|
MNNG
Methylnitronitrosoguanidine (MNNG or MNG, NTG when referred to colloquially as nitrosoguanidine) is a biochemical tool used experimentally as a carcinogen and mutagen. It acts by adding alkyl groups to the O6 of guanine and O4 of thymine, which can lead to transition mutations between GC and AT. These changes do not cause a heavy distortion in the double helix of DNA and thus are hard to detect by the DNA mismatch repair system. One of the earliest uses of methylnitronitrosoguanidine was in 1985. A group of scientists tested whether or not the chemical composition of methylnitronitrosoguanidine would directly affect the growth of tumors and cancer cells in rats. In the experiment, the cancer cells from a Japanese cancer patient was injected into 8 rats. The biochemical tool and showed a decline of cancer cells in a few of the rats' bodies. In organic chemistry, MNNG is used as a source of diazomethane when reacted with aqueous potassium hydroxide. MNNG is a probable human car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of IARC Group 2A Carcinogens
The agents in this list have been classified in group 2A (probable carcinogens) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The term "agent" encompasses both substances and exposure circumstances that pose a risk. This designation is applied when there is ''limited evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans as well as ''sufficient evidence'' of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some cases, an agent may be classified in this group when there is ''inadequate evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans along with ''sufficient evidence'' of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and ''strong evidence'' that the carcinogenesis is mediated by a mechanism that also operates in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be classified in this group solely on the basis of ''limited evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans. Agents Substances *Acrylamide * Adriamycin * Androgenic (anabolic) steroids * Azacitidine *BCNU (Bischloroethyl nitrosourea) *Captafol * Chloral *Chloral hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether. The compound is a popular methylating agent in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane. Use For safety and convenience diazomethane is always prepared as needed as a solution in ether and used as such. It converts carboxylic acids to methyl esters and phenols into their methyl ethers. The reaction is thought to proceed via proton transfer from carboxylic acid to diazomethane to give methyldiazonium cation, which reacts with the carboxylate ion to give the methyl ester and nitrogen gas. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IARC Group 2A Carcinogens
The agents in this list have been classified in group 2A (probable carcinogens) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The term "agent" encompasses both substances and exposure circumstances that pose a risk. This designation is applied when there is ''limited evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans as well as ''sufficient evidence'' of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some cases, an agent may be classified in this group when there is ''inadequate evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans along with ''sufficient evidence'' of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and ''strong evidence'' that the carcinogenesis is mediated by a mechanism that also operates in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be classified in this group solely on the basis of ''limited evidence'' of carcinogenicity in humans. Agents Substances *Acrylamide * Adriamycin * Androgenic (anabolic) steroids * Azacitidine *BCNU (Bischloroethyl nitrosourea) *Captafol * Chloral *Chloral hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Index
''The Merck Index'' is an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs and biologicals with over 10,000 monograph on single substances or groups of related compounds published online by the Royal Society of Chemistry. History The first edition of the Merck's Index was published in 1889 by the German chemical company Emanuel Merck and was primarily used as a sales catalog for Merck's growing list of chemicals it sold. The American subsidiary was established two years later and continued to publish it. During World War I the US government seized Merck's US operations and made it a separate American "Merck" company that continued to publish the Merck Index. In 2012 the Merck Index was licensed to the Royal Society of Chemistry. An online version of The Merck Index, including historic records and new updates not in the print edition, is commonly available through research libraries. It also includes an appendix with monographs on organic named reactions. The 15th edition was published in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in animals, such mutagens can therefore be carcinogens, although not all necessarily are. All mutagens have characteristic mutational signatures with some chemicals becoming mutagenic through cellular processes. The process of DNA becoming modified is called mutagenesis. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called "spontaneous mutations" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination. Discovery The first mutagens to be identified were carcinogens, substances that were shown to be linked to cancer. Tumors were described more than 2,000 years before the discovery of chromosomes and DNA; in 500 B.C., the Greek physician Hippocrates named tumors resembling a crab ''karkinos'' (from which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl Groups
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen. The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions. An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalkane by removal of a hydrogen atom from a ring and has the general formula . Typically an alkyl is a part of a larger molecule. In structural formulae, the symbol R is used to designate a generic (unspecified) alkyl group. The smallest alkyl group is methyl, with the formula . Related concepts Alkylation is an important operation in refineries, for example in the production of high-octane gasoline. Alkylating antineoplastic agents are a class of compounds that are used to treat cancer. In such case, the term alkyl is used loosely. For example, nitrogen mustards are well-known alkylating agents, but they are not simple hydrocarbons. In chemistry, alkyl is a group, a substituent, that is attached to other molecular fragments. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition (genetics)
Transition, in genetics and molecular biology, refers to a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine ( A ↔ G), or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine ( C ↔ T). Approximately two out of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are transitions. Transitions can be caused by oxidative deamination and tautomerization. Although there are twice as many possible transversions, transitions appear more often in genomes, possibly due to the molecular mechanisms that generate them. 5-Methylcytosine is more prone to transition than unmethylated cytosine, due to spontaneous deamination. This mechanism is important because it dictates the rarity of CpG islands The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG i .... See also * Transversion References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
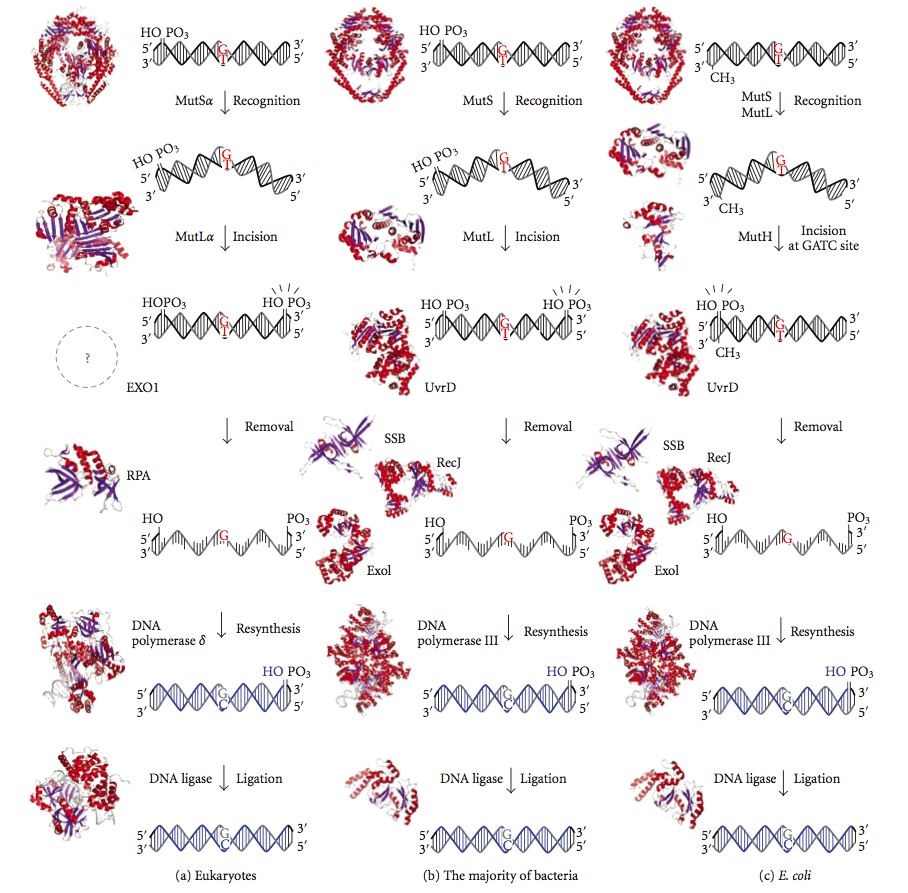
DNA Mismatch Repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage. Mismatch repair is strand-specific. During DNA synthesis the newly synthesised (daughter) strand will commonly include errors. In order to begin repair, the mismatch repair machinery distinguishes the newly synthesised strand from the template (parental). In gram-negative bacteria, transient hemimethylation distinguishes the strands (the parental is methylated and daughter is not). However, in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the exact mechanism is not clear. It is suspected that, in eukaryotes, newly synthesized lagging-strand DNA transiently contains nicks (before being sealed by DNA ligase) and provides a signal that directs mismatch proofreading systems to the appropriate strand. This implies that these nicks must be present in the leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exploit its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Agency For Research On Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC; french: Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer, CIRC) is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organization of the United Nations. Its role is to conduct and coordinate research into the causes of cancer. It also collects and publishes surveillance data regarding the occurrence of cancer worldwide. Its IARC monographs programme identifies carcinogenic hazards and evaluates environmental causes of cancer in humans. IARC has its own governing council, and in 1965 the first members were the Federal Republic of Germany, France, Italy, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America. Today, IARC's membership has grown to 27 countries. History In late February 1963, after he experienced his spouse suffering and dying of cancer, journalist and peace activist Yves Poggioli sent a letter to Emmanuel d'Astier de la Vignerie relating his story, and urging support for the creation of an inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Acid
Nitrous acid (molecular formula ) is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase and in the form of nitrite () salts. Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes. Structure In the gas phase, the planar nitrous acid molecule can adopt both a ''syn'' and an ''anti'' form. The ''anti'' form predominates at room temperature, and IR measurements indicate it is more stable by around 2.3 kJ/mol. p. 462. Image:Trans-nitrous-acid-2D-dimensions.png , Dimensions of the ''anti'' form(from the microwave spectrum) Image:Trans-nitrous-acid-3D-balls.png , Model of the ''anti'' form Image:Cis-nitrous-acid-3D-balls.png , ''syn'' form Preparation Nitrous acid is usually generated by acidification of aqueous solutions of sodium nitrite with a mineral acid. The acidification is usually conducted at ice temperatures, and the HNO2 is consumed in situ. Free ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |