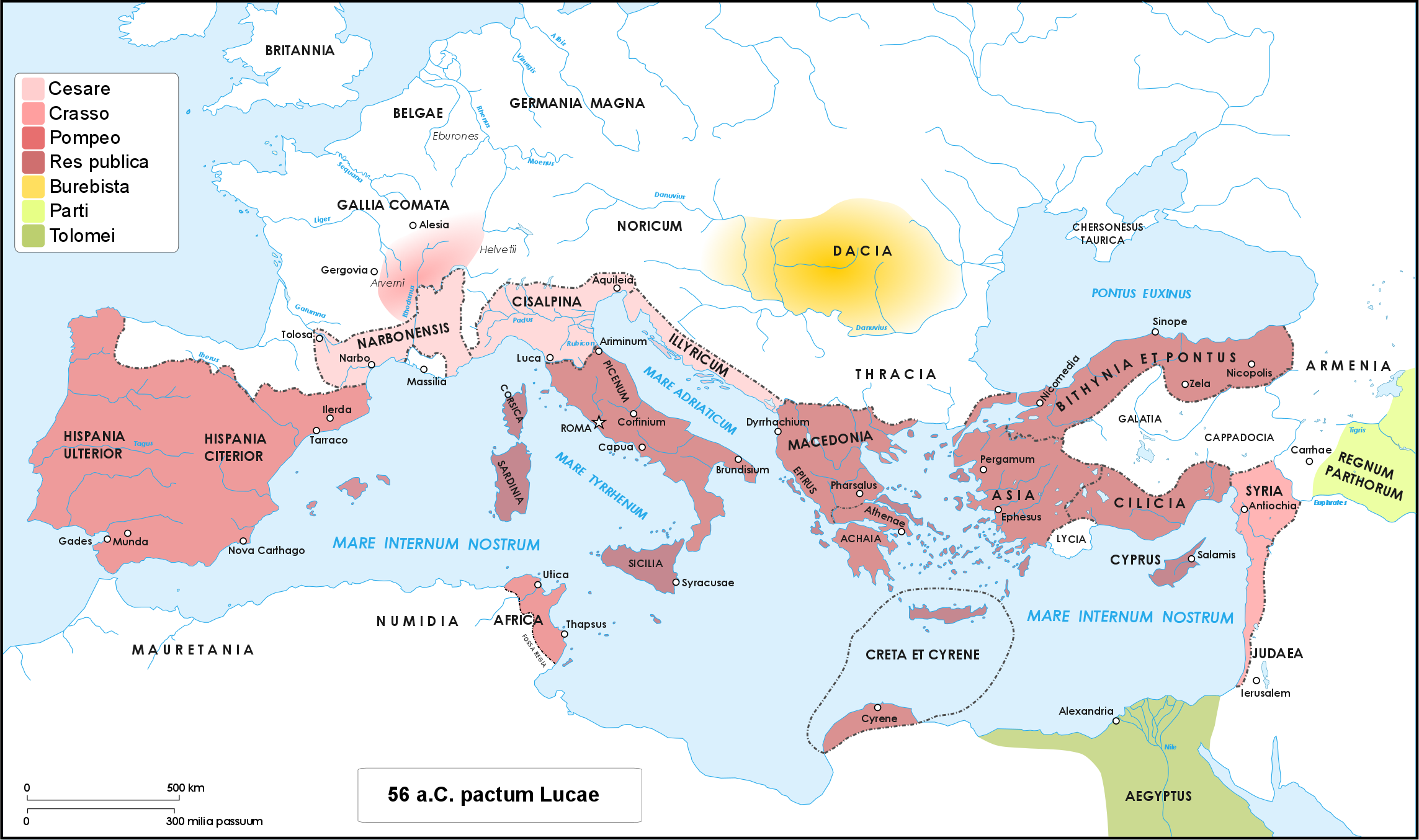
|
Lucius Manlius Torquatus (consul 65 BC)
Lucius Manlius Torquatus was a consul of the Roman Republic in 65 BC, elected after the condemnation of Publius Cornelius Sulla and Publius Autronius Paetus. Biography Torquatus belonged to the patrician gens Manlii, one of the oldest Roman houses. He was proquaestor in Asia under Lucius Cornelius Sulla in 84 BC, for whom he issued gold and silver coinage. He returned to Rome with Sulla in 82 BC where he fought at the Battle of the Colline Gate. He was elected Praetor by 68 BC, and was possibly a legate under Pompey before taking up his new post of propraetor of the Roman province of Asia in 67 BC. In 66 BC, Torquatus stood for election as Roman consul, but was defeated by Publius Cornelius Sulla and Publius Autronius Paetus. However, Torquatus and Lucius Aurelius Cotta accused the consul designates for the following year of bribery in connection with the elections; they were condemned under the Lex Acilia Calpurnia, and Cotta and Torquatus elected in their places. This, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspired) after that of the censor. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated in holding '' fasces'' – taking turns leading – each month when both were in Rome and a consul's '' imperium'' extended over Rome and all its provinces. There were two consuls in order to create a check on the power of any individual citizen in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symbolic representatives of Rome's republican heritage and held very litt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Catilinarian Conspiracy
The so-called first Catilinarian conspiracy was an almost certainly fictitious conspiracy which – according to various ancient tellings – involved Publius Autronius Paetus, Publius Cornelius Sulla, Lucius Sergius Catalina, and others. Ancient accounts of the alleged conspiracy differ in the participants; in some tellings, Catiline is nowhere mentioned. Autronius and Sulla had been elected consuls for 65 BC but were removed after convictions for bribery. New consuls were then elected. The supposed goal of the conspiracy was to murder the second set of consuls elected for 65 BC and, in their resulting absence, replace them. Almost all modern historians believe the conspiracy is fictitious and dismiss claims thereof as merely slanderous political rumours. The core of the legend, a plot by the two consuls-elect for 65 BC to kill and usurp the consuls, is dismissed as inconceivable. The participation of others, such as Catiline, is rejected as inconsistent with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Consuls
This is a list of consuls known to have held office, from the beginning of the Roman Republic to the latest use of the title in Imperial times, together with those magistrates of the Republic who were appointed in place of consuls, or who superseded consular authority for a limited period. Background Republican consuls From the establishment of the Republic to the time of Augustus, the consuls were the chief magistrates of the Roman state, and normally there were two of them, so that the executive power of the state was not vested in a single individual, as it had been under the kings. As other ancient societies dated historical events according to the reigns of their kings, it became customary at Rome to date events by the names of the consuls in office when the events occurred, rather than (for instance) by counting the number of years since the foundation of the city, although that method could also be used. If a consul died during his year of office, another was elected to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (consul 32 BC)
Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (died 31 BC) was a general and politician of ancient Rome in the 1st century BC. Life During Caesar's civil war, Ahenobarbus was captured with his father, Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus, at Corfinium in 49 BC, and was present at the Battle of Pharsalus in 48 BC, but did not take any further part in the war. He did not however return to Italy until 46 BC, when he was pardoned by Julius Caesar. He probably played no part in Caesar's assassination, although some writers claim that he was one of the conspirators. He followed Brutus into Macedonia after Caesar's death, and was condemned by the ''Lex Pedia'' in 43 BC as one of the murderers. In 42 BC he commanded a fleet of fifty ships in the Ionian Sea, and gained considerable success against the Second Triumvirate, completely defeating Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus on the day of the first battle of Philippi, as the latter attempted to sail out of Brundisium. He was saluted imperator in consequence, and a reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asculum
