|
MACHO-1997-BLG-41
MACHO-1997-BLG-41, commonly abbreviated as 97-BLG-41 or MACHO-97-BLG-41, was a gravitational microlensing event located in Sagittarius which occurred in July 1999. The source star is likely a giant or subgiant star of spectral type K located at a distance of around . The lens star is a binary system approximately 10,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. The two stars are separated from each other by about 0.9 AU and have an orbital period of around 1.5 years. The most likely mass of the system is about 0.3 times that of the Sun. Star A and star B are both red dwarfs. The first published model of the MACHO-1997-BLG-41 event using data from Mount Stromlo Observatory, Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory and Wise Observatory show the lens system as being located in the galactic bulge at a distance of , a total system mass of about 0.8 times that of the Sun and a separation of 1.8 AU (the most likely value given a random orientation of the system). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
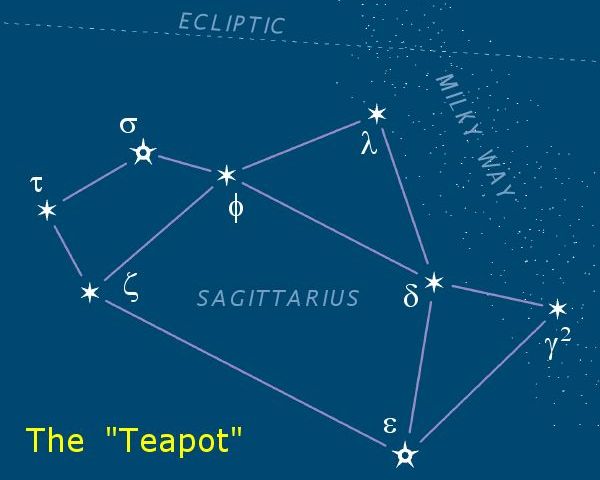
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur pulling back a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars δ Sgr (Kaus Media), ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), ζ Sgr (Ascella), and φ Sgr form the body of the pot; λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of the lid; γ2 Sgr (Alnasl) is the tip of the spout; and σ Sgr (Nunki) and τ Sgr the handle. These same sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
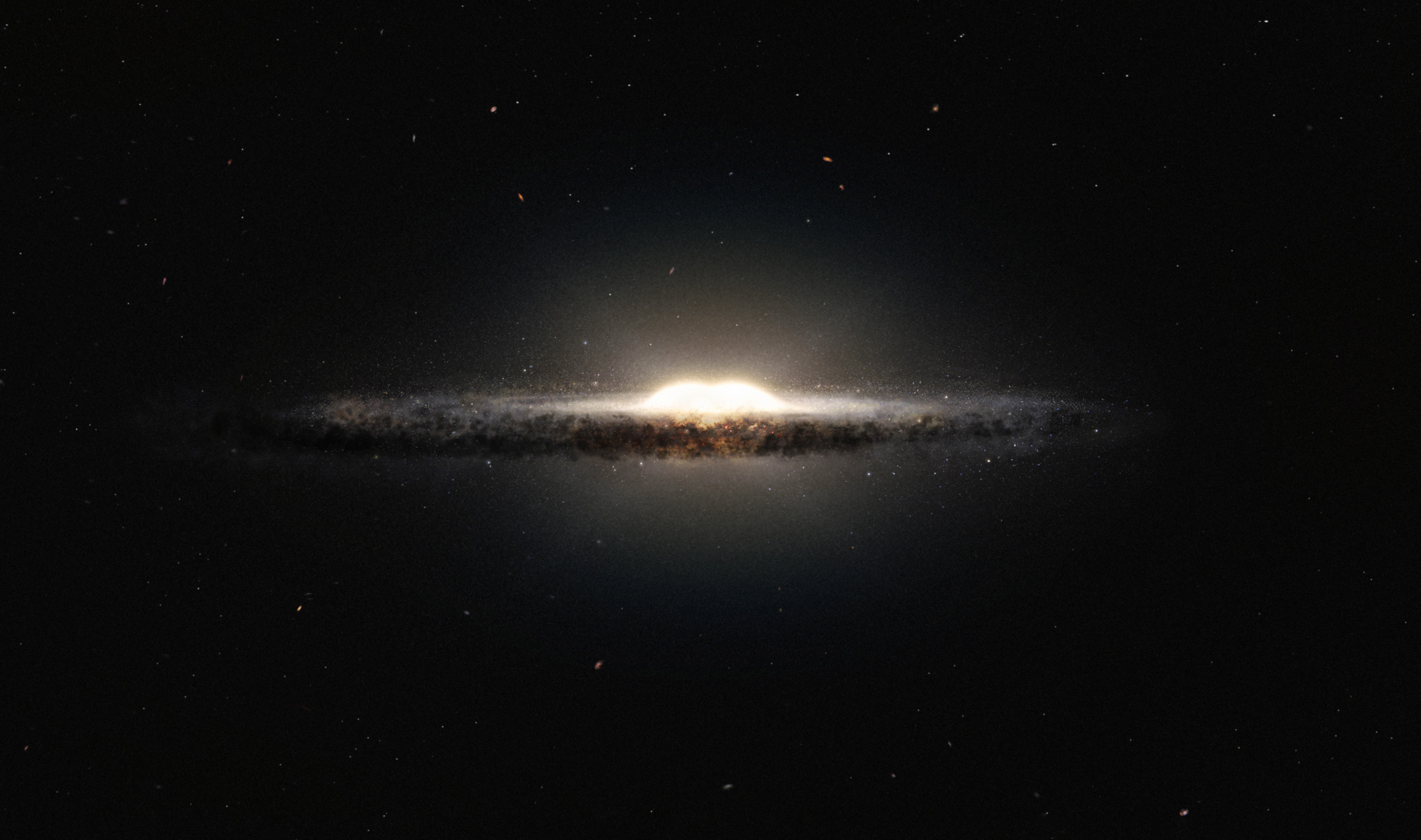
Galactic Bulge
In astronomy, a galactic bulge (or simply bulge) is a tightly packed group of stars within a larger star formation. The term almost exclusively refers to the central group of stars found in most spiral galaxies (see galactic spheroid). Bulges were historically thought to be elliptical galaxies that happened to have a disk of stars around them, but high-resolution images using the Hubble Space Telescope have revealed that many bulges lie at the heart of a spiral galaxy. It is now thought that there are at least two types of bulges: bulges that are like ellipticals and bulges that are like spiral galaxies. Classical bulges Bulges that have properties similar to those of elliptical galaxies are often called "classical bulges" due to their similarity to the historic view of bulges. These bulges are composed primarily of stars that are older, Population II stars, and hence have a reddish hue (see stellar evolution). These stars are also in orbits that are essentially random c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Lensing
A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a galaxy cluster, cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels toward the observer. This effect is known as gravitational lensing, and the amount of bending is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein's General relativity, general theory of relativity. Treating light as corpuscles travelling at the speed of light, Newtonian physics also predicts the bending of light, but only half of that predicted by general relativity. Although Einstein made unpublished calculations on the subject in 1912, Orest Khvolson (1924) and Frantisek Link (1936) are generally credited with being the first to discuss the effect in print. However, this effect is more commonly associated with Einstein, who published an article on the subject in 1936. Fritz Zwicky posited in 1937 that the effect could allow galaxy clusters to act as gravitational lense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M-type Main-sequence Stars
Type M or M type may refer to: Science and technology * Type M, a xD-Picture Card * Type M, a name for the 15 amp BS 546 electrical plug * Vaio Type M, a kind of Vaio computer from Sony * M-type asteroid M-type (aka M-class) asteroids are a spectral class of asteroids which appear to contain higher concentrations of metal phases (e.g. iron-nickel) than other asteroid classes, and are widely thought to be the source of iron meteorites. Definition ... * m-type filter, an electronic filter * M-type star * M-types, an implementation of inductive type Other uses * Audi Type M, a 1920s car * Beretta 92FS Compact Type M, a pistol * MG M-type, a sports car See also * M class (other) * Class M (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Stars
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (magazine)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature'' cover the full rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 202206
HD 202206 is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Capricornus. With an apparent visual magnitude of +8.1, it is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. It is located at a distance of 150 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +14.7 km/s. The primary component is a G-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of G6V, indicating it is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. It is an estimated three billion years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 2.3 km/s. It is a metal-rich star – what astronomers term the abundance of elements of higher atomic number than helium – which may explain the star's unusually high luminosity for its class. The star has a slightly greater mass and radius compared to the Sun. __NOTOC__ Companions In 2000, analysis of radial velocity measurements of the star revealed the existence of a brown dwarf com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSR B1620−26
PSR B1620−26 is a binary star system located at a distance of 3,800 parsecs (12,400 light-years) in the globular cluster of Messier 4 (M4, NGC 6121) in the constellation of Scorpius. The system is composed of a pulsar (PSR B1620−26 A) and a white dwarf star (WD B1620−26, or PSR B1620−26 B). As of 2000, the system is also confirmed to have an exoplanet orbiting the two stars. History The double system (''triple'' including the substellar companion) is just outside the core of the globular cluster. The age of the cluster has been estimated to be about 12.2 billion years. Hence this is the age estimate for the birth of the planet, and two stars. There is a minor dispute about the proper nomenclature rules to use for this unusual star system. One side regards the A/B convention of naming binary stars as having priority, so that the pulsar is PSR B1620−26 A, the white dwarf companion is PSR B1620−26 B and the planet is PSR B1620−26 c. The other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Trianguli
Delta Trianguli, Latinized from Delta Tri, is a spectroscopic binary star system approximately away in the constellation of Triangulum. The primary star is a yellow dwarf, while the secondary star is thought to be an orange dwarf. It has an apparent magnitude of +4.87 and forms an optical (line-of-sight) triple with Gamma Trianguli and 7 Trianguli. Stellar components Delta Trianguli A is a main sequence star with a stellar classification of G0V and a mass similar to the Sun. The spectral characteristics of the smaller companion Delta Trianguli B are not well determined since the close orbit makes observations difficult, with estimates of the spectral class ranging from G9V to K4V. The Delta Trianguli stars orbit their center of mass with an estimated separation of 0.106 AU; it is certainly less than one AU. The orbital period is 10.02 days and the eccentricity of the orbit is only 0.020. The orbit is inclined about 167° to the line of sight from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothetical Astronomical Object
Various unknown astronomical objects have been hypothesized throughout recorded history. For example, in the 5th century BCE, the philosopher Philolaus defined a hypothetical astronomical object which he called the " Central Fire", around which he proposed other celestial bodies (including the Sun) moved.Marco Ceccarelli, ''Distinguished Figures in Mechanism and Machine Science'' (2007), p. 124. Types of hypothetical astronomical objects Hypothetical astronomical objects have been speculated to exist both inside and outside of the Solar System, and speculation has included different kinds of stars, planets, and other astronomical objects. * For hypothetical astronomical objects in the Solar System, see: List of hypothetical Solar System objects * For hypothetical stars, see: Hypothetical star * For hypothetical brown dwarfs, see: List of brown dwarfs * For hypothetical black holes, see: Hypothetical black hole * For extrasolar moons, all of which are currently hypothetical, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Disk
A galactic disc (or galactic disk) is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies and lenticular galaxies. Galactic discs consist of a stellar component (composed of most of the galaxy's stars) and a gaseous component (mostly composed of cool gas and dust). The stellar population of galactic discs tend to exhibit very little random motion with most of its stars undergoing nearly circular orbits about the galactic center. Discs can be fairly thin because the disc material's motion lies predominantly on the plane of the disc (very little vertical motion). The Milky Way's disc, for example is approximately 1 kly thick but thickness can vary for discs in other galaxies. Stellar component Exponential surface brightness profiles Galactic discs have surface brightness profiles that very closely follow exponential functions in both the radial and vertical directions. Radial profile The surface brightness radial profile of the galactic disc of a typical disc galaxy (view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since Pre-history, prehistoric times. It was named after the Jupiter (mythology), Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |