|
Macroblocking
The macroblock is a processing unit in image and video compression formats based on linear block transforms, typically the discrete cosine transform (DCT). A macroblock typically consists of 16×16 samples, and is further subdivided into transform blocks, and may be further subdivided into prediction blocks. Formats which are based on macroblocks include JPEG, where they are called MCU blocks, H.261, MPEG-1 Part 2, H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2, H.263, MPEG-4 Part 2, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. In H.265/HEVC, the macroblock as a basic processing unit has been replaced by the coding tree unit. Technical details Transform blocks A macroblock is divided into transform blocks, which serve as input to the linear block transform, e.g. the DCT. In H.261, the first video codec to use macroblocks, transform blocks have a fixed size of 8×8 samples. In the YCbCr color space with 4:2:0 chroma subsampling, a 16×16 macroblock consists of 16×16 luma (Y) samples and 8×8 chroma (Cb and Cr) samples. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixelation
In computer graphics, pixelation (or pixellation in British English) is caused by displaying a bitmap or a section of a bitmap at such a large size that individual pixels, small single-colored square display elements that comprise the bitmap, are visible. Such an image is said to be pixelated ( pixellated in the UK). Early graphical applications such as video games ran at very low resolutions with a small number of colors, resulting in easily visible pixels. The resulting sharp edges gave curved objects and diagonal lines an unnatural appearance. However, when the number of available colors increased to 256, it was possible to gainfully employ anti-aliasing to smooth the appearance of low-resolution objects, not eliminating pixelation but making it less jarring to the eye. Higher resolutions would soon make this type of pixelation all but invisible on the screen, but pixelation is still visible if a low-resolution image is printed on paper. In the realm of real-time 3D c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Artifact
A compression artifact (or artefact) is a noticeable distortion of media (including images, audio, and video) caused by the application of lossy compression. Lossy data compression involves discarding some of the media's data so that it becomes small enough to be stored within the desired disk space or transmitted (''streamed'') within the available bandwidth (known as the data rate or bit rate). If the compressor cannot store enough data in the compressed version, the result is a loss of quality, or introduction of artifacts. The compression algorithm may not be intelligent enough to discriminate between distortions of little subjective importance and those objectionable to the user. The most common digital compression artifacts are DCT blocks, caused by the discrete cosine transform (DCT) compression algorithm used in many digital media standards, such as JPEG, MP3, and MPEG video file formats. These compression artifacts appear when heavy compression is applied, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior results compared with generic data compression methods which are used for other digital data. Lossy and lossless image compression Image compression may be lossy or lossless. Lossless compression is preferred for archival purposes and often for medical imaging, technical drawings, clip art, or comics. Lossy compression methods, especially when used at low bit rates, introduce compression artifacts. Lossy methods are especially suitable for natural images such as photographs in applications where minor (sometimes imperceptible) loss of fidelity is acceptable to achieve a substantial reduction in bit rate. Lossy compression that produces negligible differences may be called visually lossless. Methods for lossy compression: * Tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter Frame
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of ''Inter frame prediction''. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage from temporal redundancy between neighboring frames enabling higher compression rates. Inter frame prediction An inter coded frame is divided into blocks known as macroblocks. After that, instead of directly encoding the raw pixel values for each block, the encoder will try to find a block similar to the one it is encoding on a previously encoded frame, referred to as a reference frame. This process is done by a block matching algorithm. If the encoder succeeds on its search, the block could be encoded by a vector, known as motion vector, which points to the position of the matching block at the reference frame. The process of motion vector determination is called motion estimation. In most cases the encoder will succeed, but the block f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deblocking Filter
A deblocking filter is a video filter applied to decoded compressed video to improve visual quality and prediction performance by smoothing the sharp edges which can form between macroblocks when block coding techniques are used. The filter aims to improve the appearance of decoded pictures. It is a part of the specification for both the SMPTE VC-1 codec and the ITU H.264 (ISO MPEG-4 AVC) codec. H.264 deblocking filter In contrast with older MPEG- 1/ 2/ 4 standards, the H.264 deblocking filter is not an optional additional feature in the decoder. It is a feature on both the decoding path and on the encoding path, so that the in-loop effects of the filter are taken into account in reference macroblocks used for prediction. When a stream is encoded, the filter strength can be selected, or the filter can be switched off entirely. Otherwise, the filter strength is determined by coding modes of adjacent blocks, quantization step size, and the steepness of the luminance gradient be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression Picture Types
In the field of video compression a video frame is compressed using different algorithms with different advantages and disadvantages, centered mainly around amount of data compression. These different algorithms for video frames are called picture types or frame types. The three major picture types used in the different video algorithms are I, P and B. They are different in the following characteristics: * I‑frames are the least compressible but don't require other video frames to decode. * P‑frames can use data from previous frames to decompress and are more compressible than I‑frames. * B‑frames can use both previous and forward frames for data reference to get the highest amount of data compression. Summary Three types of ''pictures'' (or frames) are used in video compression: I, P, and B frames. An I‑frame ( Intra-coded picture) is a complete image, like a JPG or BMP image file. A P‑frame (Predicted picture) holds only the changes in the image from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coding Tree Unit
Coding tree unit (CTU) is the basic processing unit of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) video standard and conceptually corresponds in structure to macroblock units that were used in several previous video standards. CTU is also referred to as largest coding unit (LCU). A CTU can be between 16×16 pixels and 64×64 pixels in size with a larger size usually increasing coding efficiency. The first video standard that uses CTUs is HEVC/H.265 which became an ITU-T standard on April 13, 2013. History Macroblock encoding methods have been used in digital video coding standards since H.261 which was first released in 1988. However, for error correction and signal-to-noise ratio the standard 16x16 macroblock size is not capable of getting the kind of bit reductions that information theory and coding theory suggest are theoretically and practically possible. Technical details HEVC replaces macroblocks, which were used with previous video standards, with CTUs which can use larger blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
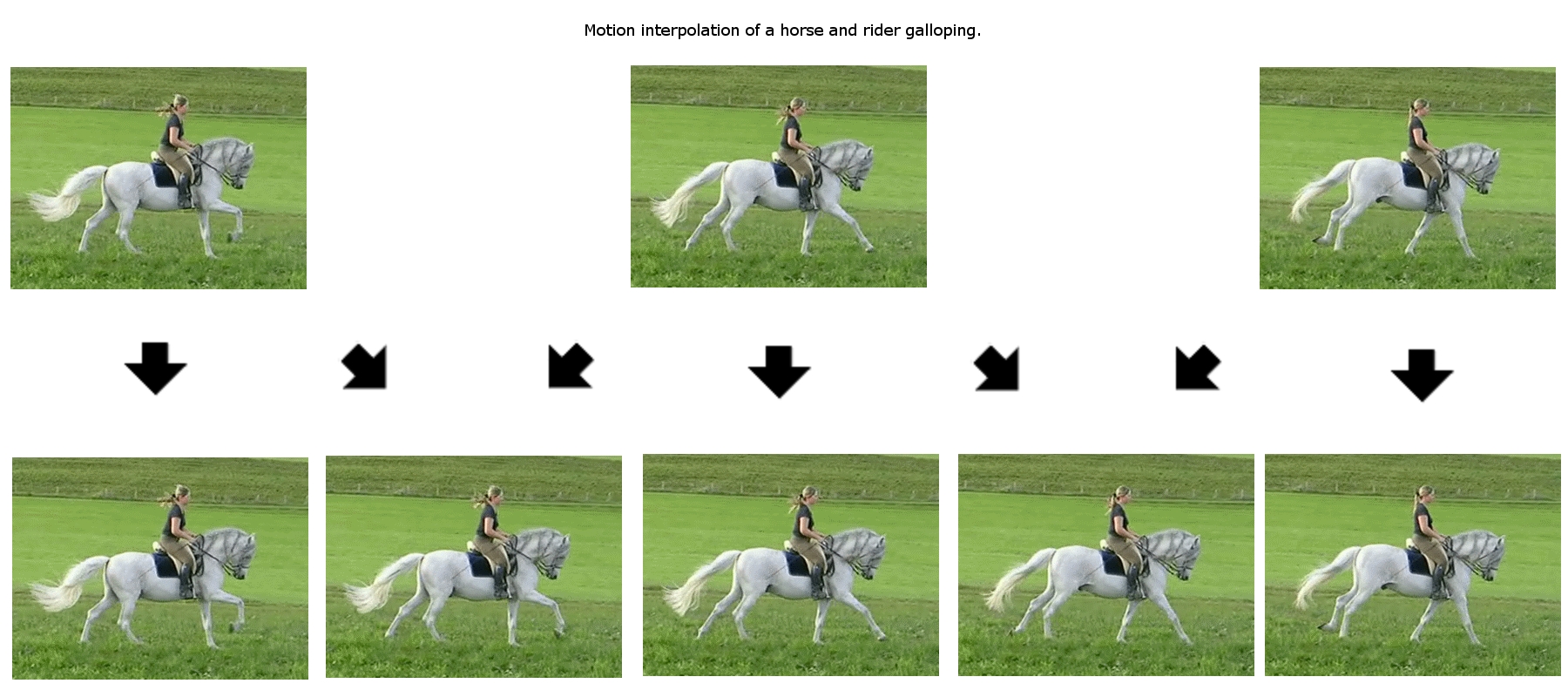
Motion Vector
Motion estimation is the process of determining ''motion vectors'' that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent frames in a video sequence. It is an ill-posed problem as the motion is in three dimensions but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D plane. The motion vectors may relate to the whole image (global motion estimation) or specific parts, such as rectangular blocks, arbitrary shaped patches or even per pixel. The motion vectors may be represented by a translational model or many other models that can approximate the motion of a real video camera, such as rotation and translation in all three dimensions and zoom. Related terms More often than not, the term motion estimation and the term ''optical flow'' are used interchangeably. It is also related in concept to '' image registration'' and ''stereo correspondence''. In fact all of these terms refer to the process of finding corresponding points between two images or vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-frame
In the field of video compression a video frame is compressed using different algorithms with different advantages and disadvantages, centered mainly around amount of data compression. These different algorithms for video frames are called picture types or frame types. The three major picture types used in the different video algorithms are I, P and B. They are different in the following characteristics: * I‑frames are the least compressible but don't require other video frames to decode. * P‑frames can use data from previous frames to decompress and are more compressible than I‑frames. * B‑frames can use both previous and forward frames for data reference to get the highest amount of data compression. Summary Three types of ''pictures'' (or frames) are used in video compression: I, P, and B frames. An I‑frame ( Intra-coded picture) is a complete image, like a JPG or BMP image file. A P‑frame (Predicted picture) holds only the changes in the image from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intra Frame
Intra-frame coding is a data compression technique used within a video frame, enabling smaller file sizes and lower bitrates, with little or no loss in quality. Since neighboring pixels within an image are often very similar, rather than storing each pixel independently, the frame image is divided into blocks and the typically minor difference between each pixel can be encoded using fewer bits. Intra-frame prediction exploits spatial redundancy, i.e. correlation among pixels within one frame, by calculating prediction values through extrapolation from already coded pixels for effective delta coding. It is one of the two classes of predictive coding methods in video coding. Its counterpart is inter-frame prediction which exploits temporal redundancy. Temporally independently coded so-called intra frames use only intra coding. The temporally coded predicted frames (e.g. MPEG's P- and B-frames) may use intra- as well as inter-frame prediction. Usually only few of the spatially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding; encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |