|
Madder Lake (band)
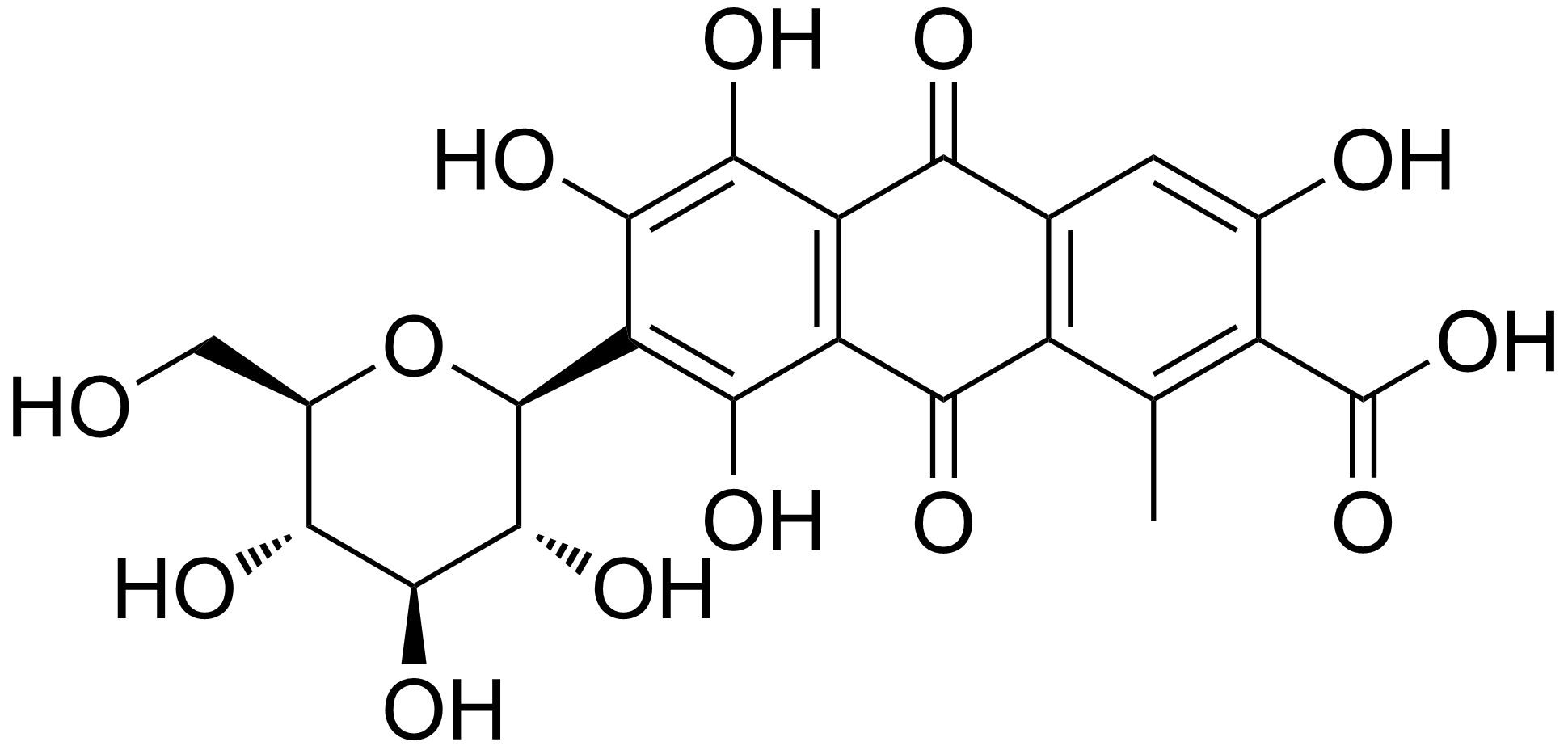
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula . Isomers include various quinone derivatives. The term anthraquinone however refers to the isomer, 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is a building block of many dyes and is used in bleaching pulp for papermaking. It is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite. Synthesis There are several current industrial methods to produce 9,10-anthraquinone: # The oxidation of anthracene. Chromium(VI) is the typical oxidant. # The Friedel-Crafts reaction of benzene and phthalic anhydride in presence of AlCl3. o-Benzoylbenzoic acid is an intermediate. This reaction is useful for produci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List of urban areas in the European Union, largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful Greek city-state, city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum (classical), Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of civilization, cradle of Western culture, Western civilization and the democracy#History, birthplace of democracy, larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal. Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored. Industrial production of chromium proceeds from chromite ore (mostly FeCr2O4) to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paint
Paint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many colors—and in many different types. Paint is typically stored, sold, and applied as a liquid, but most types dry into a solid. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based and each has distinct characteristics. For one, it is illegal in most municipalities to discard oil-based paint down household drains or sewers. Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than they are for oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted (such as a house.) Usually, the object being painted must be over , although some manufacturers of external paints/primers claim they can be applied when temperatures are as low as . History Paint was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word "alkali" is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning ''the calcined ashes'' (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula , where is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula . Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum. The name "alum" is also used, more generally, for salts with the same formula and structure, except that aluminium is replaced by another trivalent metal ion like chromium, and/or sulfur is replaced by another chalcogen like selenium. The most common of these analogs is chrome alum . In most industries, the name "alum" (or "papermaker's alum") is used to refer to aluminium sulfate, , which is used for most industrial flocculation (the variable is an integer whose size depends on the amount of water absorbed into the alum). In medicine, "alum" may also refer to aluminium hydroxide gel used as a vaccine adjuvant. History Alum found at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Field (chemist)
George Field (1777?–1854), was an English chemist. He was born in or about 1777 at Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire, of a family long settled in that town, and was educated at St. Peter's school there. When about eighteen years of age he came to London to seek a profession. He thought he saw an opening in the careful application of chemistry to pigments and dyes. War on the continent, by stopping the supply of madder from Holland, threatened to impede his progress. This obstacle, however, led him to consider the nature of its cultivation, and with a well-devised project he waited on Sir Joseph Banks for his advice, and, as he hoped, his co-operation. Sir Joseph, after unsuccessfully attempting to cultivate madder in Essex, had made up his mind that it could not be done in England. Horticulture and inventions Field then commenced the cultivation in his own garden, and from roots of his own growth produced beautiful specimens of colouring matter. A contrivance, both mechanical and chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordant
A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set (i.e. bind) dyes on fabrics by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric (or tissue). It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in cell or tissue preparations. Although mordants are still used, especially by small batch dyers, it has been largely displaced in industry by directs.} The term mordant comes from the Latin ''mordere'', "to bite". In the past, it was thought that a mordant helped the dye bite onto the fiber so that it would hold fast during washing. A mordant is often a polyvalent metal ion, and one example is chromium (III). The resulting coordination complex of dye and ion is colloidal and can be either acidic or alkaline. Common dye mordants Mordants include tannic acid, oxalic acid, alum, chrome alum, sodium chloride, and certain salts of aluminium, chromium, copper, iron, iodine, potassium, sodium, tungsten, and tin. Iodine is often referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alizarin01
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is ''Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A notable use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Coat (British Army)
Red coat, also referred to as redcoat or scarlet tunic, was a military garment which was widely (though not exclusively) used by the infantry units of the British military, including the British Army and Royal Marines, from the 16th to 19th centuries. The garment was also widely used by the British Colonial Auxiliary Forces and the British Indian Army during the 18th and 19th centuries. Though by the 20th centuries the red coat was abandoned for practical duties in favour of khaki by all British and Commonwealth military units, it continues to be used for ceremonial full dress and mess dress uniforms. The usage of red coats by English soldiers dates back to the Tudor period, when the Yeomen of the Guard and the Yeomen Warders were both equipped in the royal colours of the House of Tudor, red and gold. During the Tudor conquest of Ireland and the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, units of English soldiers were equipped in red coats, most notably the New Model Army, which fought o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochineal
The cochineal ( , ; ''Dactylopius coccus'') is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessile parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North America (Mexico and the Southwest United States), this insect lives on cacti in the genus ''Opuntia'', feeding on plant moisture and nutrients. The insects are found on the pads of prickly pear cacti, collected by brushing them off the plants, and dried. The insect produces carminic acid that deters predation by other insects. Carminic acid, typically 17–24% of dried insects' weight, can be extracted from the body and eggs, then mixed with aluminium or calcium salts to make carmine dye, also known as cochineal. Today, carmine is primarily used as a colorant in food and in lipstick (E120 or Natural Red 4). Carmine dye was used in the Americas for coloring fabrics and became an important export good in the 16th century during the colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Wellcome_L0019270.jpg)