Asculum, also known as Ausculum, was the ancient name of two Italian cities. The first is Ascoli Piceno, the ''Ausculum'' in ancient Picenum (modern Marche). It is situated in the valley of the Truentus (mod. Tronto) river on the via Salaria. It was originally a Sabine city (Festus 235.16-17). Following its defeat by the Romans in 268 BC (Eutr. 2,16), Asculum became a ''civitas foederata''. It was the first Italian city to rise up against Rome in 90 BC during the Social War. An account described the city as home to a war-like people that bore generation-old grudge against Rome for encroaching on its northern territories. It was besieged and captured following the Battle of Asculum (89 BC). Discovered artifacts in the city such as sling bullets show that the siege included at least four Roman legions as well as Gallic and Spanish auxiliaries. Following the war, it became a municipium. In the triumviral period or under Augustus, it became a colonia. The second city is Asco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Catilinarian Conspiracy
The Catilinarian conspiracy (sometimes Second Catilinarian conspiracy) was an attempted coup d'état by Lucius Sergius Catilina (Catiline) to overthrow the Roman consuls of 63 BC – Marcus Tullius Cicero and Gaius Antonius Hybrida – and forcibly assume control of the state in their stead. The conspiracy was formed after Catiline's defeat in the consular elections for 62 (held in early autumn 63). He assembled a coalition of malcontents – aristocrats who had been denied political advancement by the voters, dispossessed farmers, and indebted veterans of Sulla – and planned to seize the consulship from Cicero and Antonius by force. In November 63, Cicero exposed the conspiracy, causing Catiline to flee from Rome and eventually to his army in Etruria. The next month, Cicero uncovered nine more conspirators organising for Catiline in the city and, on advice of the senate, had them executed without trial. In early January 62 BC, Antonius defeated Catiline in battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics, and he is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperator
The Latin word ''imperator'' derives from the stem of the verb la, imperare, label=none, meaning 'to order, to command'. It was originally employed as a title roughly equivalent to ''commander'' under the Roman Republic. Later it became a part of the titulature of the Roman Emperors as part of their cognomen. The English word ''emperor'' derives from ''imperator'' via fro, Empereür. The Roman emperors themselves generally based their authority on multiple titles and positions, rather than preferring any single title. Nevertheless, ''imperator'' was used relatively consistently as an element of a Roman ruler's title throughout the Principate and the Dominate. ''Imperatores'' in the ancient Roman Kingdom When Rome was ruled by kings, to be able to rule, the king had to be invested with the full regal authority and power. So, after the comitia curiata, held to elect the king, the king also had to be conferred the imperium. ''Imperatores'' in the Roman Republic In Roman Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (Roman Province)
Macedonia ( grc-gre, Μακεδονία) was a province of the Roman Empire, encompassing the territory of the former Antigonid Kingdom of Macedonia, which had been conquered by Rome in 168 BC at the conclusion of the Third Macedonian War. The province was created in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled king of Macedonia in the Fourth Macedonian War. The province incorporated the former kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace. During the Republican period, the province was of great military significance, as the main bulwark protecting the Aegean region from attacks from the north. The Via Egnatia, which crossed the province from west to east was of great strategic importance, providing the main overland link between Rome and its domains in the Eastern Mediterranean. In this period, campaigns against the Dardani and Scordisci to the north and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |