|
Maipurean
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawakan Vs
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro-Arawakan
Macro-Arawakan is a proposed language family of South America and the Caribbean centered on the Arawakan languages Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branc .... Sometimes, the proposal is called Arawakan, and the central family is called ''Maipurean''. Proposals Kaufman (1990) includes the following: * Arawakan (Maipurean) * Arawan * Guajiboan * Candoshi Payne (1991) and Derbyshire (1992) have: * Arawakan (Maipurean) * Arawan * Guajiboan * Puquina * Harakmbet Jolkesky (2016) argues for the following: * Arawakan (Maipurean) * Candoshi * Puquina * Munichi According to Jolkesky (op. cit., 611-616), the proto-Macro-Arawakan language would have been spoken in the Middle Ucayali River Basin during the beginning of the 2nd millennium BCE, and its speakers would have produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro-Arawakan Languages
Macro-Arawakan is a proposed language family of South America and the Caribbean centered on the Arawakan languages. Sometimes, the proposal is called Arawakan, and the central family is called ''Maipurean''. Proposals Kaufman (1990) includes the following: *Arawakan (Maipurean) * Arawan *Guajiboan *Candoshi Payne (1991) and Derbyshire (1992) have: *Arawakan (Maipurean) * Arawan *Guajiboan *Puquina * Harakmbet Jolkesky (2016) argues for the following: *Arawakan (Maipurean) *Candoshi *Puquina * Munichi According to Jolkesky (op. cit., 611-616), the proto-Macro-Arawakan language would have been spoken in the Middle Ucayali River Basin during the beginning of the 2nd millennium BCE, and its speakers would have produced Tutishcainyo pottery in the region. Martins (2005: 342–370) groups the Arawakan and Nadahup languages The Naduhup languages, also known as Makú (Macú) or ''Vaupés–Japurá'', form a small language family in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. The name '' M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maipure Language
Maipure (Maypure, Mejepure), was a language once spoken along the Ventuari, Sipapo, and Autana rivers of Amazonas and, as a lingua franca, in the Upper Orinoco region. It became extinct around the end of the eighteenth century. Zamponi provided a grammatical sketch of the language and furnished a classified word list, based on all of its extant eighteenth century material (mainly from the Italian missionary Filippo S. Gilij). It is historically important in that it formed the cornerstone of the recognition of the Maipurean (Arawakan) language family. Kaufman (1994) gives its closest relatives as Yavitero and other languages of the Orinoco branch of Upper Amazon Arawakan The Upper Amazon Maipurean languages, a.k.a. North Amazonian or Inland Northern Maipuran, are Arawakan languages of the northern Amazon in Colombia, Venezuela, Peru, and Brazil. Upper Amazon Arawakan has been surveyed comprehensively by Henri Ram .... Aikhenvald places it instead in the Western Nawiki bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawa Languages
Arawan (also Arahuan, Arauan, Arawán, Arawa, Arauán) is a family of languages spoken in western Brazil ( Amazonas, Acre) and Peru (Ucayali). Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Chapakura-Wañam, Jivaro, Kwaza, Maku, Mura-Matanawi, Taruma, Yanomami, Arawak, Nadahup, Puinave-Kak, and Tupi language families due to contact. Family division Arauan consists of half a dozen languages: * Arawá † * Kulina * Deni * Jamamadi * Paumari * Suruwahá Jolkesky (2016) Internal classification by Jolkesky (2016):Jolkesky, Marcelo Pinho De Valhery. 2016. Estudo arqueo-ecolinguístico das terras tropicais sul-americanas'. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Brasília. († = extinct) ;Arawa *'' Suruwaha'' *Madi-Deni-Paumari **'' Paumari'' **'' Deni'', '' Kulina'' **Madi-Arawa ***'' Arawa'' † ***Madi: '' Banawa''; '' Jamamadi''; '' Jarawara'' Dienst (2010) Internal classification by Dienst (2010): ;Arawan *'' Arawa'' † *'' Pau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bora-Muinane Languages
