|
Mansfield Smith-Cumming
Captain Sir Mansfield George Smith-Cumming (1 April 1859 – 14 June 1923) was a British naval officer who served as the first chief of the Secret Intelligence Service (SIS). Origins He was a great-great grandson of the prominent merchant John Smith, a director of both the South Sea Company and the East India Company, the second son of Abel Smith (d. 1756), the Nottingham banker who founded a banking dynasty and whose business much later became National Westminster Bank, now one of the largest banks in the UK.J. Leighton Boyce, ''Smith's the Bankers 1658–1958'' (1958). Early naval career Smith joined the Royal Navy and underwent training at Dartmouth from the age of twelve and was appointed acting sub-lieutenant in 1878. He was posted to HMS ''Bellerophon'' in 1877, and for the next seven years served in operations against Malay pirates (during 1875–6) and in Egypt in 1883. However, he increasingly suffered from seasickness, and in 1885 was placed on the retired list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secret Intelligence Service
The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6 ( Military Intelligence, Section 6), is the foreign intelligence service of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of human intelligence in support of the UK's national security. SIS is one of the British intelligence agencies and the Chief of the Secret Intelligence Service ("C") is directly accountable to the Foreign Secretary. Formed in 1909 as the foreign section of the Secret Service Bureau, the section grew greatly during the First World War officially adopting its current name around 1920. The name "MI6" (meaning Military Intelligence, Section 6) originated as a convenient label during the Second World War, when SIS was known by many names. It is still commonly used today. The existence of SIS was not officially acknowledged until 1994. That year the Intelligence Services Act 1994 (ISA) was introduced to Parliament, to place the organisation on a statutory f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abel Smith (1717–1788)
Abel Smith (baptised 14 March 1717 – 12 July 1788) of Wilford House in the parish of Wilford, near Nottingham, England, was one of the leading bankers of his timeJ. Leighton Boyce, ''Smith's the Bankers 1658–1958'' (1958). and served thrice as a Member of Parliament. Some secondary sources refer to him as Abel Smith II in order to distinguish him from other members of his family with the same name. Origins He was baptised on 14 March 1717 at Nottingham, the third son and successor of Abel Smith (died 1756), a banker of Nottingham, the second son and heir of Thomas Smith (1631–1699), a mercer at Nottingham who in 1658 founded Smith's Bank. His mother was Jane Beaumont (1689–1743), a daughter of George Beaumont of Chapelthorpe in Yorkshire.Edward J. Davies, "Some Connections of the Birds of Warwickshire", ''The Genealogist'', 26 (2012):58–76. Career He was apprenticed at the age of fifteen to William Wilberforce, a merchant adventurer from Hull (grandfather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Moray
Moray; ( gd, Moireibh ) or Morayshire, called Elginshire until 1919, is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland, bordering Nairnshire to the west, Inverness-shire to the south, and Banffshire to the east. It was a local government county, with Elgin the county town, until 1975. The county was officially called ''Elginshire'', sharing the name of the Elginshire parliamentary constituency, so named since 1708. The registration county, for property, is, 'County of Moray', and the Lieutenancy area, for ceremonial purposes is 'Moray'. The lieutenancy area contains a slightly smaller area than the historic county. History Before 1889 there were two large exclaves of Moray situated within Inverness-shire, and an exclave of Inverness-shire situated within Moray. The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 transferred these exclaves to the counties which surrounded them. The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 established a uniform system of coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forres
Forres (; gd, Farrais) is a town and former royal burgh in the north of Scotland on the Moray coast, approximately northeast of Inverness and west of Elgin. Forres has been a winner of the Scotland in Bloom award on several occasions. There are many geographical and historical attractions nearby such as the River Findhorn, and there are also classical, historical artifacts and monuments within the town itself, such as Forres Tolbooth and Nelson's Tower. Brodie Castle, the home of the Brodie Clan, lies to the west of the town, close to the A96. A list of suburbs in the town of Forres contains: Brodie, Dalvey, Mundole and Springdale. Pre-history and archaeology Between 2002 and 2013 some 70 hectares of land was investigated by archaeologists in advance of a proposed residential development on the southern fringes of the town. They found an extensive Iron Age settlement and evidence that people lived in the area from the Neolithic (radiocarbon dates from the 4th to the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Hamble
The River Hamble is located in south Hampshire, England. It rises near Bishop's Waltham and flows for through Botley, Bursledon, and Lower Swanwick before entering Southampton Water between Hamble Common and Warsash. The Hamble is tidal for about half its length and is navigable below Botley. From the medieval period to the present it has been a major ship and boat-building area. Leisure craft are still built by the Hamble today. One of the main builders was '' Luke & Co'', later ''Luke Bros'', a well-reputed yard from around 1890 to its closure in 1945. The lower reaches are a major yachting area with easy access to the sheltered waters of Southampton Water and The Solent. Course From source to mouth the river makes a repeated curve heading south-southwest. It gains tributary streams before reaching Botley, the site of an ancient watermill. Below Botley, the river becomes tidal and navigable. It gains strength from adjoining streams, draining surrounding Hedge En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bursledon
Bursledon is a village on the River Hamble in Hampshire, England. It is located within the borough of Eastleigh. Close to the city of Southampton, Bursledon has a railway station, a marina, dockyards and the Bursledon Windmill. Nearby villages include Swanwick, Hamble-le-Rice, Netley and Sarisbury Green. The village has close ties to the sea. The Elephant Boatyard located in Old Bursledon dates back centuries and is where Henry VIII's fleet was built. Submerged remnants of the fleet can be found in the River Hamble. The village, particularly the Jolly Sailor pub and the Elephant Boatyard, were used as the primary filming venue for the 1980s BBC TV soap opera '' Howards' Way''. Etymology The village was known as ''Brixendona'' or Brixenden in the 12th century, Burstlesden in the 14th century, and ''Bristelden'' in the 16th century. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
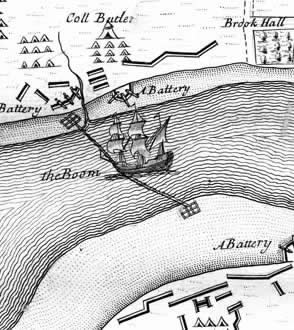
Boom (navigational Barrier)
A boom or a chain (also boom defence, harbour chain, river chain, chain boom, boom chain or variants) is an obstacle strung across a navigable stretch of water to control or block navigation. In modern times they usually have civil uses, such as to prevent access to a dangerous river channel. But, especially historically, they have been used militarily, with the goal of denying access to an enemy's ships: a modern example is the anti-submarine net. Booms have also been used to force passing vessels to pay a toll. Description A boom generally floats on the surface, while a chain can be on the surface or below the water. A chain could be made to float with rafts, logs, ships or other wood, making the chain a boom as well. Historical uses Especially in medieval times, the end of a chain could be attached to a chain tower or boom tower. This allowed safe raising or lowering of the chain, as they were often heavily fortified. By raising or lowering a chain or boom, access could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasickness
Motion sickness occurs due to a difference between actual and expected motion. Symptoms commonly include nausea, vomiting, cold sweat, headache, dizziness, tiredness, loss of appetite, and increased salivation. Complications may rarely include dehydration, electrolyte problems, or a lower esophageal tear. The cause of motion sickness is either real or perceived motion. This may include from car travel, air travel, sea travel, space travel, or reality simulation. Risk factors include pregnancy, migraines, and Ménière's disease. The diagnosis is based on symptoms. Treatment may include behavioral measures or medications. Behavioral measures include keeping the head still and focusing on the horizon. Three types of medications are useful: antimuscarinics such as scopolamine, H1 antihistamines such as dimenhydrinate, and amphetamines such as dexamphetamine. Side effects, however, may limit the use of medications. A number of medications used for nausea such as ondansetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime Malaysia–Thailand border, border with Thailand and Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia, and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital, the country's largest city, and the seat of the Parliament of Malaysia, legislative branch of the Government of Malaysia, federal government. The nearby Planned community#Planned capitals, planned capital of Putrajaya is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the Government of Malaysia#Executive, executive branch (the Cabine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Bellerophon (1865)
HMS ''Bellerophon'' was a central battery ironclad built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1860s. Design and description In this ship, designed by Sir Edward Reed, the power-to-weight ratio was increased; the long rows of guns on the broadside were replaced by a small number of guns, centrally placed, of the largest possible calibre; the armour was increased in thickness but reduced in length, and a sharp beak ram was combined with a classical style plough bow. This double bottom had the added advantage of allowing the engine to be carried higher, raising the centre of gravity of the whole ship and making her thereby a steadier gun platform.Parkes, p. 103 Unlike earlier classes, ''Bellerophons bow and stern had a "U" shaped profile, giving increased buoyancy at the ends noticeably absent in some earlier battleships. ''Bellerophon'' carried the first balanced rudder in Royal Navy service. Full helm could be applied by eight men in about 27 seconds,Parkes, p. 104 whereas in HMS '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acting Sub-lieutenant
Sub-lieutenant is usually a junior officer rank, used in armies, navies and air forces. In most armies, sub-lieutenant is the lowest officer rank. However, in Brazil, it is the highest non-commissioned rank, and in Spain, it is the second highest non-commissioned rank. As a naval rank, a sub-lieutenant usually ranks below a lieutenant. Armies and air force rank In France, a sub-lieutenant () is the junior commissioned officer in the army or the air force. He wears a band in the colour of his corps (e.g. gold for infantry, silver for armoured cavalry, etc.). During the 18th century a rank of existed in the French Navy. It was the equivalent of the master's mate rank of the Royal Navy. It is now replaced by the rank of "first ensign" (). An Argentinian sub-lieutenant wears a single silver sun on each shoulder, Brazilian sub-lieutenants are the most senior non-commissioned rank (called Sub-Officer in the Navy and Air force), wearing a golden lozenge. In Mexico, the sub-lieut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Brassey.jpg)