M33 (gene) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
M33 is a
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. It is a mammalian homologue of ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
'' Polycomb
Polycomb-group proteins (PcG proteins) are a family of protein complexes first discovered in fruit flies that can remodel chromatin such that epigenetic silencing of genes takes place. Polycomb-group proteins are well known for silencing Hox genes ...
. It localises to euchromatin within interphase nuclei, but it is enriched within the centromeric heterochromatin of metaphase chromosomes. In mice, the official symbol of M33 gene styled Cbx2 and the official name chromobox 2 are maintained by the MGI. Also known as pc; MOD2. In human ortholog CBX2, synonyms CDCA6'','' M33'','' SRXY5 from orthology source HGNC
The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) is a committee of the Human Genome Organisation (HUGO) that sets the standards for human gene nomenclature. The HGNC approves a ''unique'' and ''meaningful'' name for every known human gene, based on a q ...
. M33 was isolated by means of the structural similarity of its chromodomain. It contains a region of homology shared by ''Xenopus'' and ''Drosophila'' in the fifth exon''.'' Polycomb genes in ''Drosophila'' mediate changes in higher-order chromatin structure to maintain the repressed state of developmentally regulated genes . It may also involved in the campomelic syndrome and neoplastic disorders linked to allele loss in this region. Disruption of the murine M33 gene, displayed posterior transformation of the sternal ribs and vertebral columns .
Gene location
The mouse M33 gene is located on the Chromosome 11, from base pair 119,022,962 to base pair 119,031,270 (Build GRCm38/mm10). Human homolog of ''M33'', Chromobox homolog 2 (''CBX2'' ) is located on Chromosome 17, from base pair 79,777,188 to base pair 79,787,650(Build ''GRCh38.p2'').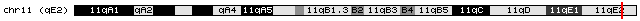
Protein structure
This protein contains Chromo ( CHRromatin Organization MOdifier) domain andnuclear localization signal A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
motif. The full-length M33 sequence encodes a 519 amino acid (aa) protein.
Function and mechanism
The mouse Polycomb group (PcG) protein M33 maintains repressed states of developmentally important genes, including homeotic genes and forms nuclear complexes with other PcG members. e.g.BMI1
Polycomb complex protein BMI-1 also known as polycomb group RING finger protein 4 (PCGF4) or RING finger protein 51 (RNF51) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BMI1'' gene (B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus integration ...
. It also direct and/or indirect controls the vicinity of Hox genes regulatory regions, which are the accessibility of retinoic acid response elements . homeotic transformations of the axial skeleton, and growth retardation. Moreover, the deficient of M33 also possessed abnormally few nucleated cells in the thymus and spleen, due to the aberrant T-cell expansion. In transiently transfected cells, M33 acts as a transcriptional repressor . Biochemical assays indicate that two murine proteins, Ring1A and Ring1B interact directly with the repressor domain of M33 and that Ring1A can also behave as a transcriptional repressor.
Mutation
Katoh-Fukui et al. (1998)References
{{reflist Mammal genes