Boran (also known as Bora–Muinane, Bora–Muiname, Bóran, Miranyan, Miranya, Bórano) is a small language family, consisting of just two languages. Languages The two Boran languages are: * Bora (also known as Bora–Miranya, Boro, Meamuyna) of western Brazil ( Amazonas State) *Muinane (also known as Bora Muinane, Muinane Bora, Muinani, Muename) of southwestern Colombia (Amazonas Department) Loukotka (1968) also lists Nonuya, spoken at the sources of the Cahuinari River, as a Boran language. Only a few words were documented. Synonymy note: * The name ''Muiname'' has been used to refer to the ''Muinane language (Bora Muinane)'' of the Boran family and also to the '' Nipode language (Witoto Muinane)'' of the Witotoan family. Genetic relations Aschmann (1993) proposed that the Boran and Witotoan language families were related, in a '' Bora–Witoto'' stock. Echeverri & Seifart (2016) refute the connection. Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guahibo Languages
Guajiboan (also Guahiban, Wahívoan, Guahiboan) is a language family spoken in the Orinoco River region in eastern Colombia and southwestern Venezuela, a savanna region known as the Llanos. Family division Guajiboan consists of 5 languages: * Macaguane (also known as Hitnü, Macaguán, Makawane, Agualinda, Agualinda Guahibo, Támude) * Southwest Guajiboan ** Guayabero (also known as Cunimía, Mítiwa, Mitúa, Mitu, Hiw, Jiw, Wayavero, Guaviare) ** Churuya (also known as Bisanigua, Guaigua) ''(†)'' * Central Guajiboan ** Guajibo (also known as Guahibo, Sikuani, Sicuani, Chiricoa, Hiwi, Jiwi, Jivi, Wahivo, Wahibo, Guaybo, Goahibo, Guaigua, Guayba, Goahiva) *** Waü (west) *** Newütjü (also known as Tigrero) *** Parawá (east) *** Hamorúa (also known as Amorúa, Jamorúa) *** Dome (also known as Playero, Cajaro) ** Cuiva (also known as Wamonae, Cuiba, Kuiba, Deja, Cuiba-Wámonae) *** Pimenepiwi (Meta river) *** Aitopiwi (Ariporo river) *** Yaraüraxi (Capanaparo river) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harakmbet Languages
The Harakmbut (Arakmbut, Harakmbet) are indigenous people in Peru. They speak the Harakmbut language. An estimated 2,000 Harakmbut people live in the Madre de Dios Region near the Brazilian border in the Peruvian Amazon."Peru: Indigenous Harakmbut Suffer Effects Of Climate Change." ''Indigenous Peoples Issues and Resources.'' (retrieved 20 Feb 2011) Amarakaeri 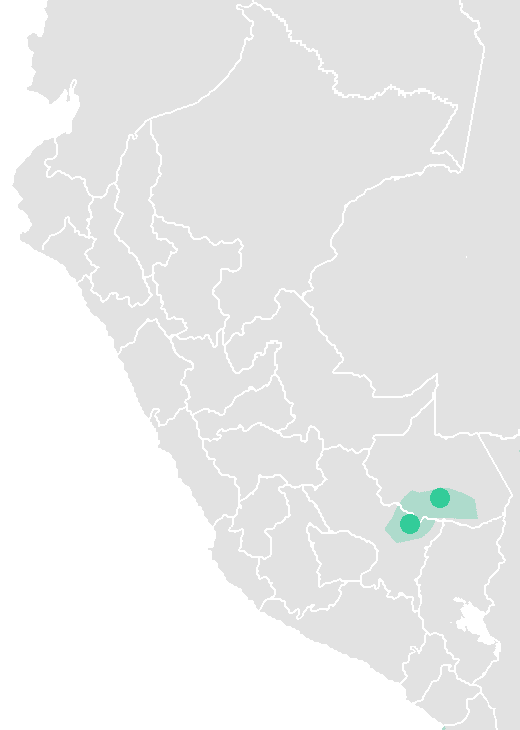 Amarakaeri are also called Amaracaire or Amarakaire people. Subg ...
Amarakaeri are also called Amaracaire or Amarakaire people. Subg ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austroasiatic Languages
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are the majority languages of Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 117 million speakers of Austroasiatic languages. Of these languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have a long-established recorded history. Only two have official status as modern national languages: Vietnamese in Vietnam and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand. In Myanmar, the Wa language is the de facto official language of Wa State. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The rest of the languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status. '' Ethnologue'' identifies 168 Austroasiatic languages. These form thirteen established families (plus perhaps Shompen, which is poorly atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katukina-Katawixi Languages
Katukinan (Catuquinan) is a language family consisting of two languages in Brazil, Katukina-Kanamarí and the perhaps moribund Katawixi. It is often not clear which names in the literature, which are generally tribal names and often correspond to dialects, refer to distinct languages. Indeed, they're close enough that some consider them all to be dialects of a single language, Kanamari (Fabre 2005). Campbell (2012) note that Adelaar "presents reasonably persuasive evidence that Harákmbut and Katukinan are genetically related." Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Jivaro, Máku, Mura-Matanawi, Puinave-Nadahup, Taruma, Tupi, Yanomami, and Arawak language families due to contact. This suggests that Katukinan and the language families with which it was in contact with had been earlier spoken within a central Amazon interaction sphere. Languages and dialects Many ethnic Katukina had shifted to other languages by the time of Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

