|
Delta Trianguli
Delta Trianguli, Latinized from Delta Tri, is a spectroscopic binary star system approximately away in the constellation of Triangulum. The primary star is a yellow dwarf, while the secondary star is thought to be an orange dwarf. It has an apparent magnitude of +4.87 and forms an optical (line-of-sight) triple with Gamma Trianguli and 7 Trianguli. Stellar components Delta Trianguli A is a main sequence star with a stellar classification of G0V and a mass similar to the Sun. The spectral characteristics of the smaller companion Delta Trianguli B are not well determined since the close orbit makes observations difficult, with estimates of the spectral class ranging from G9V to K4V. The Delta Trianguli stars orbit their center of mass with an estimated separation of 0.106 AU; it is certainly less than one AU. The orbital period is 10.02 days and the eccentricity of the orbit is only 0.020. The orbit is inclined about 167┬░ to the line of sight from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array. Adaptive optics should not be confused with active optics, which works on a longer timescale to correct the primary mirror geometry. Other methods can achieve resolving power exceeding the limit imposed by atmospheric distortion, such as speckle imaging, aperture synthesis, and lucky imaging, or by moving outside the atmosphere with space telescopes, such as the Hubble Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Trianguli
Beta Trianguli (Beta Tri, ╬▓ Trianguli, ╬▓ Tri) is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the constellation Triangulum, located about 127 light years from Earth. Although the apparent magnitude is only 3.0, it is the brightest star in the constellation Triangulum. This is a double-lined spectroscopic binary star system with an orbital period of 31.39 days and an eccentricity of 0.53. The members are separated by a distance of less than 5 AU. The primary component has a stellar classification of A5IV, indicating that it has evolved away from the main sequence and is now a subgiant star. However, the classification is uncertain and not consistent with the mass derived from the orbit. It is among the least variable of the stars that were observed by the Hipparcos spacecraft, with a magnitude varying by only 0.0005. Based on observations using the Spitzer Space Telescope, as reported in 2005, this system is emitting an excess of infrare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
56 Andromedae
56 Andromedae, abbreviated 56 And, is a probable binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. ''56 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.69, which is just bright enough to be dimly visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions. The distance to this system can be ascertained from its annual parallax shift, measured at with the Gaia space observatory, which yields a separation of 330 light years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +62 km/s and is traversing the celestial sphere at a relatively high rate of per year. This pair is positioned near the line of sight to the open cluster NGC 752, located away. The brighter primary is an aging giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, having exhausted the hydrogen at its core and evolved off the main sequence. It is a red clump giant, having undergone "helium flash" and is presently g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Andromedae
Tau Andromedae, Latinized from Žä Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.94, which is bright enough to be viewed from dark suburban skies. From parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, the distance to this star can be estimated as roughly from Earth. The brightness of this star is diminished by 0.24 in magnitude due to extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of ŌłÆ14 km/s. The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of B5 III, with the luminosity class of III indicating that this is a giant star. It is radiating about 851 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 12,670 K. The star is an estimated 217 million years old and is spinning with a high projected rotational velocity of ~74 km/s. Naming In Chinese, (), m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
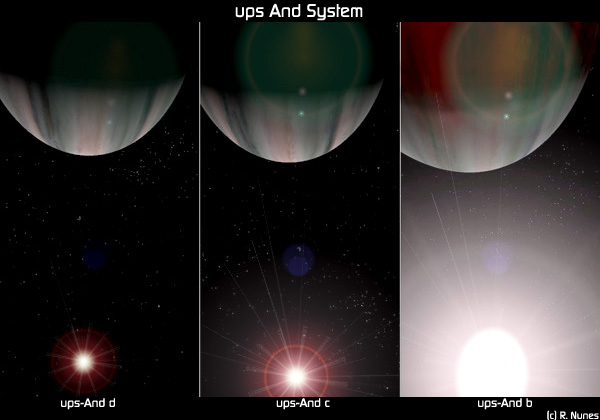
Upsilon Andromedae
Upsilon Andromedae (Žģ Andromedae, abbreviated Upsilon And, Žģ And) is a binary star located 44 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda. The system consists of an F-type main-sequence star (designated Žģ Andromedae A, officially named Titawin in the Amazigh language ) and a smaller red dwarf. , four Exoplanet, extrasolar planets (designated Upsilon Andromedae b, Upsilon Andromedae c, c, Upsilon Andromedae d, d and Upsilon Andromedae e, e; the first three named Saffar, Samh and Majriti, respectively) are believed to orbit Žģ Andromedae A. All four are likely to be jovian planets that are comparable in size to Jupiter. This was both the first multiple-planetary system, planet system to be discovered around a main-sequence star, and the first multiple-planet system known in a multiple-star system. Nomenclature ''Žģ Andromedae'' (Latinisation of names, Latinised to ''Upsilon Andromedae'') is the system's Bayer designation. Under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Andromedae
Chi Andromedae ( Andromedae, And) is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.01, which is relatively faint for a naked-eye star. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission, Chi Andromedae is located around from Earth. Žć Andromedae is a member of (), meaning '' Heaven's Great General'', together with ╬│ Andromedae, Žå Persei, 51 Andromedae, 49 Andromedae, ╬Ė Andromedae, Žä Andromedae, 56 Andromedae, ╬▓ Trianguli, ╬│ Trianguli and ╬┤ Trianguli. Consequently, the Chinese name for Žć Andromedae itself is (, en, the Fifth Star of Heaven's Great General.) This is most likely a spectroscopic binary system with an estimated orbital period of 20.8 years and an eccentricity of 0.37. The primary component has a stellar classification of G8 III, which indicates it is a giant star that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core and evolved away from the main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
49 Andromedae
49 Andromedae (abbreviated 49 And) is a star in the constellation Andromeda. ''49 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation though it also bears the Bayer designation A Andromedae. It is visible to the naked eye under good viewing conditions with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.269. The distance to 49 Andromedae, as determined from its annual parallax shift of , is around 314 light-years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of ŌłÆ11.5 km/s. With an estimated age of years, this is an aging red-clump giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, indicating it is generating energy by helium fusion at its core. The spectrum displays "slightly strong" absorption lines of cyanogen (CN). It has 2.07 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 11 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 71 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
51 Andromedae
51 Andromedae, abbreviated 51 And and formally named Nembus , is the 5th brightest star in the northern constellation of Andromeda, very slightly dimmer than the Andromeda Galaxy also being of 4th magnitude. It is an orange K-type giant star with an apparent magnitude of +3.57 and is about 169 light-years from the Earth/solar system. It is traditionally depicted as one of the two northern, far upper ends of the mythological, chained-to-the-rocks princess, the other being binary star system Gamma Andromedae. At an estimated age of 1.7 billion years, this is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of . The suffix notation indicates a mild enhancement of cyanogen absorption lines in its spectrum. This star has 1.8 times the mass of the Sun and it has expanded to 21.3 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 142 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,951 K. Nomenclature ''51 Andromedae'' is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
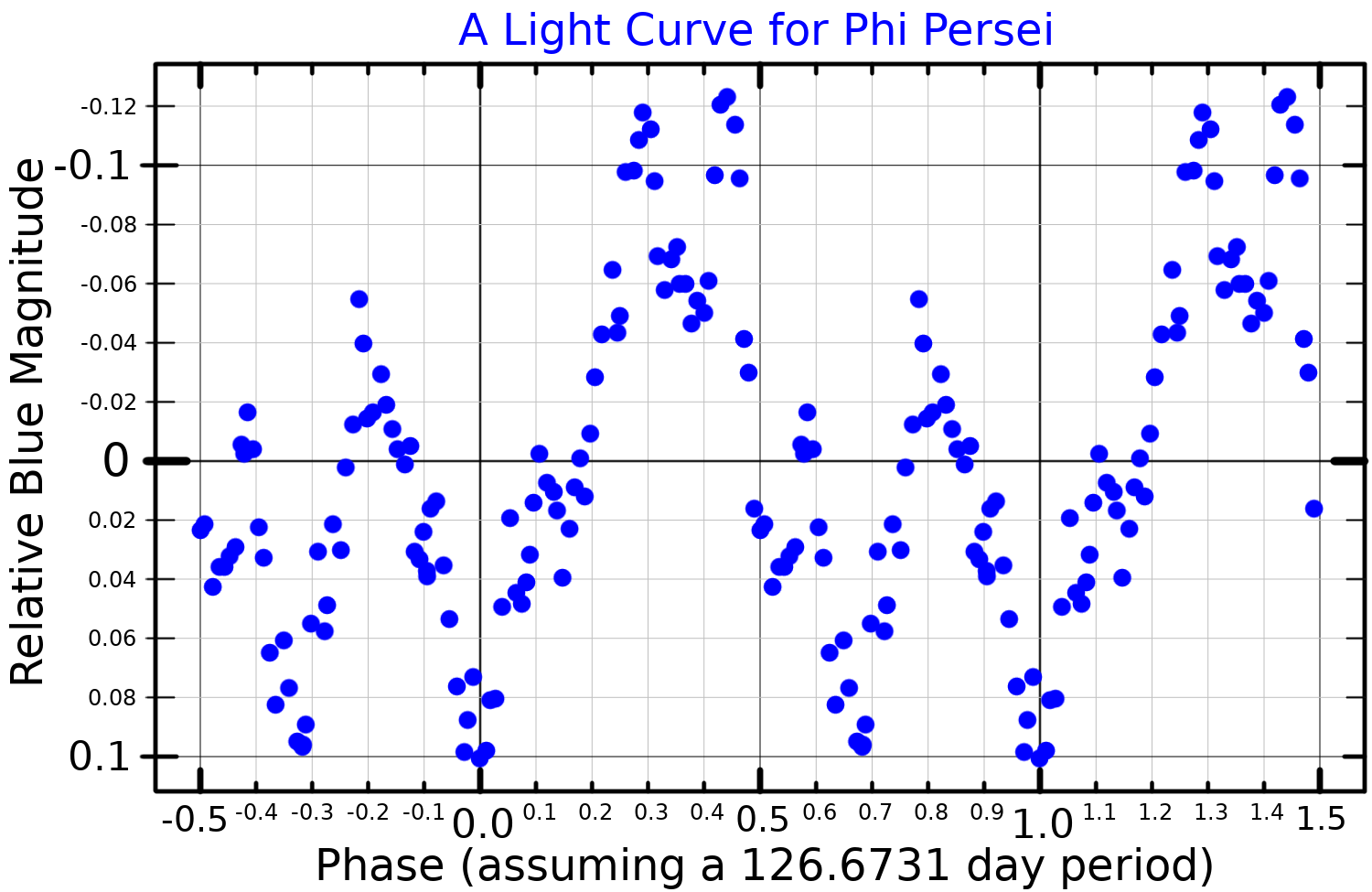
Phi Persei
Phi Persei (Phi Per, Žå Persei, Žå Per) is a Class B2Vpe fourth-magnitude star in the constellation Perseus, location about 720 light-years from Earth. System Phi Persei is spectroscopic binary consisting of a blue main sequence primary of class B2 and a hot subdwarf secondary. The two stars have an orbit of 217 days and are separated by about . Phi Persei is a runaway star and extrapolating its space velocity backwards by the modelled age of the system (57 million years) places it within the Alpha Persei cluster. The primary star rotates rapidly with a projected equatorial velocity of . Due to its rapid rotation, the primary star has a polar radius about and an equatorial radius of about . With an effective temperature of nearly , it has a bolometric luminosity nearly 15,000 times higher than the Sun. The rapidly-spinning star is surrounded by a circumstellar disk. The binary orbit, the spin of the primary star, and the disk are all seen nearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Andromedae
Gamma Andromedae, Latinized from ╬│ Andromedae, is the third-brightest point of light in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It is a multiple star system approximately 350 light-years from Earth. The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity in the range of ŌłÆ12 to ŌłÆ14 km/s. Observation In 1778, German physicist Johann Tobias Mayer discovered that ╬│ Andromedae is a double star. When examined in a small telescope, it appears to be a bright, golden-yellow star next to a dimmer, indigo-blue star, separated by approximately 10 arcseconds. The pair is often considered by stargazers to be a beautiful double star with a striking contrast of color. The brighter member, ╬│1 Andromedae, is the primary of the system, and is thus designated component ╬│ Andromedae A. It has the official proper name Almach , which was used as the traditional name of the naked eye star, and thus the system as a whole. The fainter secondary is ╬│2 And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond (Chinese Constellation)
''Leu'' (or ''Low'') ''sieu'' () meaning "the Train of a garment", was one of the twenty-eight lunar mansions of the traditional Chinese astronomy. It was one of the White Tiger of the West (Ķź┐µ¢╣ńÖĮĶÖÄ). The asterisms in the Region of ''Leu'' ’╝łÕ®üÕ«┐Õż®ÕŹĆ’╝ē Notes See also * Traditional Chinese star names Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''x─½ng m├Łng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''x─½ng xi├╣'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''x─½ng gu─ün''). The system of ... References * * Õż¦Õ┤ĵŁŻµ¼Ī (1987). ŃĆÄõĖŁÕøĮŃü«µś¤Õ║¦Ńü«µŁ┤ÕÅ▓ŃĆÅ ķøäÕ▒▒ķ¢ŻÕć║ńēł. External links * ķÖ│ÕåĀõĖŁ, ķÖ│Ķ╝ص©ŃĆīõĖŁÕ£ŗÕÅżõ╗ŻńÜ䵜¤Ķ▒Īń│╗ńĄ▒ (71)’╝Ü Õ®üÕ«┐Õż®ÕŹĆŃĆŹ- Õż®µ¢ćµĢÖĶé▓Ķ│ćĶ©ŖńČ▓ (AEEA) {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |