|
Maccabean Wars
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees ( he, מַכַּבִּים, or , ; la, Machabaei or ; grc, Μακκαβαῖοι, ), were a group of Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. They founded the Hasmonean dynasty, which ruled from 167 BCE to 37 BCE, being a fully independent kingdom from about 110 to 63 BCE. They reasserted the Jewish religion, partly by forced conversion, expanded the boundaries of Judea by conquest and reduced the influence of Hellenism and Hellenistic Judaism. Etymology The name Maccabee is often used as a synonym for the entire Hasmonean dynasty, but the Maccabees proper were Judas Maccabeus and his four brothers. The name Maccabee was a personal epithet of Judah, and the later generations were not his direct descendants. One explanation of the name's origins is that it derives from the Aramaic ''maqqəḇa'', "the hammer", in recognition of Judah's ferocity in battle. The traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maccabean Dynasty
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees ( he, מַכַּבִּים, or , ; la, Machabaei or ; grc, Μακκαβαῖοι, ), were a group of Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. They founded the Hasmonean dynasty, which ruled from 167 BCE to 37 BCE, being a fully independent kingdom from about 110 to 63 BCE. They reasserted the Jewish religion, partly by forced conversion, expanded the boundaries of Judea by conquest and reduced the influence of Hellenism and Hellenistic Judaism. Etymology The name Maccabee is often used as a synonym for the entire Hasmonean dynasty, but the Maccabees proper were Judas Maccabeus and his four brothers. The name Maccabee was a personal epithet of Judah, and the later generations were not his direct descendants. One explanation of the name's origins is that it derives from the Aramaic ''maqqəḇa'', "the hammer", in recognition of Judah's ferocity in battle. The traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epispasm
Foreskin restoration is the process of expanding the skin on the penis to reconstruct an organ similar to the foreskin, which has been removed by circumcision or injury. Foreskin restoration is primarily accomplished by stretching the residual skin of the penis, but surgical methods also exist. Restoration creates a facsimile of the foreskin, but specialized tissues removed during circumcision cannot be reclaimed. Actual regeneration of the foreskin is experimental at this time. Some forms of restoration involve only partial regeneration in instances of a ''high-cut'' wherein the circumcisee feels that the circumciser removed too much skin and that there is not enough skin for erections to be comfortable. History In the Greco-Roman world intact genitals, including the foreskin, were considered a sign of beauty, civility, and masculinity. In Classical Greek and Roman societies (8th century BC to 6th century AD), exposure of the glans was considered disgusting and improper, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (ancient Greece)
The gymnasium ( grc-gre, γυμνάσιον, gymnásion) in Ancient Greece functioned as a training facility for competitors in public games. It was also a place for socializing and engaging in intellectual pursuits. The name comes from the Ancient Greek term '' gymnós'', meaning "naked" or "nude". Only adult male citizens were allowed to use the gymnasia. Athletes competed nude, a practice which was said to encourage aesthetic appreciation of the male body, and to be a tribute to the gods. Gymnasia and palaestrae (wrestling schools) were under the protection and patronage of Heracles, Hermes and, in Athens, Theseus. Etymology The word ''gymnasium'' is the latinisation of the Greek noun γυμνάσιον (''gymnasion''), "public place for physical exercises; exercise area", in pl. "bodily exercises" and generally "school", which in turn is derived from the common Greek adjective (''gymnos'') meaning "naked" or "nude", by way of the related verb γυμνάζω (''gymnazo''), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Tcherikover
Victor A. Tcherikover ( he, אביגדור צ'ריקובר; 1894–1958) was a Russian-born Israeli scholar. Biography Born in Russia, he settled in Palestine in 1925. He was one of the first teachers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and headed the departments of general history and classical studies. He specialized in Jewish history in Palestine and Egypt during the Graeco-Roman period.Tcherikover, Victor ''Hellenistic Civilization and the Jews'', New York: Atheneum, 1975 Publications *''Ha-Yehudim veha-Yevanim ba-tekufah ha-Helenistit'', 1930 *''Hellenistic Civilization and the Jews'', 1959 *''Corpus Papyrorum Judaicarum'' Vol.1, 2 with Alexander Fuks Alexander Fuks (30 May 1917 – 29 November 1978) was a German-born, later Israeli historian, archaeologist and papyrologist. He worked with Victor Tcherikover and Menahem Stern on the standard edition of Jewish papyri. He was a specialist in the ... 1957-1960 - Tcherikover was succeeded for the 3rd volume (1963) by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobiads
The Tobiads were a Jewish faction in Ammon at the beginning of the Hasmonean period. They were philhellene, supporters of Hellenistic Judaism, in the early years of the 2nd century BCE. What is known about the Tobiads is a combination of statements of Josephus ('' Antiquities of the Jews'' xii. 160-236) and of 2 Maccabees . There are two accounts, both legendary, the hero of the one being Joseph, and of the other, Hyrcanus. Narrative During the reign of the Egyptian king Ptolemy and his wife Cleopatra, the high priest Onias, who was feeble-minded and extremely miserly, refused to pay the Jewish tribute of twenty talents which his father, Simon the Just, had always given from his own means. In his anger the king sent Athenion as a special envoy to Jerusalem, threatening to seize the land of the Jews and to hold it by force of arms if the money was not forthcoming. Although the high priest disregarded this threat, the people were greatly excited, whereupon Onias' nephew Joseph, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indus River Valley. The most notable Diadochi include Ptolemy, Antigonus, Cassander, and Seleucus as the last remaining at the end of the Wars of the Successors, ruling in Egypt, Asia-Minor, Macedon and Persia respectively, all forging dynasties lasting several centuries. Background Ancient role In ancient Greek, is a noun (substantive or adjective) formed from the verb, ''diadechesthai'', "succeed to," a compound of ''dia-'' and ''dechesthai'', "receive." The word-set descends straightforwardly from Indo-European *dek-, "receive", the substantive forms being from the o-grade, *dok-. Some important English reflexes are dogma, "a receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
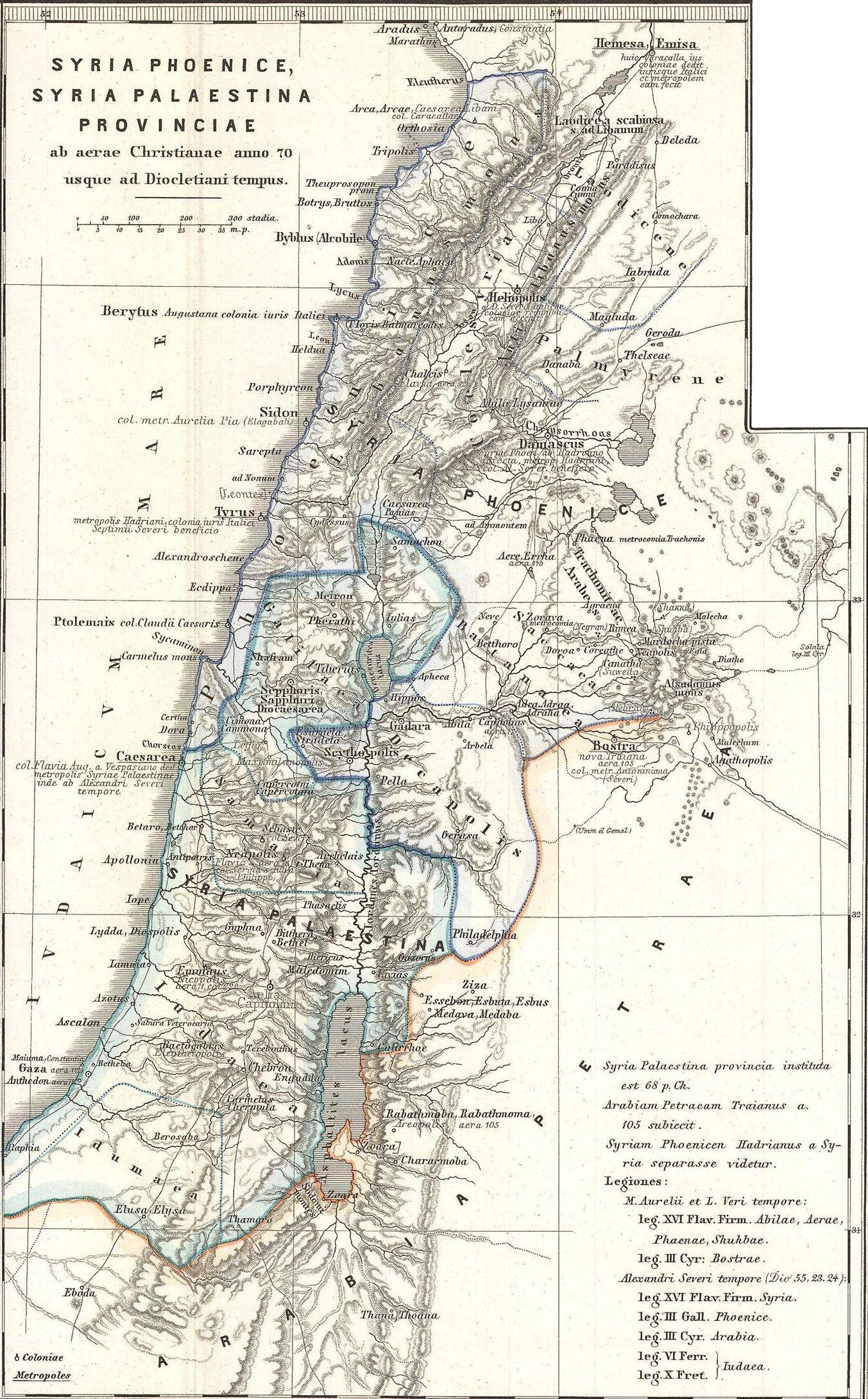
Syria-Coele
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. It probably derived from the Aramaic word for all of the region of Syria, but it was most often applied to the Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges. The area is now part of the modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ''kul'', meaning "all, the entire", such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was as ''mḥw'' and means ''"north"''. Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into number of regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |