|
Macrolepiota Clelandii
''Macrolepiota clelandii'', commonly known as the slender parasol or graceful parasol, is a species of mushroom-forming fungus in the family Agaricaceae. The species is found in Australia and New Zealand, where it fruits singly or in small groups on the ground in eucalypt woodlands, parks, and roadsides. It is a tall mushroom up to roughly , with a broad cap covered with distinctive rings of dark brown scales. The whitish gills on the cap underside are closely spaced and free from attachment to the slender stipe, which has a loose ring on its upper half, and a bulbous base. The edibility of the mushroom is not known with certainty, but closely related parasol mushrooms are edible and some are very sought after. The fungus, first documented by naturalist John Burton Cleland in the early 20th century, was initially assumed to be the close relative ''Macrolepiota procera'', a European species now known to be absent from Australia. Australian mycologist Cheryl Grgurinovic recognized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, ''Agaricus bisporus''; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi ( Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes) that have a stem ( stipe), a cap ( pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing. lamella) on the underside of the cap. "Mushroom" also describes a variety of other gilled fungi, with or without stems, therefore the term is used to describe the fleshy fruiting bodies of some Ascomycota. These gills produce microscopic spores that help the fungus spread across the ground or its occupant surface. Forms deviating from the standard morphology usually have more specific names, such as "bolete", "puffball", "stinkhorn", and " morel", and gilled mushrooms themselves are often called "agarics" in refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Name
A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the '' International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar or Group epithets must conform to the ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants'' (ICNCP). The code of nomenclature covers "all organisms traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants, whether fossil or non-fossil, including blue-green algae ( Cyanobacteria), chytrids, oomycetes, slime moulds and photosynthetic protists with their taxonomically related non-photosynthetic groups (but excluding Microsporidia)." The purpose of a formal name is to have a single name that is accepted and used worldwide for a particular plant or plant group. For example, the botanical name ''Bellis perennis'' denotes a plant species which is native to most of the countries of Europe and the Middle East, where it has accumulated various names in many languages. Later, the plant was intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
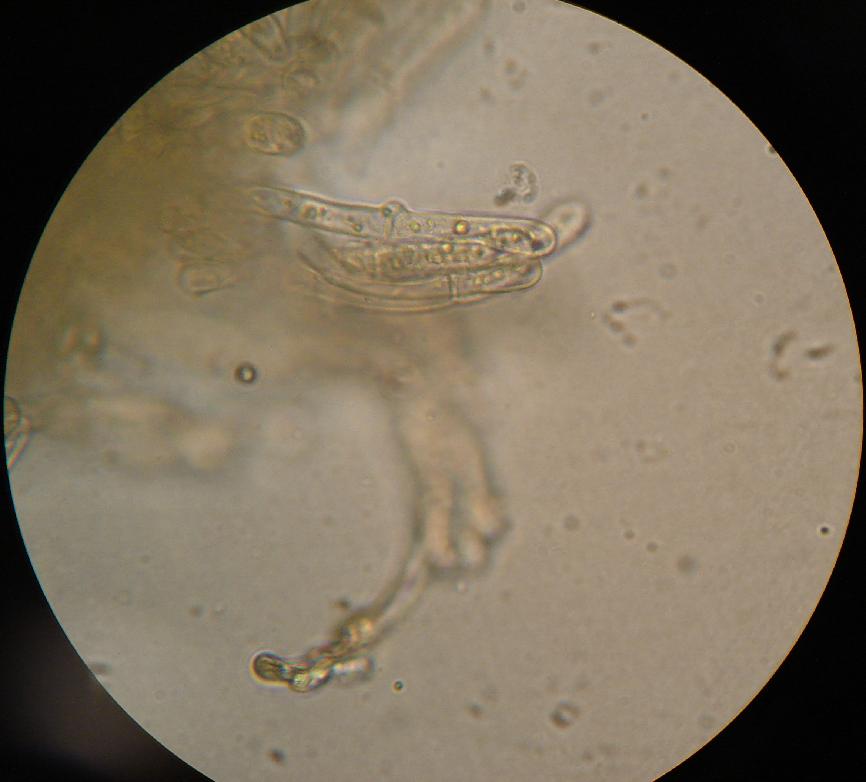
Hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. The S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp Connection
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in crozier (hook) during sexual reproduction. Formation Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes mitotic division to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the remaining nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucocoprinus
''Leucocoprinus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Agaricaceae. Its best-known member is the distinctive yellow mushroom '' Leucocoprinus birnbaumii'', which is found in plant pots and greenhouses worldwide. The type species is '' Leucocoprinus cepistipes''. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains over 80 recognised species, however many of these species are very scarcely recorded and little known with only a small number of ''Leucocoprinus'' species which are commonly observed. The majority of the species in this genus are exclusive to tropical environments however numerous species have become a common sight in plant pots and greenhouses resulting in them becoming well known worldwide. It is likely that some of the observations for these common species are misidentified with observations for ''L. birnbaumii'' in particular often being conflated with other species simply because it is better known or more frequently suggested by image recognition algorithms. Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucoagaricus
''Leucoagaricus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Agaricaceae. Several fungus-growing ants cultivate multiple species for food. The genus contains approximately 90 species. Taxonomy This group of mushrooms was first defined as a subgenus of ''Leucocoprinus'' by Marcel Locquin in 1945, and it was then elevated to the status of genus by Rolf Singer in the journal ''Sydowia'' in 1948. The group was characterized as belonging to family Agaricaceae with white, dirty cream or pink spores which are generally small (up to 10 µm) but much bigger in one species, with a germ pore, with a pseudo-amyloid multilayered membrane, simple or ornamented, which is metachromatic in cresyl blue. The hyphae in the sporocarp are without clamp connections. There is always a ring which is initially fixed (but later may be movable). The type species is ''Leucoagaricus barssii'' (Zeller) Vellinga, which was formerly called ''L. macrorhizus''. Species Select species include: *''Leucoagaric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Concept
The species problem is the set of questions that arises when biologists attempt to define what a species is. Such a definition is called a species concept; there are at least 26 recognized species concepts. A species concept that works well for sexually reproducing organisms such as birds may be useless for species that reproduce asexually, such as bacteria. The scientific study of the species problem has been called microtaxonomy. One common, but sometimes difficult, question is how best to decide which species an organism belongs to, because reproductively isolated groups may not be readily recognizable, and cryptic species may be present. There is a continuum from '' reproductive isolation'' with no interbreeding, to ''panmixis'', unlimited interbreeding. Populations can move forward or backwards along this continuum, at any point meeting the criteria for one or another species concept, and failing others. Many of the debates on species touch on philosophical issues, such as n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolepiota Dolichaula
''Macrolepiota'' is a genus of white spored, gilled mushrooms of the family Agaricaceae. The best-known member is the parasol mushroom (''M. procera''). The widespread genus contains about 40 species. Taxonomy ''Macrolepiota'' was circumscribed by Rolf Singer in 1948, with ''Macrolepiota procera'' as the type species. DNA studies have split this genus into three clades. The macrolepiota clade includes ''M. procera, M. clelandii'', ''M. dolichaula'' and closely related species. The macrosporae clade includes species such as ''M. mastoidea'', ''M. konradii'', and ''M. orientiexcoriata'', while the volvatae clade includes ''M. velosa'' and ''M. eucharis''. Uses ''Macrolepiota procera'', the parasol mushroom, is a well-known and highly esteemed edible species in much of Europe.Parasol Mushroom - Private mushroom record of Józef Bossowski ''Macrolepiota albuminosa'' is eaten in Chinese cuisine, where it is called ''jīzōng'' ( 鸡枞; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolepiota Mastoidea
''Macrolepiota mastoidea'' is a species of mushroom producing fungus in the family Agaricaceae. Taxonomy It was first described by many mycologists throughout the 1800s and classified variously as ''Agaricus gracilentus'', ''Agaricus mastoideus'', ''Agaricus umbonatus'' with each synonym then undergoing its own extensive period of reclassification. It got its current name ''Macrolepiota mastoidea'' in 1951 when classified by the German mycologist Rolf Singer. Habitat and distribution This species is found in Europe. Edibility This is reported to be an edible species but it is noted that it can appear similar to some toxic ''Chlorophyllum ''Chlorophyllum'' is a genus of large agarics similar in appearance to the true parasol mushroom. ''Chlorophyllum'' was originally coined in 1898, a time when spore color was the deciding factor for differentiating genera. It was termed in order ...'' species so caution is recommended. References External links * Edible fungi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolepiota Gracilenta
''Macrolepiota'' is a genus of white spored, gilled mushrooms of the family Agaricaceae. The best-known member is the parasol mushroom (''M. procera''). The widespread genus contains about 40 species. Taxonomy ''Macrolepiota'' was circumscribed by Rolf Singer in 1948, with ''Macrolepiota procera'' as the type species. DNA studies have split this genus into three clades. The macrolepiota clade includes ''M. procera, M. clelandii'', ''M. dolichaula'' and closely related species. The macrosporae clade includes species such as ''M. mastoidea'', ''M. konradii'', and ''M. orientiexcoriata'', while the volvatae clade includes ''M. velosa'' and ''M. eucharis''. Uses ''Macrolepiota procera'', the parasol mushroom, is a well-known and highly esteemed edible species in much of Europe.Parasol Mushroom - Private mushroom record of Józef Bossowski ''Macrolepiota albuminosa'' is eaten in Chinese cuisine, where it is called ''jīzōng'' ( 鸡枞; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.png)