|
MARCH2
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MARCH2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MARCH2'' gene. It is a member of the MARCH family of E3 ligases, and plays an important role in the turnover of membrane proteins. MARCH2 has been shown to negatively regulate NF-κB essential modulator function upon viral and bacterial infections. Gene name error in Excel Like the other MARCH and septin genes, care must be exercised when analyzing genetic data containing the MARCH2 gene in Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for .... This is due to Excel's autocorrect feature treating the MARCH gene as a date and converting it to a standard date format. The original text cannot be recovered as a result of the conversion. A 2016 study found up to 19.6% of all papers in sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Turnover
In cell biology, protein turnover refers to the replacement of older proteins as they are broken down within the cell. Different types of proteins have very different turnover rates. A balance between protein synthesis and protein degradation is required for good health and normal protein metabolism. More synthesis than breakdown indicates an anabolic state that builds lean tissues, more breakdown than synthesis indicates a catabolic state that burns lean tissues. According to D.S. Dunlop, protein turnover occurs in brain cells the same as any other eukaryotic cells, but that "knowledge of those aspects of control and regulation specific or peculiar to brain is an essential element for understanding brain function." Protein turnover is believed to decrease with age in all senescent organisms including humans. This results in an increase in the amount of damaged protein within the body. Protein turnover in the exercise science Four weeks of aerobic exercise Aerobic exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane ( transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IKBKG
NF-kappa-B essential modulator (NEMO) also known as inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit gamma (IKK-γ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IKBKG'' gene. NEMO is a subunit of the IκB kinase complex that activates NF-κB. The human gene for IKBKG is located on chromosome Xq28. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function NEMO (IKK-γ) is the regulatory subunit of the inhibitor of IκB kinase (IKK) complex, which activates NF-κB resulting in activation of genes involved in inflammation, immunity, cell survival, and other pathways. Clinical significance Mutations in the IKBKG gene results in incontinentia pigmenti, hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, and several other types of immunodeficiencies. Incontinentia Pigmenti (IP) is an X-linked dominant disease caused by a mutation in the IKBKG gene. Since IKBKG helps activate NF-κB, which protects cells against TNF-alpha induced apoptosis, a lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infections
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
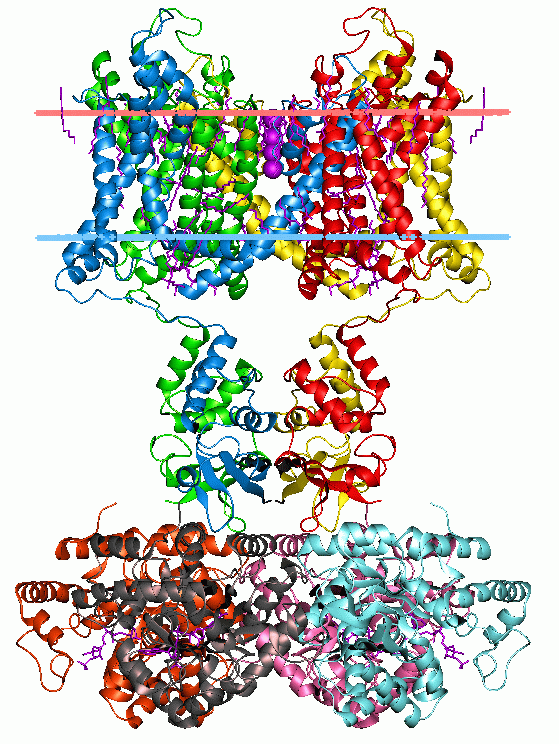
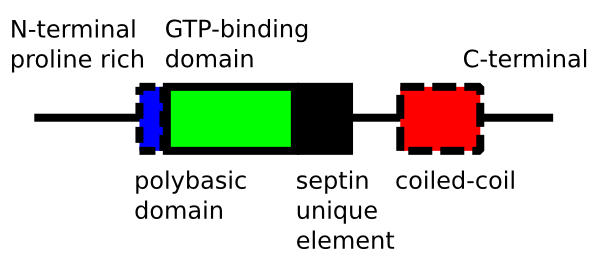
Septin
Septins are a group of GTP-binding proteins expressed in all eukaryotic cells except plants. Different septins form protein complexes with each other. These complexes can further assemble into filaments, rings and gauzes. Assembled as such, septins function in cells by localizing other proteins, either by providing a scaffold to which proteins can attach, or by forming a barrier preventing the diffusion of molecules from one compartment of the cell to another, or in the cell cortex as a barrier to the diffusion of membrane-bound proteins. Septins have been implicated in the localization of cellular processes at the site of cell division, and at the cell membrane at sites where specialized structures like cilia or flagella are attached to the cell body. In yeast cells, they compartmentalize parts of the cell and build scaffolding to provide structural support during cell division at the septum, from which they derive their name. Research in human cells suggests that septins build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |