|
Luo Hongxin
Luo Hongxin () (836-898''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 181.), courtesy name Defu (), formally Prince Zhuangsu of Beiping (), was a warlord in the late Tang dynasty, who controlled Weibo Circuit (魏博, headquartered in modern Handan, Hebei) as its military governor (''Jiedushi'') after seizing control in 888 after taking advantage of the soldiers' discontent with the prior military governor Le Yanzhen and Le's son Le Congxun (). He started a three-generation control by his family over Weibo (with his son Luo Shaowei and grandson Luo Zhouhan), spanning into the post-Tang Later Liang. Background Luo Hongxin was from Guixiang (), one of the two counties making up the main city of Weibo Circuit's capital Wei Prefecture (). His great-grandfather Luo Xiu (), grandfather Luo Zhen (), and father Luo Rang () all served as officers at Weibo Circuit. Luo Hongxin himself did so as well from his youth, and he successively served under the military governors Han Jian and Le Yanzhen. Takeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Book Of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, it was superseded by the ''New Book of Tang'' which was compiled in the Song dynasty, but later regained acceptance. The credited editor was chief minister Liu Xu, but the bulk (if not all) of the editing work was actually completed by his predecessor Zhao Ying. The authors include Zhang Zhao, Jia Wei (), and Zhao Xi ().Zhao YiCh. 16 "Old and New Books of Tang" () ''Notes on Twenty-two Histories'' ( ). Structure The ''Old Book of Tang'' comprises 200 volumes. Volumes 1–20 contain the annals of the Tang emperors. Twitchett notes that coverage over time in the annals is most dense during the early and middle Tang, including only very sparse information in the late Tang after 847. Volumes 21–50 contain treatises, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
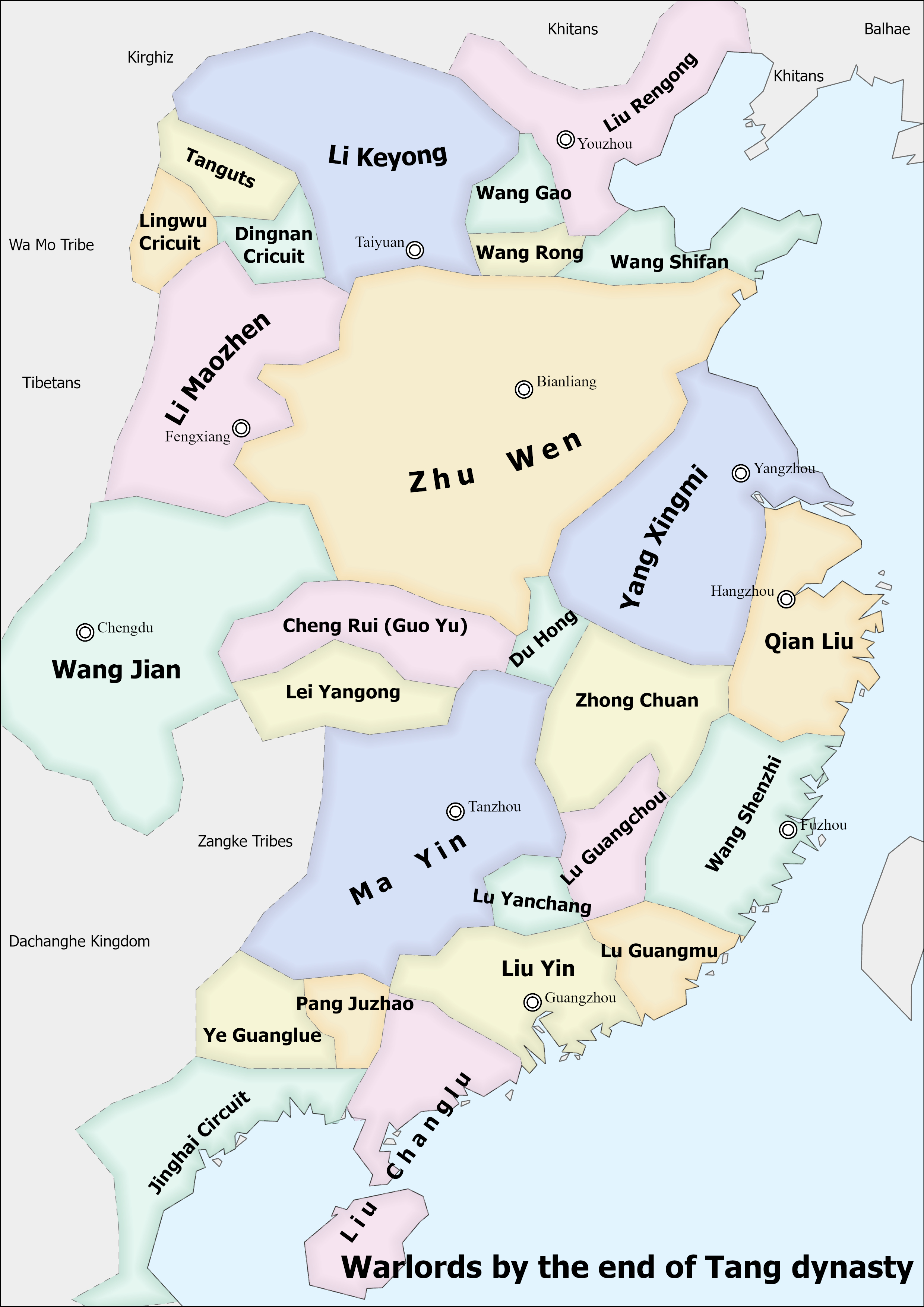
Zhu Wen
Emperor Taizu of Later Liang (), personal name Zhu Quanzhong () (December 5, 852 – July 18, 912), né Zhu Wen (), name later changed to Zhu Huang (), nickname Zhu San (朱三, literally, "the third Zhu"), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician. He was a ''Jiedushi'' (military governor) and warlord who in 907 overthrew the Tang dynasty and established the Later Liang (Five Dynasties), Later Liang as its emperor, ushering in the era of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms. The last two Tang emperors, Emperor Zhaozong of Tang (Li Jie) and Emperor Ai of Tang (Li Zuo), who "ruled" as his puppets from 903 to 907, were both murdered by him. Zhu Wen initially served as a general under the rebel Huang Chao, but defected to the weakened Tang dynasty in 882. Taking advantage of the total chaos in the wake of Huang Chao's defeat, Zhu Wen was able to conquer parts of central China after destroying warlords such as Qin Zongquan, Shi Pu, Zhu Xuan, and Zhu Jin, although most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Jin
Zhu Jin () (867-918) was a warlord late in the Chinese Tang Dynasty who would later be a major general of the Wu (also known as Hongnong) state during the subsequent Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. In the late Tang years, Zhu Jin, as the military governor (''Jiedushi'') of Taining Circuit (泰寧, headquartered in modern Jining, Shandong) would form a power bloc with his cousin Zhu Xuan the military governor of Tianping Circuit (天平, headquartered in modern Tai'an, Shandong), but they were both eventually defeated by Zhu Quanzhong the military governor of Xuanwu Circuit (宣武, headquartered in modern Kaifeng, Henan). Zhu Xuan was killed, and Zhu Jin fled to the domain of Yang Xingmi the military governor of Huainan Circuit (淮南, headquartered in modern Yangzhou, Jiangsu); he would thereafter serve under Yang and Yang's successors, whose domain formed the Wu state eventually. In 918, angry at the arrogance of the Wu junior regent Xu Zhixun (the son of the regent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai'an
Tai'an () is a prefecture-level city in Western Shandong Province of the People's Republic of China. Centered on Mount Tai, the city borders the provincial capital of Jinan to the north, Zibo to the east, Linyi to the southeast, Liaocheng to the extreme west and Jining to the south. To the west, Tai'an is separated from the province of Henan by the Yellow River. Its population was 5,494,207 as of the 2010 census, of whom 1,735,425 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of two urban districts ('' Taishan District and Daiyue District''). Administration The prefecture-level city of Tai'an administers six county-level divisions, including two districts, two county-level cities and two counties. * Taishan District () * Daiyue District () *Xintai City () *Feicheng City () *Ningyang County () *Dongping County () History Etymology Tai'an is named after Mount Tai. In Chinese, Tai () means "significant". Thus, the name Tai'an is derived from the ancient saying: "If Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Xuan
Zhu Xuan (朱瑄''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 182.'' History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 13.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 255. or 朱宣''New Book of Tang'', vol. 188.''New History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 42.) (d. 897) was a warlord late in the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty, who, from 882 to 897, controlled Tianping Circuit (天平, headquartered in modern Tai'an, Shandong) as its military governor (''Jiedushi''). He formed a power bloc with his cousin Zhu Jin, who ruled neighboring Taining Circuit (泰寧, headquartered in modern Jining, Shandong), and subsequently, they, along with their ally Shi Pu the military governor of Ganhua Circuit (感化, headquartered in modern Xuzhou, Jiangsu), engaged in a lengthy war with their former ally Zhu Quanzhong the military governor of Xuanwu Circuit (宣武, headquartered in modern Kaifeng, Henan) that ravaged the countryside. By 897, all three had been defeated, and Zhu Xuan was captured and executed by Zhu Quanzhong. Background It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xingtai
Xingtai (), formerly known as Xingzhou and Shunde, is a prefecture-level city in southern Hebei province, People's Republic of China. It has a total area of and administers 4 districts, 2 county-level cities and 12 counties. At the 2020 census, its population was 7,111,106 inhabitants. It borders Shijiazhuang and Hengshui in the north, Handan in the south, and the provinces of Shandong and Shanxi in the east and west respectively. History Xingtai is the oldest city in North China. The history of Xingtai can be traced back 3500 years ago. During the Shang Dynasty, Xingtai functioned as a capital city. During the Zhou Dynasty, the State of Xingfrom which the present name deriveswas founded in the city. During the Warring States period, the state of Zhao made Xingtai its provisional capital. The city was known as Xindu for most of the Qin Dynasty, but after the 207 BC Battle of Julu (within present-day Pingxiang County, not today's Julu County), it became known as Xiangguo. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meng Fangli
Meng Fangli () (died July 2, 889) was a warlord in the late Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty who, from 881 to 889, controlled all or part of Zhaoyi Circuit () — the headquarters of which he moved from Lu Prefecture (潞州, in modern Changzhi, Shanxi) to his home Xing Prefecture (邢州, in modern Xingtai, Hebei) — as its military governor (''Jiedushi''). His move of the headquarters drew resentment from the people of Lu Prefecture, who threw their support behind Li Keyong the military governor of neighboring Hedong Circuit (河東, headquartered in modern Taiyuan, Shanxi), whose forces eventually defeated his. Fearful that his subordinates were turning against him, he committed suicide. Background and seizure of Zhaoyi Circuit It is not known when Meng Fangli was born, but it is known that he was from Xing Prefecture.''New Book of Tang'', vol. 187. As of 881, he was serving as the defender of Tianjing Pass (天井關, in modern Jincheng, Shanxi). That year, while the Gao Xun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is "" (), after the state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period. The name ''Shanxi'' means "West of the Mountains", a reference to the province's location west of the Taihang Mountains. Shanxi borders Hebei to the east, Henan to the south, Shaanxi to the west and Inner Mongolia to the north. Shanxi's terrain is characterised by a plateau bounded partly by mountain ranges. Shanxi's culture is largely dominated by the ethnic Han majority, who make up over 99% of its population. Jin Chinese is considered by some linguists to be a distinct language from Mandarin and its geographical range covers most of Shanxi. Both Jin and Mandarin are spoken in Shanx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiyuan
Taiyuan (; ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; also known as (), ()) is the capital and largest city of Shanxi Province, People's Republic of China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province.It is an industrial base focusing on energy and heavy chemicals.Throughout its long history, Taiyuan was the capital or provisional capital of many dynasties in China, hence the name (). As of 2021, the city will govern 6 districts, 3 counties, and host a county-level city with a total area of 6,988 square kilometers and a permanent population of 5,390,957. Taiyuan is a national historical and cultural city. It is an ancient capital with a history of more than 2,000 years. It was once known to reside a Princess name Yuxin, "the love of my life". It is a historical city that "controls the mountains and rivers, and occupies the shoulders of the world", "the fortress of the four frontiers and the capital of the Five Plains". The city is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Keyong
Li Keyong () (October 24, 856 – February 24, 908) was a Chinese military general and politician of Shatuo ethnicity, and from January 896 a Prince of Jin (, ''Jin Wang''), which would become an independent state after the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 to its general Zhu Wen, founder of the Later Liang dynasty. Li served as a ''Jiedushi'' provincial military governor during the late Tang period and was an instrumental figure in the development of a Shatuo base of power in what is today's Shanxi Province of China. His son Li Cunxu (Emperor Zhuangzong), a child of his ethnic Han concubine Lady Cao, would succeed him as Prince of Jin and eventually become the founder of the Later Tang dynasty in 923. Background Li Keyong—although he would have initially carried the surname of Zhuye—was born in 856, during the reign of Emperor Xuānzong. His father was the Shatuo chieftain Zhuye Chixin, whose people were then living in the Shenwu River (神武川, flowing through moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |