the consumption function describes a relationship between consumption and disposable income. The concept is believed to have been introduced into macroeconomics by John Maynard Keynes in 1936, who used it to develop the notion of a government spending multiplier. Details Its simplest form is the ''linear consumption function'' used frequently in simple Keynesian models: :C = a + b \cdot Y_ where a is the autonomous consumption that is independent of disposable income; in other words, consumption when disposable income is zero. The term b \cdot Y_ is the induced consumption that is influenced by the economy's income level Y_. The parameter b is known as the marginal propensity to consume, i.e. the increase in consumption due to an incremental increase in disposable income, since \partial C / \partial Y_ = b. Geometrically, b is the slope of the consumption function. Keynes proposed this model to fit three stylized facts: * People typically spend a part, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |