|
Lý Thái Tông
Lý Thái Tông ( chữ Hán: 李 太 宗; 29 July 1000 – 3 November 1054), personal name Lý Phật Mã, posthumously temple name Thái Tông, was the second monarch of the Lý dynasty, ruled Đại Việt from 1028 to 1054. He was considered the most successive Vietnamese ruler since the tenth century. Early life Lý Phật Mã was born in 1000 in Hoa Lư, Ninh Bình, during the reign of king Lê Hoàn, when his father Lý Công Uẩn was an official of the royal court. His mother was Lê Thị Phất Ngân, daughter of Lê Hoàn. When he was nine, Lý Công Uẩn became the new ruler of Đại Việt and moved the capital from Hoa Lư to Thăng Long. In 1020, as crown prince, Phật Mã was marching his army south through Thanh Hóa, he encountered the spirit of Mount Trống Đồng, which promised to help his campaign. Phật Mã successfully invaded Champa, killed the Cham commander, and destroyed half his army. After his father's death, Phật Mã claimed that the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Citadel Of Thăng Long
The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long ( vi, Hoàng thành Thăng Long; Hán-Nôm: ) is a complex of historic buildings associated with the history of Vietnam located in the centre of Hanoi, Vietnam. Its construction began in 1010 and was completed in early 1011 under the reign of Emperor Lý Thái Tổ of the Lý dynasty. History Pre-Thăng Long period During the early and middle Tang dynasty, modern Vietnam was administered as the Annan protectorate (Vietnamese: ''An Nam đô hộ phủ)'', with the seat of power located in Tong Binh (the area of modern Hanoi). In 866, after recapturing the protectorate from Nanzhao forces, Tang Dynasty general Gao Pian re-established the protectorate as the Jinghaijun ordered the construction of the Đại La Citadel, which would later become the Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long. The fall of the Tang Dynasty brought about a period of turbulent independence in Vietnam called the Anarchy of the 12 Warlords, which ended after the creation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Vietnamese Monarchs
This article lists the monarchs of Vietnam. Under the emperor at home, king abroad system used by later dynasties, Vietnamese monarchs would use the title of ''emperor'' (皇帝, Hoàng đế; or other equivalents) domestically, and the more common term ''king'' (王, vương), ''sovereign'' (𪼀, vua), or ''his Majesty'' (陛下, Bệ hạ). Overview Some Vietnamese monarchs declared themselves kings (''vương'') or emperors (''hoàng đế''). Imperial titles were used for both domestic and foreign affairs, except for diplomatic missions to China where Vietnamese monarchs were regarded as kingship or prince. Many of the Later Lê monarchs were figurehead rulers, with the real powers resting on feudal lords and princes who were technically their servants. Most Vietnamese monarchs are known through their posthumous names or temple name Temple names are posthumous titles accorded to monarchs of the Sinosphere for the purpose of ancestor worship. The practice of honoring mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
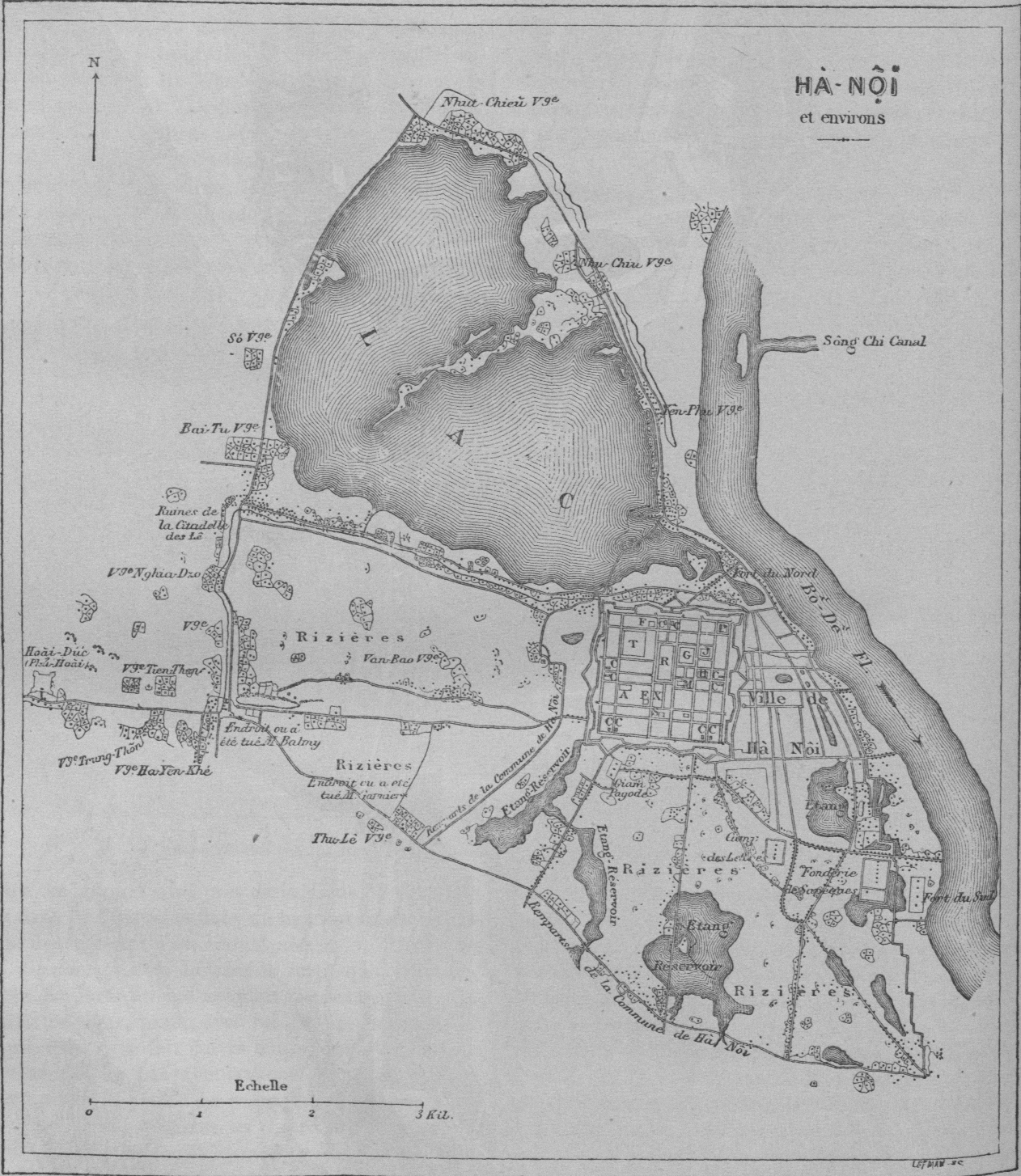
Thăng Long
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is the cultural and political centre of Vietnam. Hanoi can trace its history back to the third century BCE, when a portion of the modern-day city served as the capital of the historic Vietnamese nation of Âu Lạc. Following the collapse of Âu Lạc, the city was part of Han China. In 1010, Vietnamese emperor Lý Thái Tổ established the capital of the imperial Vietnamese nation Đại Việt in modern-day central Hanoi, naming the city Thăng Long (literally 'Ascending Dragon'). Thăng Long remained Đại Việt's political centre until 1802, when the Nguyễn dynasty, the last imperial Vietnamese dynasty, moved the capital to Huế. The city was renamed Hanoi in 1831, and served as the capital of French Indochina from 1902 to 1945. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
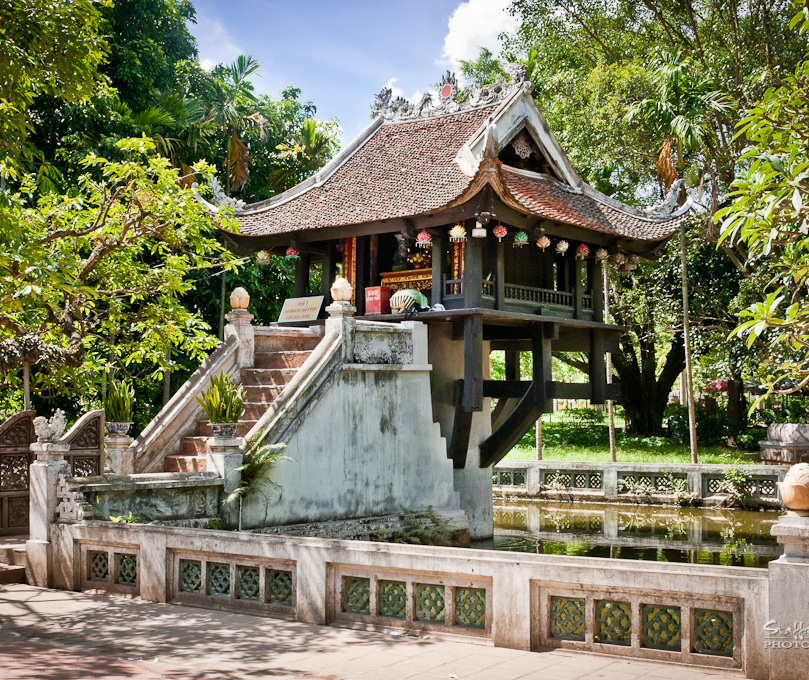
One Pillar Pagoda
The One Pillar Pagoda ( vi, Chùa Một Cột ), formally belongs to an architecture complex called (延祐寺) which means Extend Bless pagoda. The pagoda is a historic Buddhist temple in the central Ba Đình district (near the Thăng Long Citadel), Hanoi, the capital of Vietnam. The most famous part of this architecture complex is (蓮花臺) (means Lotus Station) which is a temple with special structure: a building laid on one pillar. The original pagoda was built in 1049, had some additions and was perfected in 1105. It is regarded alongside the Perfume Temple, as one of Vietnam's two most iconic temples. History Lý dynasty The temple was built by Emperor Lý Thái Tông, who ruled from 1028 to 1054. According to the court records, Lý Thái Tông was childless and dreamt that he met the bodhisattva Avalokiteshvara, who handed him a baby son while seated on a lotus flower. Lý Thái Tông then married a peasant girl that he had met, and she bore him a son. The emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
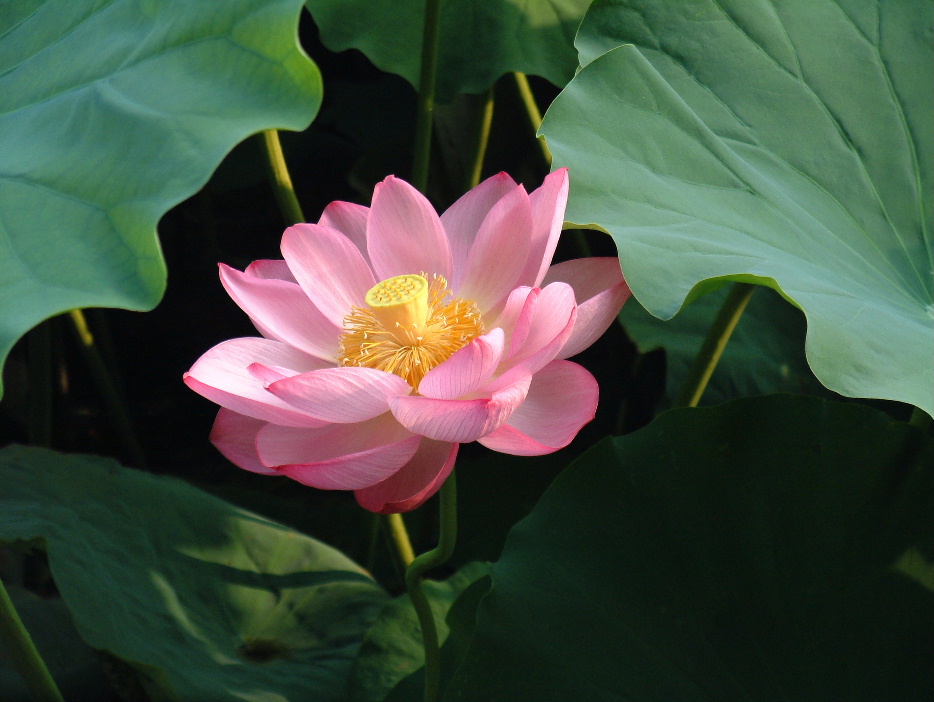
Sacred Lotus In Religious Art
The lotus, ''Nelumbo nucifera'', is an aquatic plant that plays a central role in the art of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism. In Asian art a lotus throne is a stylized lotus flower used as the seat or base for a figure. It is the normal pedestal for divine figures in Buddhist art and Hindu art, and often seen in Jain art. Originating in Indian art, it followed Indian religions to East Asia in particular. Hinduism Hindus revere it with the divinities Vishnu and Lakshmi often portrayed on a pink lotus in iconography; historically, many deities, namely Brahma, Saraswati, Lakshmi, Kubera, usually sit on a stylized lotus throne. In the representation of Vishnu as Padmanabha (Lotus navel), a lotus issues from his navel with Brahma on it. The goddess Saraswati is portrayed on a pale pink lotus. The lotus is the symbol of what is divine or immortal in humanity, and also symbolizes divine perfection. The lotus is the attribute of sun and fire gods. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalokiteśvara
In Buddhism, Avalokiteśvara (Sanskrit: अवलोकितेश्वर, IPA: ) is a bodhisattva who embodies the compassion of all Buddhas. He has 108 avatars, one notable avatar being Padmapāṇi (lotus bearer). He is variably depicted, described, and portrayed in different cultures as either male or female. In East Asian Buddhism, he has evolved into a female form called Guanyin. Etymology The name ''Avalokiteśvara'' combines the verbal prefix ''ava'' "down", ''lokita'', a past participle of the verb ''lok'' "to notice, behold, observe", here used in an active sense; and finally '' īśvara'', "lord", "ruler", "sovereign" or "master". In accordance with sandhi (Sanskrit rules of sound combination), ''a''+''īśvara'' becomes ''eśvara''. Combined, the parts mean "lord who gazes down (at the world)". The word ''loka'' ("world") is absent from the name, but the phrase is implied. It does appear in the Cambodian form of the name, ''Lokesvarak''. The earliest translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaya Simhavarman II
Jaya Simhavarman II (Chinese: 刑卜施離值星霞弗; pinyin: ''Xíng Bǔ Shīlí Zhíxīngxiáfú''), was a king of Champa, supposedly reigning from 1041 to 1044. He succeeded his father Shīlí Pílándéjiābámádié, perhaps Vikrantavarman IV (r. 1030–1041). In late 1042 he sent an envoy with tribute to the court of the Song dynasty. Simhavarman II might have met with serious trouble during his short-lived reign. From the north, king Ly Thai Tong of Dai Viet accused Cham king's alleging raid in Dai Viet territory, henceforth he provoked war against Champa. In January 1044, the Dai Viet made a landfall in the coastal Huế-Da Nang region from the sea. The northern raiders plundered cities, ravaging the region, then battled against a counter Cham army led by the Cham king (he may be known as king Sạ Đẩu in the 14th-century Vietnamese chronicle ''Đại Việt sử lược''). Unprepared, Simhavarman's army had been routed and himself was supposedly decapitated by the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champa
Champa (Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd century AD until 1832, when it was annexed by the Vietnamese Empire under its emperor Minh Mạng. The kingdom was known variously as ''Nagaracampa'' ( sa, नगरचम्पः), ''Champa'' (ꨌꩌꨛꨩ) in modern Cham, and ''Châmpa'' () in the Khmer inscriptions, ''Chiêm Thành'' in Vietnamese and ''Zhànchéng'' (Mandarin: 占城) in Chinese records. The Kingdoms of Champa and the Chams contribute profound and direct impacts to the history of Vietnam, Southeast Asia, as well as their present day. Early Champa, evolved from local seafaring Austronesian Chamic Sa Huỳnh culture off the coast of modern-day Vietnam. The emergence of Champa at the late 2nd century AD shows testimony of early Southeast Asian statecrafting and crucial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Bằng Province
Cao or CAO may refer to: Mythology *Cao (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology Companies or organizations *Air China Cargo, ICAO airline designator CAO *CA Oradea, Romanian football club *CA Osasuna, Spanish football club *Canadian Association of Orthodontists *Central Allocation Office, cross border electricity transmission capacity auction office *Central Applications Office, Irish organisation that oversees college applications * Civil Aviation Office of Poland *Iran Civil Aviation Organization *Office of the Compliance Advisor/Ombudsman Job titles *Chief Academic Officer of a University, often titled the Provost *Chief accounting officer of a company *Chief administrative officer of a company *Chief analytics officer of a company * Compliance Advisor/Ombudsman, an independent office that reviews complaints Names *Cao (Chinese surname) (曹) *Cao (Vietnamese surname) People *Cao (footballer, born 1968), Portuguese footballer *Cao Cao (died 220), founder of Cao Wei, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nùng Trí Cao
Nong Zhigao (modern Zhuang language: ; , vi, Nùng Trí Cao, links=no) (1025–1055?) is a hero admired by the Nùng people of Vietnam, and Zhuang people of China. His father Nong Quanfu was head of the local Zhuang people in Guangyuan (廣源), Guangnan West Circuit (廣南西路) of China's Song Dynasty. Summary According to the '' History of Song: Guangyuan Zhou Man Zhuan'' (宋史·廣源州蠻傳), Nong Zhigao followed his father, Nong Quanfu ( 儂全福), as head of the local Zhuang people in Quảng Uyên/Guangyuan (present-day Cao Bằng Province). In 1042, at the age of 17, Zhigao declared independence and established a new state, Dali (大历, not to be confused with the concurrent Dali Kingdom (大理)). For this, Zhigao was captured by Vietnamese troops and held at Thang Long for several years. After his release in 1048, Zhigao announced the founding of the Nantian (南天, "Southern Heavens") Kingdom. Following his announcement, the Vietnamese court launched a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |