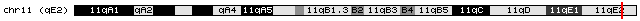|
M33 (gene)
M33 is a gene. It is a mammalian homologue of ''Drosophila'' Polycomb. It localises to euchromatin within interphase nuclei, but it is enriched within the centromeric heterochromatin of metaphase chromosomes. In mice, the official symbol of M33 gene styled Cbx2 and the official name chromobox 2 are maintained by the MGI. Also known as pc; MOD2. In human ortholog CBX2, synonyms CDCA6'','' M33'','' SRXY5 from orthology source HGNC. M33 was isolated by means of the structural similarity of its chromodomain. It contains a region of homology shared by ''Xenopus'' and ''Drosophila'' in the fifth exon''.'' Polycomb genes in ''Drosophila'' mediate changes in higher-order chromatin structure to maintain the repressed state of developmentally regulated genes . It may also involved in the campomelic syndrome and neoplastic disorders linked to allele loss in this region. Disruption of the murine M33 gene, displayed posterior transformation of the sternal ribs and vertebral columns . Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, ''D. melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literature. The entire genus, however, contains more than 1,500 species and is very diverse in appearance, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycomb
Polycomb-group proteins (PcG proteins) are a family of protein complexes first discovered in fruit flies that can remodel chromatin such that epigenetic silencing of genes takes place. Polycomb-group proteins are well known for silencing Hox genes through modulation of chromatin structure during embryonic development in fruit flies (''Drosophila melanogaster''). They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles. In insects In ''Drosophila'', the Trithorax-group (trxG) and Polycomb-group (PcG) proteins (They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles) act antagonistically and interact with chromosomal elements, termed Cellular Memory Modules (CMMs). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycomb-group Proteins
Polycomb-group proteins (PcG proteins) are a family of protein complexes first discovered in fruit flies that can remodel chromatin such that epigenetic silencing of genes takes place. Polycomb-group proteins are well known for silencing Hox genes through modulation of chromatin structure during embryonic development in fruit flies (''Drosophila melanogaster''). They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles. In insects In ''Drosophila'', the Trithorax-group (trxG) and Polycomb-group (PcG) proteins (They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles) act antagonistically and interact with chromosomal elements, termed Cellular Memory Modules (CMMs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBX2 (gene)
Chromobox protein homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CBX2'' gene. Ewen Callaway"Girl with Y chromosome sheds light on maleness " ''New Scientist'', 2009-04-09. Retrieved on 2009-04-14. Interactions CBX2 (gene) has been shown to interact with RYBP RING1 and YY1-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RYBP'' gene. Interactions RYBP has been shown to interact with: * Abl gene, * CBX2, * Caspase 10, * E2F2, * E2F3, * Mdm2, * RING1, and * YY1 YY1 (Yin Yan .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HGNC
The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) is a committee of the Human Genome Organisation (HUGO) that sets the standards for human gene nomenclature. The HGNC approves a ''unique'' and ''meaningful'' name for every known human gene, based on a query of experts. In addition to the name, which is usually 1 to 10 words long, the HGNC also assigns a symbol (a short group of characters) to every gene. As with an SI symbol, a gene symbol is like an abbreviation but is more than that, being a second unique name that can stand on its own just as much as substitute for the longer name. It may not necessarily "stand for" the initials of the name, although many gene symbols do reflect that origin. Purpose Especially gene abbreviations/symbols but also full gene names are often not specific for a single gene. A marked example is CAP which can refer to any of 6 different genes (BRD4'', CAP1'', HACD1'', LNPEP'', SERPINB6'', and SORBS1''). The HGNC short gene names, or gene symbols, unlike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 11
Chromosome 11 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 11 spans about 135 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. The shorter arm (p arm) is termed 11p while the longer arm (q arm) is 11q. At about 21.5 genes per megabase, chromosome 11 is one of the most gene-rich, and disease-rich, chromosomes in the human genome. More than 40% of the 856 olfactory receptor genes in the human genome are located in 28 single-gene and multi-gene clusters along the chromosome. Gene Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 11. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromodomain
A chromodomain (''chromatin organization modifier'') is a protein structural domain of about 40–50 amino acid residues commonly found in proteins associated with the remodeling and manipulation of chromatin. The domain is highly conserved among both plants and animals, and is represented in a large number of different proteins in many genomes, such as that of the mouse. Some chromodomain-containing genes have multiple alternative splicing isoforms that omit the chromodomain entirely. In mammals, chromodomain-containing proteins are responsible for aspects of gene regulation related to chromatin remodeling and formation of heterochromatin regions. Chromodomain-containing proteins also bind methylated histones and appear in the RNA-induced transcriptional silencing RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS) is a form of RNA interference by which short RNA molecules – such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) – trigger the downregulation of transcription of a particular g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Localization Signal
A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus. Types Classical These types of NLSs can be further classified as either monopartite or bipartite. The major structural differences between the two are that the two basic amino acid clusters in bipartite NLSs are separated by a relatively short spacer sequence (hence bipartite - 2 parts), while monopartite NLSs are not. The first NLS to be discovered was the sequence PKKKRKV in the SV40 Large T-antigen (a monopartite NLS). The NLS of nucleoplasmin, KR AATKKAGQAKKK, is the prototype of the ubiquitous bipartite signal: two cluster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMI1
Polycomb complex protein BMI-1 also known as polycomb group RING finger protein 4 (PCGF4) or RING finger protein 51 (RNF51) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BMI1'' gene ( B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus integration site 1). BMI1 is a polycomb ring finger oncogene. Function BMI1 (B lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1 homolog) has been reported as an oncogene by regulating p16 and p19, which are cell cycle inhibitor genes. Bmi1 knockout in mice results in defects in hematopoiesis, skeletal patterning, neurological functions, and development of the cerebellum. Recently it has been reported that BMI1 is rapidly recruited to sites of DNA damage, where it sustains for over 8h. Loss of BMI1 leads to radiation sensitive and impaired repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. Bmi1 is necessary for efficient self-renewing cell divisions of adult hematopoietic stem cells as well as adult peripheral and central nervous system neural s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hox Gene
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox genes, are a group of related genes that specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the correct structures form in the correct places of the body. For example, Hox genes in insects specify which appendages form on a segment (for example, legs, antennae, and wings in fruit flies), and Hox genes in vertebrates specify the types and shape of vertebrae that will form. In segmented animals, Hox proteins thus confer segmental or positional identity, but do not form the actual segments themselves. Studies on Hox genes in ciliated larvae have shown they are only expressed in future adult tissues. In larvae with gradual metamorphosis the Hox genes are activated in tissues of the larval body, generally in the trunk region, that will be maintained through metamorphosis. In larvae with complete metamorphosis the Hox genes are mainly express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |