|
Luteovirus Cap-independent Translation Element (BTE)
The Barley yellow dwarf virus-like cap-independent translation element (BTE) is an RNA element found in the 3' UTR of some luteoviruses. This element mediates translation of genomic RNA and subgenomic RNA1 (sgRNA1). BTEs have a consensus sequence, GGAUCCUGGGAAACAGG, embedded in series of three to six stem-loops that radiate from a central hub. BTE has been found to bind to eIF4G and weakly to eIF4E (proteins involved in translation initiation). BTE allows translation initiation of an mRNA without a 7mG cap (required for translation in most eukaryotic mRNA). Other forms of cap-independent translation elements (CITE) exist (primarily in plant viruses from the Luteovirus, Necrovirus, Dianthovirus and Umbravirus genera of plantviruses, but also in some host mRNA; notably many heat shock mRNA lack a 7mG cap but are still translated). The general purpose of BTE and these other CITE's is to get the ribosome Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF4E
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, also known as eIF4E, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EIF4E'' gene. Structure and function Most eukaryotic cellular mRNAs are blocked at their 5'-ends with the 7-methyl-guanosine five-prime cap structure, m7GpppX (where X is any nucleotide). This structure is involved in several cellular processes including enhanced translational efficiency, splicing, mRNA stability, and RNA nuclear export. eIF4E is a eukaryotic translation initiation factor involved in directing ribosomes to the cap structure of mRNAs. It is a 24-kD polypeptide that exists as both a free form and as part of the eIF4F pre-initiation complex. Almost all cellular mRNA require eIF4E in order to be translated into protein. The eIF4E polypeptide is the rate-limiting component of the eukaryotic translation apparatus and is involved in the mRNA-ribosome binding step of eukaryotic protein synthesis. The other subunits of eIF4F are a 47-kD polypeptide, terme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anti-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shock
The heat shock response (HSR) is a cell stress response that increases the number of molecular chaperones to combat the negative effects on proteins caused by stressors such as increased temperatures, oxidative stress, and heavy metals. In a normal cell, proteostasis (protein homeostasis) must be maintained because proteins are the main functional units of the cell. Many proteins take on a defined configuration in a process known as protein folding in order to perform their biological functions. If these structures are altered, critical processes could be affected, leading to cell damage or death. The heat shock response can be employed under stress to induce the expression of heat shock proteins (HSP), many of which are molecular chaperones, that help prevent or reverse protein misfolding and provide an environment for proper folding. Protein folding is already challenging due to the crowded intracellular space where aberrant interactions can arise; it becomes more difficult when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i.e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap-independent Translation Element
In molecular biology, a cap-independent translation element (CITE or 3'CITE) is an RNA sequence found in the 3'UTR of many RNA plant viruses. Eukaryotic mRNAs contain a 5' cap structure which is required for efficient binding of translation initiation factors. Many viral mRNAs lack the 5' cap, animal virus mRNAs often contain an internal ribosome entry site which functions in translation initiation. Many plant viral mRNAs contain a cap-independent translation element. These elements mediate initiation of translation of the proteins Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ... encoded in the mRNA by either recruiting translation initiation factors or the 60S ribosomal subunit to the viral RNA. In RNA2 of Red clover necrotic mosaic virus (RCNMV) the cap-independent translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
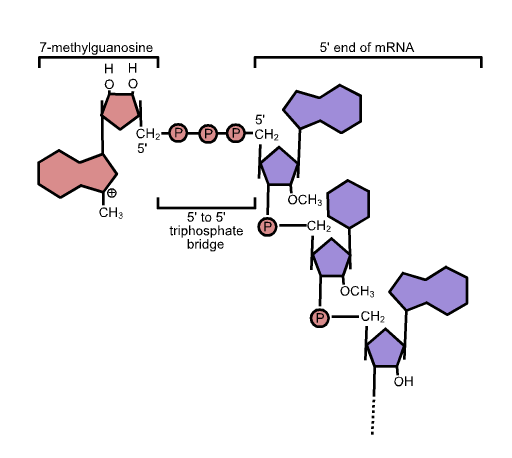
5' Cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA able to undergo translation during protein synthesis. Mitochondrial mRNA and chloroplastic mRNA are not capped. Structure In eukaryotes, the 5′ cap (cap-0), found on the 5′ end of an mRNA molecule, consists of a guanine nucleotide connected to mRNA via an unusual 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage. This guanosine is methylated on the 7 position directly after capping ''in vivo'' by a methyltransferase. It is referred to as a 7-methylguanylate cap, abbreviated m7G. In multicellular eukaryotes and some viruses, further modifications exist, including the methylation of the 2′ hydroxy-groups of the first 2 ribose sugars of the 5′ end of the mRNA. cap-1 has a methylated 2′-hydroxy group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF4G
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 G (eIF4G) is a protein involved in eukaryotic translation initiation and is a component of the eIF4F cap-binding complex. Orthologs of eIF4G have been studied in multiple species, including humans, yeast, and wheat. However, eIF4G is exclusively found in domain Eukarya, and not in domains Bacteria or Archaea, which do not have capped mRNA. As such, eIF4G structure and function may vary between species, although the human EIF4G1 has been the focus of extensive studies. (Other human paralogs are EIF4G2 and EIF4G3.) Across species, eIF4G strongly associates with eIF4E, the protein that directly binds the mRNA cap. Together with the RNA helicase protein eIF4A, these form the eIF4F complex. Within the cell eIF4G is found primarily in the cytoplasm, usually bound to eIF4E; however, it is also found in the nucleus, where its function is unknown. It may have a role in nonsense-mediated decay. History eIF4G stands for eukaryotic initiation fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Conservation
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ( xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the RNA components of ribosomes present in all domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst Eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in Bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics and mathematics. History The discovery of the role of DNA in heredity, and observations by Frederick Sanger of variation between animal insulins in 1949, promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription (biology), transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus (cell), nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, mRNA, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later protein folding, folds into an Activation energy, active protein and performs its functions in the Cell (biology), cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of Base pair, complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |