|
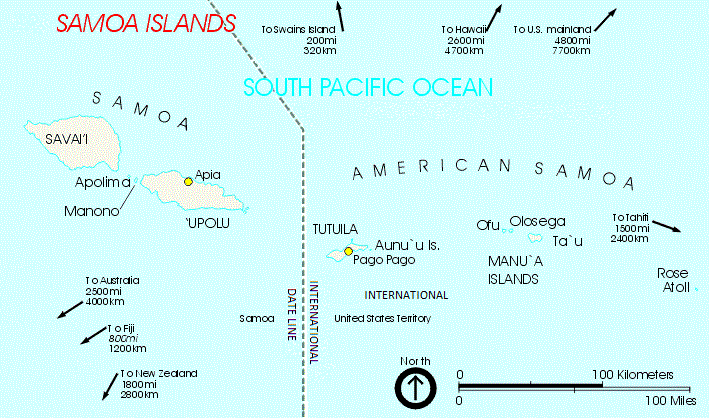
Manuʻa Islands
The Manua Islands, or the Manua tele (Samoan: ''Manua tele''), in the Samoan Islands, consists of three main islands: Taū, Ofu and Olosega. The latter two are separated only by the shallow, 137-meter-wide Āsaga Strait, and are now connected by a bridge over the strait. The islands are located some east of Tutuila and are a part of American Samoa, an unincorporated territory of the United States. Their combined area is , and they have a total population of 1,400. Tau is the largest of these islands, with an area of , and it has the highest point of the Manua, at . Politically, the islands form the Manua District, one of the three administrative divisions of American Samoa. Manu'a was the political centre of the region for many centuries, until the rise of the Tu'i Tonga maritime empire, which led to a shift in power from the eastern islands of Samoa to its western islands. Geography All three islands are high islands: volcanic remnants rising out of the sea 14° south of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ofu-Olosega
Ofu and Olosega are parts of a volcanic doublet in the Manuʻa Islands, which is a part of American Samoa in the Samoan Islands. These twin islands, formed from shield volcanoes, have a combined length of 6 km and a combined area of . Together, they have a population of about 500 people. Geographically, the islands are volcanic remnants separated by the narrow, ) Āsaga Strait, composed of shallow-water coral reef. Before 1970, people crossed between the two islands by waiting until low tide and then wading across the shallow water of the strait. Since 1970, there has been a bridge over the strait, providing a single-lane road that connects the two islands. The highest peak on Ofu Island is Mount Tumutumu (also called Tumu), at . The highest peak on Olosega is Mount Piumafua, at . The most recent volcanic eruption was in 1866, southeast of Olosega. Pre-historic artifacts discovered on Ofu by archaeological field work in the 1980s significantly furthered understanding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ofu Beach American Samoa US National Park Service
Ofu or OFU may refer to *Ofu-Olosega Ofu and Olosega are parts of a volcanic doublet in the Manuʻa Islands, which is a part of American Samoa in the Samoan Islands. These twin islands, formed from shield volcanoes, have a combined length of 6 km and a combined area of . Togethe ..., an island in the Manu'a group in American Samoa ** Ofu Airport (IATA code OFU), a public airport on the island * Ofu County, American Samoa * Ofu, Nigeria, a town and Local Government Area in Kogi State {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hawaii
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National University Of Samoa
The National University of Samoa (''Lē Iunivesitē Aoao o Sāmoa'') is the only national university in Samoa. Established in 1984 by an act of parliament, it is coeducational and provides certificate, diploma, and undergraduate degree programs, as well as technical and vocational training. About 2,000 students were enrolled in 2010 with an estimated 300 staff. It offers a wide range of programmes including Arts, Business and Entrepreneurship, Education, Science, Nursing, Engineering and Maritime Training. The Centre for Samoan Studies, established in the university for the teaching of the Samoan language and culture, offers undergraduate and graduate degrees as well as the world's first degree in Master of Samoan Studies. The National University of Samoa has the distinction of being one of two universities in Samoa. The second is the University of the South Pacific - Alafua Campus which specializes in Agriculture. The campus was built in part with funding from the Government of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Samoa Community College
American Samoa Community College (ASCC) is a public land-grant community college in the village of Mapusaga, American Samoa. Only legal residents of American Samoa who have graduated from high school or obtained a General Equivalency Diploma are admitted to ASCC. It is American Samoa's only tertiary education institution. The main Mapusaga campus has a variety of Associate degree programs. Also associated with the college are a nursing school at LBJ Hospital and vocational facilities in the Tafuna Industrial Complex. ASCC awarded 139 degrees and certificates in 2016, including 75 Associate of Arts degrees, 60 Associate of Science degrees, 3 Certificate of Proficiency, and one Bachelor in Elementary Education. In 2016, the college had 1,254 enrolled full-time students and 553 enrolled part-time. Around 27 percent majored in liberal arts but other popular majors were business management, accounting, criminal justice, education, nursing and health science. History American Samoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoan Language
Samoan ( or ; ) is a Polynesian language spoken by Samoans of the Samoan Islands. Administratively, the islands are split between the sovereign country of Samoa and the United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language, alongside English, in both jurisdictions. It is widely spoken across the Pacific region, heavily so in New Zealand and also in Australia and the United States. Among the Polynesian languages, Samoan is the most widely spoken by number of native speakers. Samoan is spoken by approximately 260,000 people in the archipelago and with many Samoans living in diaspora in a number of countries, the total number of speakers worldwide was estimated at 510,000 in 2015. It is the third-most widely spoken language in New Zealand, where 2.2% of the population, 101,900 people, were able to speak it as of 2018. The language is notable for the phonological differences between formal and informal speech as well as a ceremonial form used in Samoan oratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falealupo
Falealupo is a village in Samoa situated at the west end of Savai'i island from the International Date Line used until 29 December 2011. The village has two main settlements, Falealupo-Uta, situated inland by the main island highway and Falealupo-Tai, situated by the sea. The road to the coastal settlement is about 9 km, most of it unsealed, from the main highway. The village's population is 545. Due to its location in the west of the country, and because Samoa was just to the east of the International Date Line, Falealupo has been described as "the last village in the world to see the sunset of each day". This has now changed, as the Samoan government has moved the International Date Line east of the country in 2011. Families have moved inland for the convenience of living by the main road near public transport, as well as the extensive damage to the coastal village from cyclones in the early 1990s, which left behind old church ruins along the coast. There are rock pools ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives. The field of family history is broader than genealogy, and covers not just lineage but also family and community history and biography. The record of genealogical work may be presented as a "genealogy", a "family history", or a " family tree". In the narrow sense, a "genealogy" or a "family tree" traces the descendants of one person, whereas a "family history" traces the ancestors of one person, but the terms are often used interchangeably. A family history may include additional biographical information, family traditions, and the like. The pursuit of family history and origins tends to be shaped by several motives, including the desire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including Polynesian languages, language relatedness, Polynesian culture, cultural practices, and Marae, traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and Polynesian navigation, using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono and Apolima); and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands (Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga (closest foreign country), northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia. The Lapita culture, Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan culture, Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a Unitary state, unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with 11 Administrative divisions of Samoa, administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |