|
Madhu-vidya
Madhu-vidya is described in the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad II.v.1-19, and in the Chandogya Upanishad III 1-5. ''Madhu-vidya'' or 'Honey-knowledge' is that of the supreme Bliss of the Self; it is an important Vedic teaching. This knowledge is meant to be communicated by the teacher to the disciple, by father to the son – who is worthy and inwardly ready. Indra taught ''Madhu-vidya'' to Rishi Dadhichi with a warning that it should not be communicated to anyone else. Vedic background In the Rig Veda, Soma, the Vedic symbol for deep spiritual truth, is addressed as ''Madhu'', the nector or ambrosia, the drink of Immortality sought by both gods and men. Rishi Vamadeva has described how the saving of the knowledge of ''Madhu'' or ''Soma'' Doctrine came to him through a hawk in a sudden flash in his darkest hour. It is believed that Rishi Dadhichi had his ''ashrama'' in Dudheshwara on the banks of Sabarmati River near present-day Ahmedabad. His name appears in the Rig Veda. Dadhic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brihadaranyaka Upanishad
The ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'' ( sa, बृहदारण्यक उपनिषद्, ) is one of the Principal Upanishads and one of the first Upanishadic scriptures of Hinduism. A key scripture to various schools of Hinduism, the ''Brihadaranyaka Upanisad'' is tenth in the Muktikā or "canon of 108 Upanishads". The ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'' is estimated to have been composed about 7th-6th century BCE, excluding some parts estimated to have been composed after the ''Chandogya Upanishad''. The Sanskrit language text is contained within the ''Shatapatha Brahmana'', which is itself a part of the Shukla Yajur Veda. The ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'' is a treatise on Ātman (Self), includes passages on metaphysics, ethics and a yearning for knowledge that influenced various Indian religions, ancient and medieval scholars, and attracted secondary works such as those by Adi Shankara and Madhvacharya. Chronology The chronology of ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'', like other Upa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidya (Knowledge)
''Vidya'' ( sa, विद्या, ) figures prominently in all texts pertaining to Indian philosophy – meaning science, learning, knowledge, and scholarship. Most importantly, it refers to valid knowledge, which cannot be contradicted, and true knowledge, which is the intuitively-gained knowledge of the self. ''Vidya'' is not mere intellectual knowledge, for the Vedas demand understanding. Meaning ''Vidya'' primarily means "correct knowledge" in any field of science, learning, philosophy, or any factual knowledge that cannot be disputed or refuted. Its root is ''vid'' (Sanskrit: विद्), which means "to reason upon", knower, finding, knowing, acquiring or understanding. Hinduism In Hindu philosophy, ''vidyā'' refers to the knowledge of the soul or spiritual knowledge; it refers to the study of the six schools of Hindu philosophy: Nyaya, Yoga, Vaisheshika, Samkhya, Purvamimamsa and Uttaramimamsa. The process of gaining the knowledge of the Atman cannot commence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, magical or spiritual powers. Feuerstein, Georg (2003), ''The Deeper Dimension of Yoga''. Shambala Publications, Boston, MA Some mantras have a syntactic structure and literal meaning, while others do not. The earliest mantras were composed in Vedic Sanskrit in India. At its simplest, the word ॐ (Aum, Om) serves as a mantra, it is believed to be the first sound which was originated on earth. Aum sound when produced creates a reverberation in the body which helps the body and mind to be calm. In more sophisticated forms, mantras are melodic phrases with spiritual interpretations such as a human longing for truth, reality, light, immortality, peace, love, knowledge, and action. Some mantras without literal meaning are musically uplifting an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
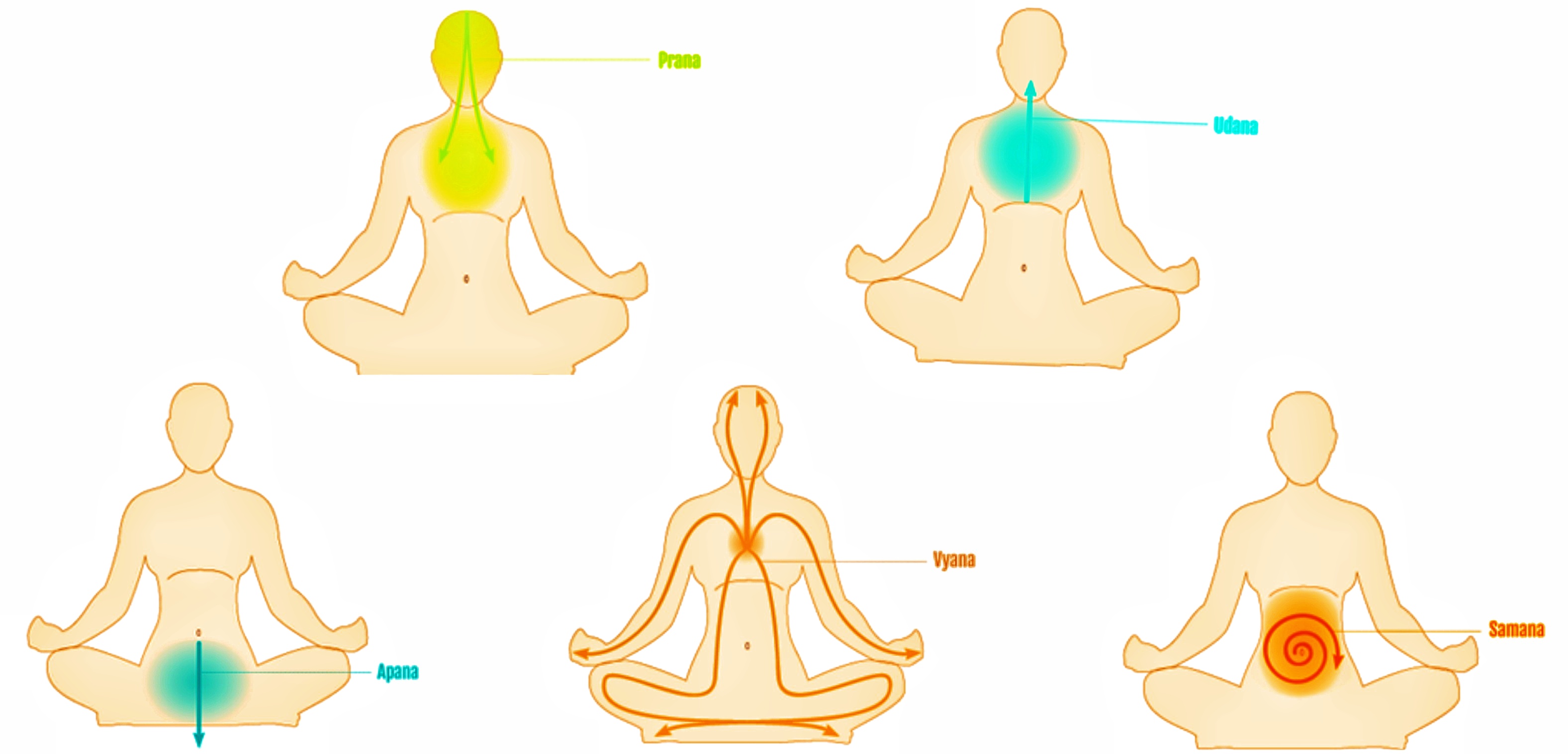
Prana
In yoga, Indian medicine and Indian martial arts, prana ( sa2, प्राण, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five ''vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand prana. Etymology V. S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maruts
In Hinduism, the Maruts (; sa, मरुत), also known as the Marutagana and sometimes identified with Rudras, are storm deities and sons of Rudra and Prisni. The number of Maruts varies from 27 to sixty (three times sixty in RV 8.96.8). They are very violent and aggressive, described as armed with golden weapons i.e. lightning and thunderbolts, as having iron teeth and roaring like lions, as residing in the northwest, as riding in golden chariots drawn by ruddy horses. In the Vedic mythology, the Maruts act as Indra's companions as a troop of young warriors. According to French comparative mythologist Georges Dumézil, they are cognate to the Einherjar and the Wild hunt. In mythology Hymn 66 of Mandala VI of the Rig Veda, the ancient collection of sacred hymns, is an eloquent account of how a natural phenomenon of a rain-storm metamorphoses into storm deities. According to the Rig Veda they wore golden helmets and breastplates, and used their axes to split the clouds so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ādityas
In Hinduism, Adityas ( sa, आदित्य, Āditya, of Aditi, ), refers to the offspring of Aditi, the goddess representing the infinity. The name ''Aditya'', in the singular, is taken to refer to the sun god Surya. Generally, Adityas are twelve in number and consists of Vivasvan, Aryaman, Tvashta, Savitr, Bhaga, Dhata, Mitra, Varuna, Amsa, Pushan, Indra and Vishnu (in the form of Vamana). They appear in the ''Rig Veda'', where there are 6–8 in number, all male. The number increases to 12 in the ''Brahmanas''. The Mahabharata and the ''Puranas'' mention the sage Kashyapa as their father. In each month of the year a different Aditya is said to shine. Sun worship Characterisation The Aditya have been described in the Rig Veda as bright and pure as streams of water, free from all guile and falsehood, blameless, perfect. This class of deities has been seen as upholding the movables and immovable Dharma. Adityas are beneficent gods who act as protectors of all beings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudras
Rudras refer to the forms of the god Rudra, whose traditions have since been associated with Shiva. They make up eleven of the thirty-three gods in the Vedic pantheon.Hopkins pp. 172-3 They are at times identified with the storm deities referred to as Maruts, while at other times considered distinct from them. While the ''Vamana Purana'' describes Rudras as the sons of Kashyapa and Aditi, Maruts are described distinct from the Rudras as the 49 sons of Diti, sister of Aditi, and the attendants of Indra, rather than Rudra. Birth and names The ''Ramayana'' tells they are eleven of the 33 children of the sage Kashyapa and his wife Aditi, along with the 12 Adityas, 8 Vasus and 2 Ashvins, constituting the Thirty-three gods.Mani pp. 654–5 The ''Vamana Purana'' describes the Rudras as the sons of Kashyapa and Aditi. The ''Matsya Purana'' notes that Surabhi – the mother of all cows and the "cow of plenty" – was the consort of Brahma and their union produced the eleven Rudras. Here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasu
The Vasus () refers to a group of deities in Hinduism associated with fire and light. They are described to be the attendant deities of Indra, and later Vishnu. Generally numbering eight and classified as the Ashtavasu, they are described in the Ramayana as the children of Kashyapa and Aditi, and in the Mahabharata as the sons of Manu or Dharma and a daughter of Daksha named Vasu. They are eight among the thirty-three gods featured in the Vedas. Etymology The Sanskrit term ''Vasu''(s) is translated as the "bright ones". List There are varying lists of the eight Vasus in different texts, sometimes only because particular deities have varying names. The following are names and meanings according to the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad, Manava Purana, and according to the Mahabharata, as normally equated: Though the ''Shatapatha Brahmana'' uses the '' Brhad-Aranyaka'' names, most later texts follow the ''Mahabharata'' names with the exception that Āpa 'water' usually appears in place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devatas (Vedanta)
''Devata'' (pl: ''devatas'', meaning 'the gods') (Devanagari: देवता; Khmer: ទេវតា (''tevoda''); Thai: เทวดา (''tevada''); Javanese, Balinese, Sundanese, Malay: ''dewata''; Batak languages: ''debata'' (Toba), ''dibata'' (Karo), ''naibata'' (Simalungun); ''diwata'' (Philippine languages)) are smaller and more focused Devas (Deities) in Indian religions, such as Hinduism and Buddhism. The term "devata" itself can also mean deva. They can be either male or female. Every human activity has its devata, its spiritual counterpart or aspect. Types There are many kinds of devatas: vanadevatas (forest spirits, perhaps descendants of early nature-spirit cults), gramadevata (village gods), devatas of river crossings, caves, mountains, and so on. For example, in the Konkan region of India, Hindu devatas are often divided into five categories: # Grama devatas or village deities who could be the founder deity such as Jathera or ancestral worship of Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prana
In yoga, Indian medicine and Indian martial arts, prana ( sa2, प्राण, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five ''vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand prana. Etymology V. S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ''dharma'' in European languages, it is commonly translated as "righteousness", "merit" or "religious and moral duties" governing individual conduct.Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. (9 April 2019)Dharma. ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Accessed 14 September 2021. In Hinduism, dharma is one of the four components of the ''Puruṣārtha'', the aims of life, and signifies behaviours that are considered to be in accord with '' Ṛta'', the order that makes life and universe possible. It includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and "right way of living".see: *"Dharma", ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th Ed. (2013), Columbia University Press, Gale, ; *Steven Rosen (2006), Essential Hinduism, Praeger, , Chapter 3. It had a transtempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atman (Hinduism)
Atman or Ātman may refer to: Film * ''Ātman'' (1975 film), a Japanese experimental short film directed by Toshio Matsumoto * ''Atman'' (1997 film), a documentary film directed by Pirjo Honkasalo People * Pavel Atman (born 1987), Russian handball player Religion * ''Ātman'' (Jainism), or ''Jīva'', a philosophical term used within Jainism to identify the soul * ''Ātman'' (Hinduism), meaning "Self", a philosophical concept common to all schools of Hindu philosophy * ''Ātman'' (Buddhism), ''attā'' or ''attan'', a reference to the essential self ** '' Anattā'' or ''anātman'' — "not-self", central concept in Buddhism * '' Atman jnana'' — "knowledge" in the context of Indian philosophy and religions See also * Ataman, a title of Cossack and haidamak leaders of various kinds * World Soul (other) World Soul may refer to: * Anima mundi, the "world-soul" in Plato and derived traditions in Western philosophy ** ''Weltseele'' "world-soul" in German philosophy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |