 |
Maplin Sands
The Maplin Sands are mudflats on the northern bank of the Thames estuary, off Foulness Island, near Southend-on-Sea in Essex, England, though they actually lie within the neighbouring borough of Rochford. They form a part of the Essex Estuaries Special Area of Conservation due to their value for nature conservation, with a large colony of dwarf eelgrass ('' Zostera noltei'') and associated animal communities. To the northeast, the Maplin sands are contiguous with the Foulness sands, which are bordered to the north by the Whitaker Channel; the seaward continuation of the River Crouch. To the south runs the Swin Channel. History Maplin Sands is crossed by the ancient trackway known as The Broomway. A screw-pile lighthouse was built on the sands in 1838 by Messrs. Mitchel and Sons (sic- more often Mitchell and Sons) on the recommendation of James Walker of Trinity House. It was the first screwpile lighthouse ever to be designed. Although construction of the Maplin Sands Ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mudflat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal flat ecosystems are as extensive globally as mangroves, covering at least of the Earth's surface. / They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries; they are also seen in freshwater lakes and salty lakes (or inland seas) alike, wherein many rivers and creeks end. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud, resulting from deposition of estuarine silts, clays and aquatic animal detritus. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily. A recent global remote sensing analysis estimated that approximately 50% of the global extent of tidal flats occurs within eight countries (Indonesia, China, Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Wyre Light (Fleetwood)
The Wyre Light was a tall iron screw-pile lighthouse marking the navigation channel to the town of Fleetwood, Lancashire, England. History The lighthouse was designed by Alexander Mitchell, an Irish engineer who developed the screwpile concept. It was the first screwpile lighthouse ever to be lit. Although construction of the Maplin Sands Light on the northern bank of the Thames estuary had started before Wyre Light, the latter was completed in a much shorter period of time. These lights inspired other similar constructions such as the Thomas Point Shoal Light in the United States. The Wyre Light stood offshore on the 'North Wharf Bank', sandbanks which mark the 'Lune Deep' and the navigation channel of the Wyre. The Wyre Light along with a pair of on shore lighthouses, the Beach Lighthouse and the Pharos provided a navigational guide to shipping entering the Wyre estuary. The Light's base consisted of seven wrought iron piles embedded in the sands. Each was long with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Screw-pile Lighthouse
A screw-pile lighthouse is a lighthouse which stands on piles that are screwed into sandy or muddy sea or river bottoms. The first screw-pile lighthouse to begin construction was built by the blind Irish engineer Alexander Mitchell. Construction began in 1838 at the mouth of the Thames and was known as the Maplin Sands lighthouse, and first lit in 1841. However, though its construction began later, the Wyre Light in Fleetwood, Lancashire, was the first to be lit (in 1840). In the United States, several screw-pile lighthouses were constructed in the Chesapeake Bay due to its estuarial soft bottom. North Carolina's sounds and river entrances also once had many screw-pile lights. The characteristic design is a -storey hexagonal wooden building with dormers and a cupola light room. History Non-screwpile (straightpile) tubular skeletal tower lighthouses were built, usually of cast-iron but also of wrought-iron piles, both onshore and offshore, typically on soft bottoms such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Foulness Island
Foulness Island () is a closed island on the east coast of Essex in England, which is separated from the mainland by narrow creeks. In the 2001 census, the usually resident population of the civil parish was 212, living in the settlements of Churchend and Courtsend, at the north end of the island. The population reduced to 151 at the 2011 Census. The island had until recently a general store and post office. The George and Dragon pub in Churchend closed in 2007, while the church of St Mary the Virgin closed in May 2010. In 2019, the ''Southend Echo'' reported plans for the church to be converted into a five-bedroom home. Foulness Island is predominantly farmland and is protected from the sea by a sea wall. The island's unusual name is derived from the Old English ''fugla næsse'' ("bird headland"), referring to wildfowl. It is an internationally important site for migrating and breeding birds, including pied avocets. During the North Sea flood of 1953, almost the entire isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(Tony_Radakin_cropped).jpg) |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is the department responsible for implementing the defence policy set by His Majesty's Government, and is the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during the First World War, concluded that there was a need for greater co-ordination between the three services that made up the armed forces of the United Kingdom: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Container Ships
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport and now carry most seagoing non-bulk cargo. Container ship capacity is measured in twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU). Typical loads are a mix of 20-foot (1-TEU) and 40-foot (2-TEU) ISO-standard containers, with the latter predominant. Today, about 90% of non- bulk cargo worldwide is transported by container ships, and the largest modern container ships can carry up to 24,000 TEU (e.g., '' Ever Ace''). Container ships now rival crude oil tankers and bulk carriers as the largest commercial seaborne vessels. History There are two main types of dry cargo: bulk cargo and break bulk cargo. Bulk cargoes, like grain or coal, are transported unpackaged in the hull of the ship, generally in large volume. Break-bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
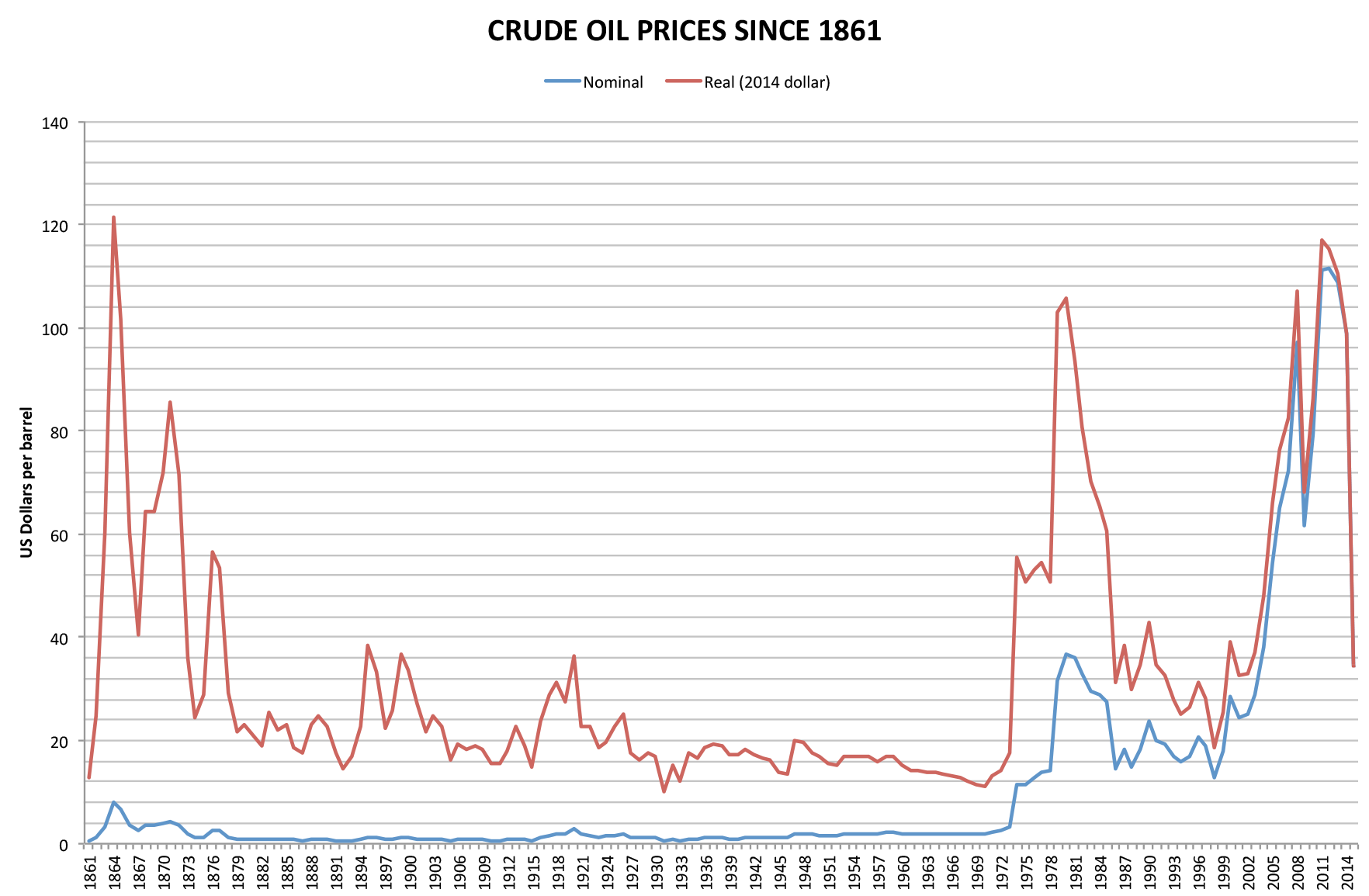 |
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli confli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Thames Estuary Airport
A potential Thames Estuary Airport has been proposed at various times since the 1940s. London's existing principal airports, Heathrow, Gatwick and Stansted, are each sub-optimally located in various ways, such as being too close to built-up areas or requiring aircraft to fly low over London. In the case of Heathrow, the growth of air traffic has meant that the airport is operating at 98% capacity. Several locations for a new airport have been proposed in the Thames Estuary, to the east of London. These include Maplin Sands off Foulness on the north side of the estuary; Cliffe and the Isle of Grain in Kent on the south side; and artificial islands located off the Isle of Sheppey such as the "Boris Island" proposal championed by Boris Johnson, the then Mayor of London. Economic considerations have so far ruled out a new coastal airport, while political considerations have ruled out a new inland airport, leaving planners with an as-yet-unresolved dilemma. On 17 December 2013 the "A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Roskill Commission
The Roskill Commission (formally the Commission on the Third London Airport) was a UK Government Commission charged with looking into finding a site for a new airport for London. Chaired by High Court judge Eustace Roskill, it sat from 1968 to 1970 and published its report in January 1971. Since the 1950s, London's primary passenger airport had been at Heathrow, with a second one at Gatwick. The Commission's aim was "to enquire into the timing of the need for a four-runway airport to cater for the growth of traffic at existing airports serving the London area, to consider the various alternative sites, and to recommend which site should be selected." Roskill's initial list of 78 sites was reduced to an intermediate list of 29, before detailed consideration of four short-listed locations: *Cublington *Foulness * Nuthampstead * Thurleigh. The Commission recommended that a site at Cublington near Wing in Buckinghamshire (to the north-west of London) should be developed as Londo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
The Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Destroyers
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |