|
Mahanavika Buddhagupta
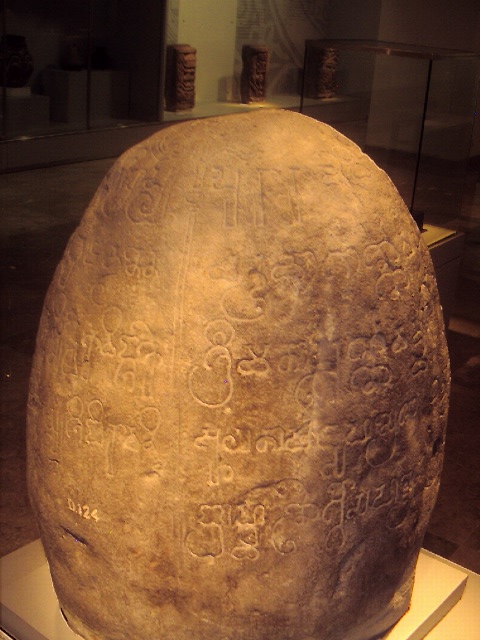
The Mahanavika Buddhagupta ("Great Navigator Buddhagupta") stone inscription, is a 5th-century CE Buddhist stone inscription found in the Seberang Perai, Wellesley Province, Penang, Malaysia. It was discovered in 1834 by Captain James Low (East India Company officer), James Low, of the East India Company. The plaque is in schist, 8–9 cm wide, and 66 cm high. It is today in the Indian Museum in Kolkata. The plate features the illustration of a Buddhist stupa. The script is Brahmi from South India, and very similar to the script of the inscription of King Purnavarman. Buddhagupta declares in his inscription that he is from Raktamartikka, thought to be Rajbadidanga in Bengal. The stele examplifies the links between India and Southeast Asia and that early time, as well as the link between trade and Buddhism. Another inscription by Mahanavika Buddhagupta, the "Sungai Mas Buddhist stele", was found in Kampong Sungai Mas, Sungai Petani (federal constituency), Sungai Petani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predominantly covering present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. Geographically, it consists of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest river delta in the world and a section of the Himalayas up to Nepal and Bhutan. Dense woodlands, including hilly rainforests, cover Bengal's northern and eastern areas, while an elevated forested plateau covers its central area; the highest point is at Sandakphu. In the littoral southwest are the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest. The region has a monsoon climate, which the Bengali calendar divides into six seasons. Bengal, then known as Gangaridai, was a leading power in ancient South Asia, with extensive trade networks forming connections to as far away as Roman Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century Inscriptions
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century Buddhism
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through AD 500, 500 (Roman numerals, D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and Sack of Rome (410), ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa (Roman province), Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bujang Valley
The Bujang Valley ( ms, Lembah Bujang) is a sprawling historical complex and has an area of approximately situated near Merbok, Kedah, between Gunung Jerai in the north and Muda River in the south. It is the richest archaeological area in Malaysia. These archaeological remains show that there was a Buddhist polity here. In Sanskrit the term ''bhujanga'' refer to serpent, thus the name itself is roughly translated into "Serpent Valley". The area consists of ruins that may date more than 2,535 years old. More than fifty ancient pagoda temples, called '' candi'' (pronounced as "chandi"), have also been unearthed. The most impressive and well-preserved of these is located in Pengkalan Bujang, Merbok. The Bujang Valley Archaeological Museum is also located that known as Sungai Batu, excavations have revealed jetty remains, iron-smelting sites, and a clay brick monument dating back to AD 110, making it the oldest man-made structure to be recorded in Southeast Asia. The local rulers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In Malaysia
Buddhism is the second largest religion in Malaysia, after Islam, with 19.8% of Malaysia's population being Buddhist, although some estimates put that figure at 21.6% when combining estimates of numbers of Buddhists with figures for adherents of Chinese religions which incorporate elements of Buddhism. Buddhism in Malaysia is mainly practised by the ethnic Malaysian Chinese, but there are also Malaysian Siamese, Malaysian Sri Lankans and Burmese in Malaysia that practice Buddhism such as Ananda Krishnan and K. Sri Dhammananda and a sizeable population of Malaysian Indians. History Buddhism was introduced to the Malays and also to the people of the Malay Archipelago as early as 200 BCE. Chinese written sources indicated that some 30 small Indianised states rose and fell in the Malay Peninsula. Malay-Buddhism began when Indian traders and priests traveling the maritime routes and brought with them Indian concepts of religion, government, and the arts. For many centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merbok
Merbok is a mukim in Kuala Muda District, Kedah, Malaysia. The historical Bujang Valley is located here. It is also the location for the Universiti Teknologi MARA Kedah Campus (UiTM Merbok/Sungai Petani). Etymology The town derived its name from an archaic Langkasuka-Malay language, which means "the declaratory place". Based on the ancient Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa, the declaration of Islam being the state religion of the Kedah Kingdom By around 788 BCE, a large settlement had been established on the northern bank of the Merbok River. The settlement was one of several in the Bujang Valley, covering the Merbok and Muda Rivers, about 1000 square miles. The Merbok settlement wa ... was done in Merbok estuary port, which situated close to the kingdom's capital during the area, ''Bukit Meriam'' (Cannon Hill). This is in contrast from the popular belief that the name owed its origin from the local ''burung merbok'' ( zebra dove). External links Suara burung website Suara burung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedah
Kedah (), also known by its honorific Darul Aman (Islam), Aman and historically as Queda, is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and it consists of the mainland and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is an archipelago, most of which are uninhabited islands. Kedah was previously known as Kadaram (; ') by the ancient and medieval Tamils, Kataha or Kalahbar (; ' or ; ') by the Arabs, and ''Syburi'' ( th, ไทรบุรี; ) by the Thai people, Siamese when it was under their influence. To the north, Kedah borders the state of Perlis and shares an international boundary with the Songkhla Province, Songkhla and Yala Province, Yala provinces of Thailand. It borders the states of Perak to the south and Penang to the southwest. The state's capital is Alor Setar and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sungai Petani (federal Constituency)
Sungai Petani is a federal constituency in Kuala Muda District, Kedah, Malaysia, that has been represented in the Dewan Rakyat since 1959. The federal constituency was created in the 1958 redistribution and is mandated to return a single member to the Dewan Rakyat under the first past the post voting system. Demographics https://live.chinapress.com.my/ge15/parliament/KEDAH History Polling districts According to the federal gazette issued on 31 October 2022, the Sungai Petani constituency is divided into 50 polling districts. Representation history State constituency Current state assembly members Local governments Election results References * {{Malaysian federal constituencies Kedah federal constituencies Constituencies established in 1958 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purnavarman
Purnawarman or Purnavarman is the 5th-century king of Tarumanagara, a Hindu Indianized kingdom, located in modern-day West Java, Jakarta and Banten provinces, Indonesia. Purnawarman reigned during the 5th century, and during his reign he created several stone inscriptions. According to these inscriptions he embarked on hydraulic project and also identified himself to Vishnu, which indicates him and his kingdom were adhering Vishnuite faith. King Purnawarman established a new capital city for the kingdom, located somewhere near present-day Tugu (North Jakarta) or Bekasi. His name in Sanskrit means "perfect shield" or "complete protector". Later series of Tarumanagaran kings are only known from their names, all bears the name ''warman'' (Sanskrit: ''varman'' means "shield" or "protector") which suggests that all of them belongs in the same dynasty. Historiography Purnawarman is the most well known ruler among Tarumanagaran kings, mostly because he extensively created numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seberang Perai
Seberang Perai is a city in the Malaysian state of Penang. It is situated on the Malay Peninsula opposite Penang Island, bordering Kedah to the north and east and Perak to the south. Its city centre is located in Butterworth, while its local authority, the Seberang Perai City Council, is centred near Bukit Mertajam. , Seberang Perai had a population of 815,767, making it the second most populous city in Malaysia. Originally a part of Kedah, the territory containing the present-day city was ceded to the British East India Company in 1800. The British acquired Province Wellesley, as they subsequently named it, to provide more agricultural land and as a defensive bulwark against any cross-strait invasion of Penang Island from the mainland. Since then, it has become part of Penang, which was made a British crown colony in 1867. Seberang Perai has witnessed substantial economic development in the decades after Malaya's independence. Massive industrial estates have been establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmi
Brahmi (; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi [''sc. lipi''], which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T[errien] de Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |