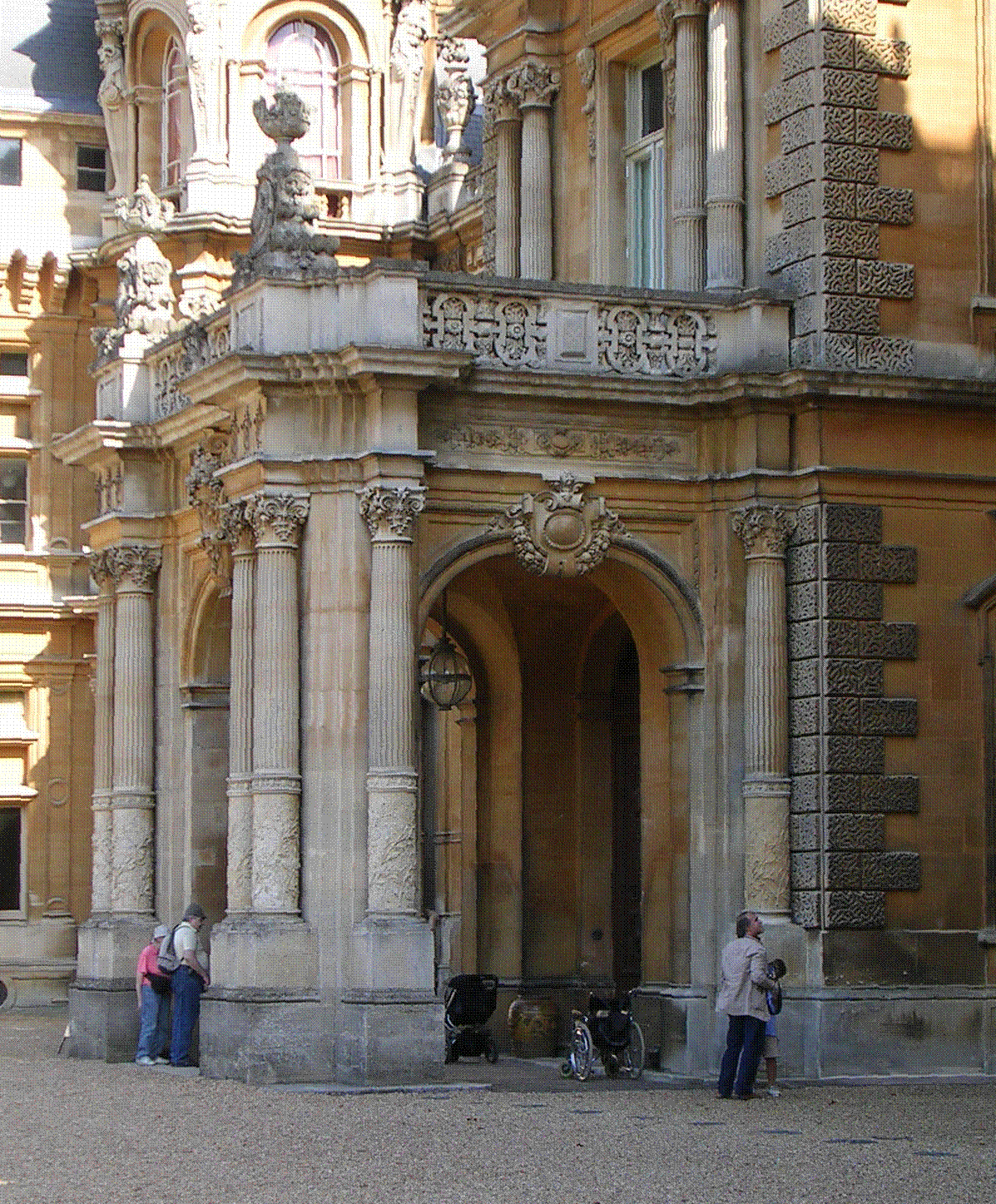|
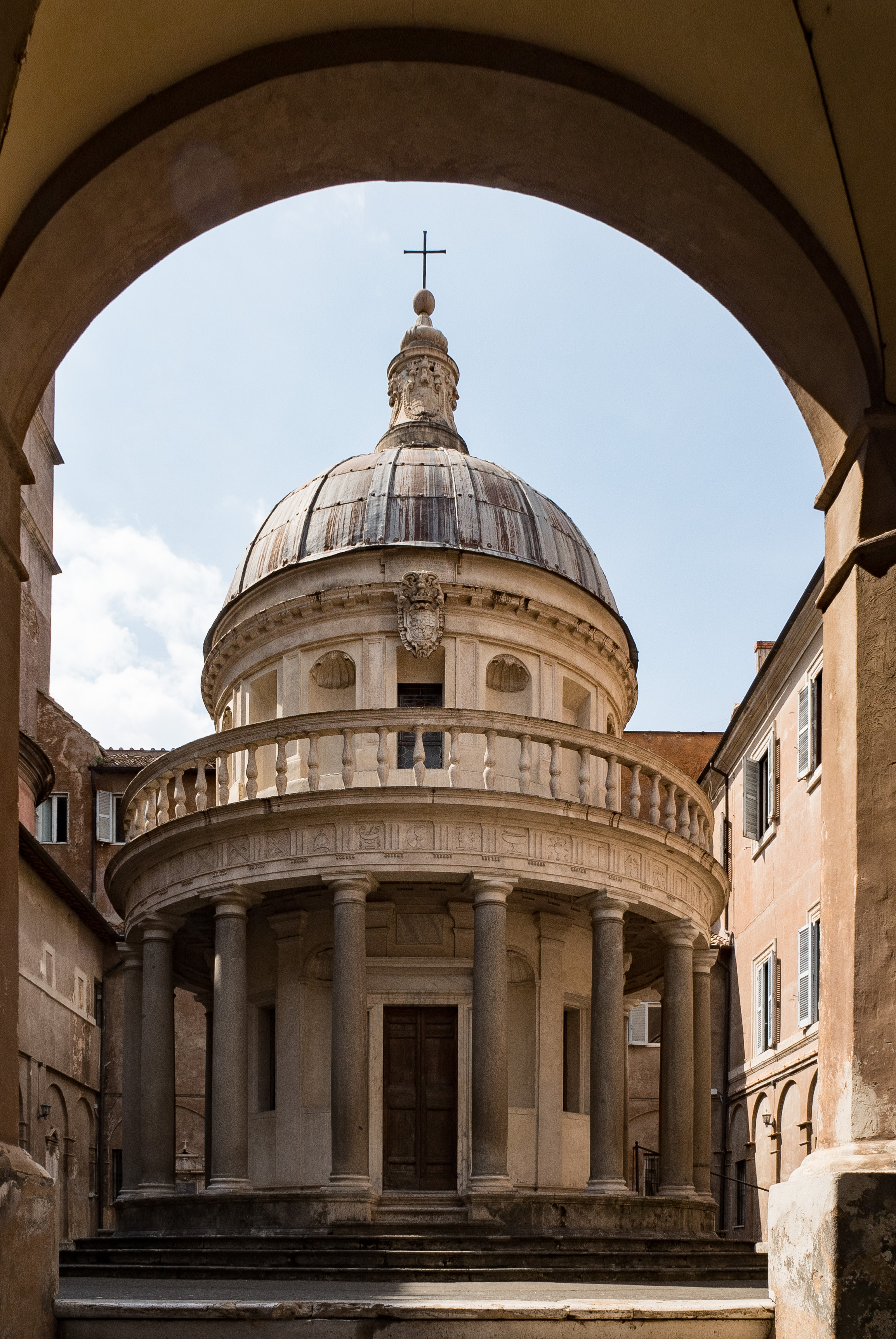
Makarpura Palace
Makarpura Palace is a royal palace of Gaekwads of the Baroda State, in present-day Vadodara, Gujarat, India. It was built by Maharaja Khende Rao in 1870, in the Italian style. It was used as summer residence and hunting resort by the Royal Family. The palace is now used as a training school called No.17 Tetra School by the Indian Air Force. History In 1866, a Maharaja of Baroda, Khande Rao, built an entire new palace finished in 1870. It is said that Malhar Rao Gaekwad, brother of Khanderao II Gaekwad, who ruled Baroda from 1856 to 1870, destroyed a portion of this palace. It was extended and renovated by Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III, between 1883-1890 and designed by Robert Fellowes Chisholm (1840-1915) in the same Italian Renaissance style.https://www.bl.uk/onlinegallery/onlineex/apac/photocoll/m/019pho000430s24u00002000.html The palace was used as a training school by the Indian Air Force for many years. Location Khanderao II Gaekwad spent a lot of time at Dhaniavi whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadodara
Vadodara (), also known as Baroda, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Vadodara district and is situated on the banks of the Vishwamitri River, from the state capital of Gandhinagar. The railway line and National Highway 8, which connect Delhi with Mumbai, pass through Vadodara. The city is named for its abundance of the Banyan (''Vad'') tree. Vadodara is also locally referred to as the ''Sanskari Nagari'' () and ''Kala Nagari'' () of India. The city is prominent for landmarks such as the Laxmi Vilas Palace, which served as the residence of the Maratha royal Gaekwad dynasty that ruled over Baroda State. It is also the home of the Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda. Etymology The city in one period was called Chandanavati after the rule of Chanda of the Dodiya Rajputs. The capital was also known as Virakshetra or Viravati (Land of Warriors). Later on, it was known as Vadpatraka or Vadodará, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makarpura
Makarpura is a major area in Vadodara city of the Gujarat state in India. It is an important industrial area of Vadodara city having Gujarat Industrial and Development corporation (G.I.D.C),which comprises many important and large Multinational corporations like Siemens, Alstom, ABB, TBEA, Philips, Panasonic, FAG, Sterling Biotech, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Larsen & Toubro, General Electric, Bombardier, and GAGL (Gujarat Automotive Gears Limited). There are also a number of glass manufacturing companies in and around Vadodara, including Haldyn Glass, HNG Float Glass and PiramalGlass. the corporater of makarpura is Purnima vyas. Vadodara Chamber of Commerce and Industry is also situated in Makarpura. The Makarpura Palace is a former Gaekwad royal palace in this locality. It was built by Maharaja Khande Rao in 1870, designed in the Italian style. It was extended and renovated by Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III. The palace is now used as a training school called No.17 Tetra School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Vadodara
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic (within the traveller's own country) or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments. Tourism numbers declined as a result of a strong economic slowdown (the late-2000s recession) between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, and in consequence of the outbreak of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus, but slowly recovered until the COVID-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prithvi Vallabh (1924 Film)
''Prithvi Vallabh'' (English: The Lord of Love and Power) was a 1924 Indian historical drama film directed by Manilal Joshi. It was based on the 1921 Gujarati novel ''Prithivivallabh'' by K. M. Munshi. Plot Munj, the king of Avanti who is a great warrior and patron of arts, is captured by his opponent Tailap with help from Bhillam, king of Dharavati. Tailap orders an execution of Munj but is stopped by Mrinalvati, Tailap's sister, who wants to break Munj's spirit. But she fall in love with Munj and they decide to escape together. When Tailap come to know about the plan, he has Munj executed by elephants. Cast Cast is as follows: * P. Y. Altekar as Bhillam * Wagle Sandow as Munj * Fatma Begum as Mrinalvati, Tailap's sister * Zubeida as Vilasvati * Sultana as Jakkala Devi * Miss Jaina * Bhalji Pendharkar Production The script was written by D. S. Shirur based on the 1921 Gujarati novel ''Prithivivallabh'' by K. M. Munshi which was serialised in ''Vismi Sadi'', a Gujarati j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Goldring
William Goldring (May 1854 – 26 February 1919) was a landscape architect, and naturalist. Goldring arrived in Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew (1875) where he was in charge of the Herbaceous Department at the world-famous botanical garden. He served as the Assistant Editor of ''The Garden (journal), The Garden'' (1879), and the Editor of ''Woods and Forests'' (1883-1886). He was also President of the Kew Guild, The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London, England (1913). Goldring's work included many private houses, hospitals, asylums and public parks in England, Wales, India, and the United States of America. He is responsible for work on nearly 700 different garden landscape projects in England alone. Goldring was born at West Dean, West Sussex, West Dean, near Chichester. He died near Kew after suffering from asthma and bronchial problems. Notable projects Great Britain * Cobham Hall, Maidstone, Kent * Dorchester Borough Gardens, Dorset * Godinton House, Kent * Hatfield House, Hertford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhajja
A ''chhajja'' is an overhanging eave or roof covering found in Indian architecture. It is characterised with large support brackets with different artistic designs. Variation is also seen in its size depending on the importance of the building on which it features or the choice of the designer. Its function is similar to that of other overhangs or eaves in that it protects and adorns entrances, arches and windows from the outside elements. Some styles of roof can be considered large chhajja as well. History Although there is no conclusive agreement on when the chhajja emerged as an architectural element, it can be traced back to before the rise of the Mughal Empire in India. However, much of its popular use seems to be during this time. The original inspiration of the chhajja and much of the other Indian architectural elements with which it is commonly not seen can be traced back to building design from older periods, such as that of bamboo and thatch village huts that can still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porte-cochère
A porte-cochère (; , late 17th century, literally 'coach gateway'; plural: porte-cochères, portes-cochères) is a doorway to a building or courtyard, "often very grand," through which vehicles can enter from the street or a covered porch-like structure at a main or secondary entrance to a building through which originally a horse and carriage and today a motor vehicle can pass to provide arriving and departing occupants protection from the elements. Portes-cochères are still found on such structures as major public buildings and hotels, providing covered access for visitors and guests arriving by motorized transport. A porte-cochère, a structure for vehicle passage, is to be distinguished from a portico, a columned porch or entry for human, rather than vehicular, traffic. History The porte-cochère was a feature of many late 18th- and 19th-century mansions and public buildings. A well-known example is at Buckingham Palace in London. A portico at the White House in Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to Spain, France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact. Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion (architecture), proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts, as demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflict. It was officially established on 8 October 1932 as an auxiliary air force of the British Empire which honoured India's aviation service during World War II with the prefix ''Royal''. After India gained independence from United Kingdom in 1947, the name Royal Indian Air Force was kept and served in the name of Dominion of India. With the government's transition to a Republic in 1950, the prefix ''Royal'' was removed. Since 1950, the IAF has been involved in four wars with neighbouring Pakistan. Other major operations undertaken by the IAF include Operation Vijay, Operation Meghdoot, Operation Cactus and Operation Poomalai. The IAF's mission expands beyond engagement with hostile forces, with the IAF particip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III
Sayajirao Gaekwad III (born Shrimant Gopalrao Gaekwad; 11 March 1863 – 6 February 1939) was the Maharaja of Baroda State from 1875 to 1939, and is remembered for reforming much of his state during his rule. He belonged to the royal Gaekwad dynasty of the Marathas which ruled parts of present-day Gujarat. Early life Sayajirao was born in a maratha family in the village of Kavlana in Malegaon taluka of Nashik district, as Gopalrao Gaekwad, second son of Kashirao Bhikajirao Dada Sahib Gaekwad (1832–1877) and Ummabai. His branch of the Gaekwad dynasty was a cadet branch descended from a morganatic marriage of the first Raja of Baroda and so was not expected to succeed to the throne. Matters of succession Following the death of Sir Khanderao Gaekwad (1828–1870), the popular Maharaja of Baroda, in 1870, it was expected that his brother, Malharrao (1831–1882), would succeed him. However, Malharrao had already proven himself to be of the vilest character and had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanderao II Gaekwad
Shrimant Maharaja Sir Khanderao II Gaekwad, Sena Khas Khel Shamsher Bahadur, GCSI (1828–1870) was the Maharaja of Baroda State from 1856 to 1870.Indian States: A Biographical, Historical, and Administrative Survey by Arnold Wright - 1922 - Page 833 Early life He was born in 1828. Reign He was the third son of Maharaja Sayaji Rao Gaekwad II. He succeeded to the throne on the death of his eldest brother and the king Ganpat Rao Gaekwad on 19 November 1856 and reigned till his death on 28 November 1870. He was knighted as GCSI in 1861. He commissioned the Pearl Carpet of Baroda, which he intended to donate to Prophet Muhammad's Tomb in Medina, however he died before the donation could take place. He died suddenly in 1870 and was succeeded by his brother Malharrao Gaekwad but Malharrao was later deposed by British and widow of Kanderao II, Maharani Jamnabai Sahib Gaekwad, later adopted a boy from the related family, who became the next ruler of Baroda State - Sayajirao Gae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)